Abstract
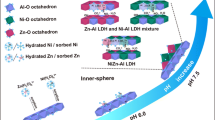
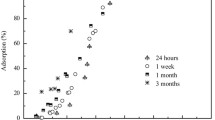
Co(II) and Ni(II) are two common toxic heavy metals, and may simultaneously exist in contaminated water, soil, and sediment systems in Earth’s surface environment. Under this circumstance, competitive adsorption between the two metals may influence their migration, toxicity, and bioavailability. In this research, the competitive sorption of Co(II) and Ni(II) on γ-Al2O3 was studied using both macroscopic sorption experiments and extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectroscopy. Results suggest that Ni(II) reduced the amount of Co(II) sorption in a binary-solute system at pH 6.0. This is because both Co(II) and Ni(II) form inner-sphere surface complexes during sorption on γ-Al2O3 and compete for the surface reactive sites. However, Co(II) exhibited a negligible influence on sorption amount of Ni(II) under the same conditions, which suggests Ni(II) has a stronger affinity to alumina surface. At pH 7.5, Co(II) and Ni(II) sorption density were much higher than that at pH 6.0, but there no mutual competitive effect was observed. EXAFS analysis further revealed that formation of layered double-hydrated precipitates was the dominant sorption mechanism for both Co(II) and Ni(II) at pH 7.5. Because this type of sorption does not rely on surface reactive sites, there was no competition between Co(II) and Ni(II). This finding sheds light on risk assessment and remediation of Ni/Co pollution.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aimoz L, Taviotguého C, Churakov SV, Chukalina M, Dähn R, Curti E, Bordet P, Vespa M (2012) Anion and cation order in iodide-bearing Mg/Zn–Al layered double hydroxides. J Phys Chem C 116(9):5460–5475
Li K, Xue D (2006) Estimation of electronegativity values of elements in different valence states. J Phys Chem A 110(39):11332–11337
Li W, Livi KJ, Xu W, Siebecker MG, Wang Y, Phillips BL, Spark DL (2012) Formation of crystalline Zn–Al layered double hydroxide precipitates on γ-alumina: the role of mineral dissolution. Environ Sci Technol 46(21):11670–11677
Sparks DL (2005) Toxic metals in the environment: the role of surfaces. Elements 1(4):193–197
Thompson HA, Parks GA, Brown GE (1999) Dynamic interactions of dissolution, surface adsorption, and precipitation in an aging cobalt(II)-clay-water system. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63(11–12):1767–1779
Voegelin A, Kretzschmar R (2005) Formation and dissolution of single and mixed Zn and Ni precipitates in soil: evidence from column experiments and extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 39(14):5311–5318
Acknowledgements
This study was co-funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41473084), the Project of China Geological Survey (No. 12120114092001), the 1000 Youth Talent program. We are also grateful to the Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF) and Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF) for use of the synchrotron radiation facilities at beamline 1W1B and 14W, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The 11th International Symposium on Geochemistry of the Earth’s Surface.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gou, W., Ji, J. & Li, W. An EXAFS investigation of the mechanism of competitive sorption between Co(II) and Ni(II) at γ-alumina/solution interface. Acta Geochim 36, 462–464 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-017-0196-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-017-0196-9