Abstract
Objective
To identify the differentially expressed microRNAs (miRNAs) profiles of yang and yin syndromes in patients with acute ischemic stroke, and to provide the molecular basis of the classification of these two syndrome types in acute ischemic stroke patients.
Methods
A microarray assay was performed to assess the expression pattern of miRNAs in the lymphocyte of acute ischemic stroke patients. Target genes for the deregulated miRNAs were predicated using the online bioinformatic algorithms and functional annotation via Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes pathway analysis for miRNAs predicted targets was carried out. Based on the predicted target genes of differentially expressed miRNAs, the miRNA-gene-network and miRNA-pathway-network were constructed.
Results
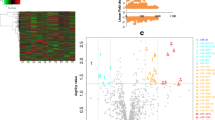
Yang score based on tongue texture, urine, dejecta, and appearance, etc. showed that clinical symptoms were distinct between yang and yin syndromes. There were significantly higher total leukocyte number and lower total protein level in patients with yang syndrome compared with those in patients with yin syndrome (P<0.05). Comprehensive miRNA analysis identified 36 unique down-regulated miRNAs in yang syndrome group, and 20 unique down-regulated and 2 unique up-regulated miRNAs in yin syndrome group. The key regulatory miRNAs, gene, and pathways in the yang syndrome were hsa-miR-93-5p and -320b, enabled homolog, the metabolic pathways and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways, respectively, while those in the yin syndrome were hsa-miR-424-5p and -106b-5p, CNOT4, hepatitis B and pathways in cancer, respectively.
Conclusion
These results offered insight into the molecular basis underlying the different pathogenesis of yang or yin syndrome, providing clues for the individualized therapeutic strategies of acute ischemic stroke.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feigin VL, Roth GA, Naghavi M, Parmar P, Krishnamurthi R, Chugh S, et al. Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol 2016;15:913–924.
Sherzai AZ, Elkind MS.Advances in stroke prevention. Ann N YAcad Sci 2015;1338:1–15.
Caldeira MV, Salazar IL, Curcio M, Canzoniero LM, Duarte CB.Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in brain ischemia: friend or foe? Prog Neurobiol 2014;112:50–69.
Gilca M, Gaman L, Lixandru D, Stoian I. Estimating the yinyang nature of Western herbs: a potential tool based on antioxidation-oxidation theory. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med 2014;11:210–216.
Ge JR, Xie LH, Chen J, Li SQ, Xu HJ, Lai YL,et al. Liuwei Dihuang Pill treats postmenopausal osteoporosis with Shen (Kidney) yin deficiency via Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription signal pathway by up-regulating cardiotrophin-like cytokine factor 1 expression. Chin J Integr Med 2016 Dec 27. doi: 10.1007/s11655-016-2744-2.
You J, Huang Y, Cai Y, Guo J, Liang W, Huang P, et al. Characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine syndromes in patients with acute ischemic stroke of yin or yang syndrome: a multicenter trial. J Chin Integr Med (Chin) 2008;6:346–351.
Guan S, Chen J, Ma Y. Clinical study on the relationship between Huo-Re (fire-heat) syndrome and plasma immune cell factor level changes at initial condition of acute cerebral infarction. J Radioimmunol (Chin) 2000;13:331–333.
Guan S, Chen J, Ding P. Study on relationship between heat syndrome in TCM and pituitariuno-adrenal axis hormones in initial condition of acute cerebral infarction. J Emerg Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2001;10:338–339.
Sun J, Shi Y, Huang P. The correlation analysis between yang syndrome and plasma cholecystokinin-8 in acute ischemic stroke. Henan Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2006;26:28–29.
Wang P, Gao L, Li N, Liu Q, Liu P, Luo Y. A comparative study of the effect of traditional Chinese medicine injection through differentiation method and non-differentiation method on patients with acute cerebral infarction. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Intens Crit Care (Chin) 2008;15:78–80.
Li Z, Huang X, Wang N, Chen W. Comparative study on survival quality of cerebral infarction patients with and without heat-syndrome. Chin J Inf Tradit Chinese Med (Chin) 2009;16:21–23.
Lin JX, Feng Y, Gao Y, Chen JL, Zhang YZ, Ma CM,et al. Study of the correlation between TCM fire-heat syndrome and modern medical diagnostic criteria of apoplexy at the acute stage. J Beijing Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2004;27:77–80.
Wen Y, Wang Y, Feng TT, Wei SB.Differential proteomics analysis of endometriosis in blood stasis syndrome. Chin J Integr Med 2017 Jan 24. doi: 10.1007/s11655-017-2401-4.
Rink C, Khanna S. MicroRNA in ischemic stroke etiology and pathology. Physiol Genomics 2011;43:521–528.
Felling RJ, Song H. Epigenetic mechanisms of neuroplasticity and the implications for stroke recovery. Exp Neurol 2015;268:37–45.
Disease Control Department of Ministry of Health of China, Neurology Branch of Chinese Medical Association. China guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of acute cerebral ischemic stroke in 2010. Chin J Front Med Sci (Electronic Version, Chin) 2010;4:50–59.
Collaborative Group of Acute Encephalopathy Affiliated to State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of China. Standard for diagnosis and therapeutic effect evaluation of stroke. J Beijing Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 1996;19:55–56.
Collaborative Group of Acute Encephalopathy Affiliated to State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of China. Diagnosis standard for syndrome differentiation of stroke. J Beijing Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 1994;17:64–66.
Ghandehari K. Challenging comparison of stroke scales. J Res Med Sci 2013;18:906–910.
Sørensen SS, Nygaard AB, Nielsen MY, Jensen K, Christensen T. miRNA expression profiles in cerebrospinal fluid and blood of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Transl Stroke Res 2014;5:711–718.
Zhang J, Yuan L, Zhang X, Hamblin MH, Zhu T, Meng F. Altered long non-coding RNA transcriptomic profiles in brain microvascular endothelium after cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol 2016;277:162–170.
Chen R, Liu H, Cheng Q, Jiang B, Peng R, Zou Q, et al. MicroRNA-93 promotes the malignant phenotypes of human glioma cells and induces their chemoresistance to temozolomide. Radiat Oncol 2013;8:296.
Zhu ZJ, Huang P, Chong YX, Kang LX, Huang X, Zhu ZX,et al. MicroRNA-181a promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by suppressing CFIm25 in osteosarcoma. Mol Med Rep 2016;14:4271–4278.
Somel M, Liu X, Tang L, Yan Z, Hu H, Guo S. MicroRNAdriven developmental remodeling in the brain distinguishes humans from other primates. PLoS Biol 2011;9:e1001214.
Muñoz-Culla M, Irizar H, Castillo-Triviño T, Sáenz-Cuesta M, Sepúlveda L, Lopetegi I. Blood miRNA expression pattern is a possible risk marker for natalizumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in multiple sclerosis patients. Mult Scler 2014;20:1851–1859.
Yang ZB, Luo XJ, Ren KD, Peng JJ, Tan B, Liu B. Beneficial effect of magnesium lithospermate B on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats involves the regulation of miR-107/glutamate transporter 1 pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 2015;766:91–98.
Chen L, Li ZY, Xu SY, Zhang XJ, Zhang Y, Luo K. Upregulation of miR-107 inhibits glioma angiogenesis and VEGF expression. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2016;36:113–120.
Zhao H, Wang J, Gao L, Wang R, Liu X, Gao Z. miRNA-424 protects against permanent focal cerebral ischemia injury in mice involving suppressing microglia activation. Stroke 2013;44:1706–1713.
Liu P, Zhao H, Wang R, Wang P, Tao Z, Gao L. MicroRNA-424 protects against focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in mice by suppressing oxidative stress. Stroke 2015;46:513–519.
Li P, Teng F, Gao F, Zhang M, Wu J, Zhang C. Identification of circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for detecting acute ischemic stroke. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2015;35:433–447.
Liang H, Studach L, Hullinger RL, Xie J, Andrisani OM.Down-regulation of RE-1 silencing transcription factor (REST) in advanced prostate cancer by hypoxia-induced miR-106b~25. Exp Cell Res 2014;320:188–199.
Feng M, Luo X, Gu C, Li Y, Zhu X, Fei J. Systematic analysis of berberine-induced signaling pathway between miRNA clusters and mRNAs and identification of mir- 99a~125b cluster function by seed-targeting inhibitors in multiple myeloma cells. RNA Biol 2015;12:82–91.
Fallah P, Amirizadeh N, Poopak B, Toogeh G, Arefian E, Kohram F, et al. Expression pattern of key microRNAs in patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase. Int J Lab Hematol 2015;37:560–568.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Hp., Liu, P., Xu, Cm. et al. Unique MicroRNAs Signature of Lymphocyte of Yang and Yin Syndromes in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 25, 590–597 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-018-2843-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-018-2843-3