Abstract
Objective
To observe the efficacy of retention enema with Huchang Jiedu Decoction (护肠解毒汤, HJD) in treating chronic severe hepatitis B (CSHB).
Methods
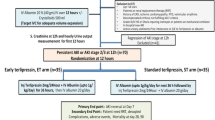
Sixty patients of CSHB were equally randomized into the treated group and the control group. Both groups were treated with conventional integrative medicine, but to patients in the treated group, retention enema with HJD was given in addition, once every day for 3 weeks. The dominant symptoms, physical signs, and related biochemical indices, as well as the incidence of complications in patients before and after treatment, were observed.
Results
Good therapeutic effects were shown in the treated group, with a total effective rate better than that in the control group (83.3% versus 60.0%, P<0.05), superior in terms of lowering alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total bilirubin (TBil), globulin (Glb), and endotoxin (ET) levels and increasing prothrombin activity (PTA), total cholesterol (TC), and calcium (Ca) levels, as well as eliminating ascites and preventing hepatic encephalopathy (P<0.05); especially in treating middle/early stage patients with Chinese medicine syndrome differentiated as water-toxin accumulation pattern.
Conclusion
Retention enema with HJD is surely effective in treating CSHB, and its primary mechanism may be related to the mitigation of enterogenous endotoxemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qian Y. Present situation and thinking on severe hepatitis treated by traditional Chinese medicine. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis (Chin) 2002;12:129–130.
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Diagnostic standard of viral hepatitis. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis (Chin) 2001;11:56–60.
Qiu H, Mao DW, Hu ZB, Wei X. Statistical analysis of TCM syndrome patterns-associated literature of severe hepatitis. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2008;10(4):9–11.
Nie G, Yu SY, Jiang FS, Zhu QJ, Zhang CZ. A pilot study on syndrome patterns-diagnostic standard for severe hepatitis. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Intensive Crit Care (Chin) 2001; 8:172–176.
Ye RG, Lu ZY, eds. Internal medicine. 6th ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House; 2005:448.
State Administration of traditional Chinese Medicine, P. R. China. Standard for diagnosis and efficacy evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine diseases and syndromes. Nanjing: Nanjing University Press;2003:10.
Zheng XY, ed. Guiding principle of clinical research on new drugs of traditional Chinese medicine. Beijing: China Medic-Pharmaceutical Sciences and Technology Publishing House;2002:143.
Han DW. Intestinal endotoxemia as a pathogenetic mechanism in liver failure. World J Gastroenterol 2002;8:961–965.
Su GL. Lipopolysaccharides in liver injury: molecular mechanisms of Kupffer cell activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2002;283:256–265.
Liang KH, Li SB, eds. Hepotology. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House;2003:515–534.
Zhang JJ, Huang JQ. Clinical study on treatment of severe hepatitis by removing dampness and purgative method of TCM. Chin J Integr Tradit Chin West Med (Chin) 2008;28:13–16.
Xie KH. Thirty-five patients of severe hepatitis treated by enema with Tongfu Jiedu Liangxue Decoction. Chin J Integr Tradit Chin West Med (Chin) 2004;24:272.
Wang BE, Zhang DF, eds. Modern hepatology. Beijing: Science Press;2003:409–410.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Keystone Item of Shandong Provincial Science and Technique Development Plan (No. 2007GG 2NS02076)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Wang, L., Su, C. et al. Clinical observation on the treatment of chronic severe hepatitis B by retention enema with Huchang Jiedu Decoction (护肠解毒汤). Chin. J. Integr. Med. 16, 348–352 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-010-0519-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-010-0519-8