Abstract
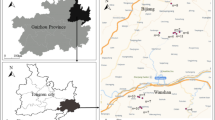
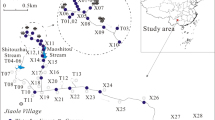
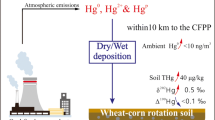
To date, the Xunyang mercury (Hg) mining district is the only ongoing large-scale Hg mining district in China. To understand the influence of Hg contamination mode from the Hg mining and smelting activities, 27 sampling sites in the Xunyang Hg mining district were chosen in this study. Total gaseous mercury (TGM) in ambient air was measured using a Lumex-RA915 automatic Hg analyzer in 2011. Rice samples and soil samples from rhizosphere were collected systematically and simultaneously. Total Hg (THg) and methylmercury (MeHg) concentrations in rice grain and soil samples and Hg speciation with modified sequential selective extractions were measured. The local environment was seriously polluted with Hg. The TGM (302 ± 376 ng·m−3, ranging from 24 to 2220 ng·m−3) in the local ambient air, THg (28 ± 30 mg·kg−1, ranging from 0.31 to 121 mg·kg−1) and MeHg (2.3 ± 1.9 μg·kg−1, ranging from 0.24 to 8.9 μg·kg−1) in soil samples were at the sample level with Hg contaminated area. The THg concentration (26 ± 16 μg·kg−1 ranging from 4.5 to 71 μg·kg−1) in most of the rice grain samples clearly exceeds the threshold level (20 μg·kg−1) in the Chinese national guidelines for cereals (NY 861-2004). The inorganic mercury (IHg) (9.1 ± 5.6 μg·kg−1, ranging from 1.2 to 24 μg·kg−1) and MeHg (14 ± 9.8 μg·kg−1, ranging from 2.1 to 59 μg·kg−1) concentration in rice grain samples were at the same level with Hg contaminated area. The main species of Hg in paddy soils reveal strong complex Hg and residue Hg. According to the correlation analysis, a Hg pollution mode from local Hg mining and smelting was hypothesized, including Hg emission, transportation, methylation, and uptake process.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appleton JD, Weeks JM, Calvez JPS, Beinhoff C (2006) Impacts of mercury contaminated mining waste on soil quality, crops, bivalves, and fish in the Naboc River area, Mindanao, Philippines. Sci Total Environ 354:198–211. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.01.042
Bailey EA, Gray JE, Theodorakos PM (2002) Mercury in vegetation and soils at abandoned mercury mines in southwestern Alaska, USA. Geochem Explor Environ Anal 2:275–285
Bao Z, Wang J, Feng X, Shang L (2011) Distribution of mercury speciation in polluted soils of the Wanshan mercury mining area in Guizhou. Chin J Ecol 30:907–913
Bloom NS, Preus E, Katon J, Hiltner M (2003) Selective extractions to assess the biogeochemically relevant fractionation of inorganic mercury in sediments and soils. Anal Chim Acta 479:233–248. doi:10.1016/s0003-2670(02)01550-7
Bullock OR, Brehme KA, Mapp GR (1998) Lagrangian modeling of mercury air emission, transport and deposition: An analysis of model sensitivity to emissions uncertainty. Sci Total Environ 213:1–12. doi:10.1016/s0048-9697(98)00066-7
Cheng Z et al (2013) Dietary exposure and risk assessment of mercury via total diet study in Cambodia. Chemosphere 92:143–149. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.025
China agriculture industry standard, NY/T 1377-2007 (2007) Determination of pH in soil (ISO 10390:2005 (E): Soil Quality-Determination of pH, MOD). Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China
China agriculture industry standard, NY 861-2004 (2004) Limits of eight elements in cereals, legume, tubes, and its products. Ministry of Agricultrure of the People’s Republic of China
Fu XW, Feng XB, Zhu WZ, Wang SF, Lu JL (2008) Total gaseous mercury concentrations in ambient air in the eastern slope of Mt. Gongga, South-Eastern fringe of the Tibetan plateau, China. Atmos Environ 42:970–979. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.10.018
Higueras P, Oyarzun R, Biester H, Lillo J, Lorenzo S (2003) A first insight into mercury distribution and speciation in soils from the Almaden mining district, Spain. J Geochem Explor 80:95–104. doi:10.1016/s0375-6742(03)00185-7
Krisnayanti BD et al (2012) Assessment of environmental mercury discharge at a four-year-old artisanal gold mining area on Lombok Island, Indonesia. J Environ Monit 14:2598–2607. doi:10.1039/c2em30515a
Lenka M, Panda KK, Panda BB (1992) Monitoring and assessment of mercury pollution in the vicinity of a chloralkali plant.4. Bioconcentration of mercury in in-situ aquatic and terrestrial plants at Ganjam, India. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 22:195–202
Li P, Feng X, Qiu G, Shang L, Wang SF (2008) Mercury exposure in the population from Wuchuan mercury mining area, Guizhou, China. Sci Total Environ 395:72–79. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.02.006
Li P, Feng XB, Qiu GL, Shang LH, Wang SF (2012) Mercury pollution in Wuchuan mercury mining area, Guizhou, Southwestern China: the impacts from large scale and artisanal mercury mining. Environ Int 42:59–66. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2011.04.008
Liang L, Horvat M, Cernichiari E, Gelein B, Balogh S (1996) Simple solvent extraction technique for elimination of matrix interferences in the determination of methylmercury in environmental and biological samples by ethylation gas chromatography cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Talanta 43:1883–1888. doi:10.1016/0039-9140(96)01964-9
Liang L, Horvat M, Feng XB, Shang LH, Lil H, Pang P (2004) Re-evaluation of distillation and comparison with HNO3 leaching/solvent extraction for isolation of methylmercury compounds from sediment/soil samples. Appl Organomet Chem 18:264–270. doi:10.1002/aoc.617
Lindqvist O et al (1991) Mercury in the Swedish environment—recent research on causes, consequences and corrective methods. Water Air Soil Pollut. doi:10.1007/bf00542429
Lucotte M, Mucci A, Hillairemarcel C, Pichet P, Grondin A (1995) Anthropogenic mercury enrichment in remote lakes of northern Quebec (Canada). Water Air Soil Pollut 80:467–476. doi:10.1007/bf01189696
Meng B et al (2010) Distribution patterns of inorganic mercury and methylmercury in tissues of rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants and possible bioaccumulation pathways. J Agric Food Chem 58:4951–4958. doi:10.1021/Jf904557x
Meng B, Feng XB, Qiu GL, Liang P, Li P, Chen CX, Shang LH (2011) The process of methylmercury accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Sci Technol 45:2711–2717. doi:10.1021/es103384v
Morishita T, Kishino K, Idaka S (1982) Mercury contamination of soils, rice plants, and human-hair in the vicinity of a mercury mine in mie prefecture, Japan. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 28:523–534
National Standard of China, GB15618-1995 (1995) Environmental quality standards for soils. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China
Orihel DM, Paterson MJ, Blanchfield PJ, Bodaly RA, Gilmour CC, Hintelmann H (2008) Temporal changes in the distribution, methylation, and bioaccumulation of newly deposited mercury in an aquatic ecosystem. Environ Pollut 154:77–88. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2007.12.030
Pataranawat P, Parkpian P, Polprasert C, Delaune RD, Jugsujinda A (2007) Mercury emission and distribution: Potential environmental risks at a small-scale gold mining operation, Phichit province, Thailand. J Environ Sci Health Part A Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 42:1081–1093. doi:10.1080/1093452071418573
Paterson MJ et al (2006) Bioaccumulation of newly deposited mercury by fish and invertebrates: an enclosure study using stable mercury isotopes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 63:2213–2224. doi:10.1139/f06-118
Qiu GL, Feng XB, Wang SF, Shang LH (2005) Mercury and methylmercury in riparian soil, sediments, mine-waste calcines, and moss from abandoned Hg mines in east Guizhou Province, southwestern China. Appl Geochem 20:627–638. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.09.006
Qiu GL, Feng XB, Wang SF, Mao TF (2006a) Mercury contaminations from historic mining to water, soil and vegetation in Lanmuchang, Guizhou, southwestern China. Sci Total Environ 368:56–68
Qiu GL, Feng XB, Wang SF, Shang LH (2006b) Environmental contamination of mercury from Hg-mining areas in Wuchuan, northeastern Guizhou, China. Environ Pollut 142:549–558. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.10.015
Qiu GL, Feng XB, Li P, Wang SF, Li GH, Shang LH, Fu XW (2008) Methylmercury accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown at abandoned mercury mines in Guizhou, China. J Agric Food Chem 56:2465–2468. doi:10.1021/jf073391a
Qiu GL, Feng XB, Meng B, Sommar J, Gu CH (2012) Environmental geochemistry of an active Hg mine in Xunyang, Shaanxi Province. China App Geochem 27:2280–2288. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.08.003
Rolfhus KR et al (2003) Distribution and fluxes of total and methylmercury in Lake Superior. Environ Sci Technol 37:865–872. doi:10.1021/es026065e
Rothenberg SE, Feng XB, Dong B, Shang LH, Yin RS, Yuan XB (2011) Characterization of mercury species in brown and white rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown in water-saving paddies. Environ Pollut 159:1283–1289. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2011.01.027
Schroeder WH, Munthe J (1998) Atmospheric mercury—an overview. Atmos Environ 32:809. doi:10.1016/S1352-2310(97)00293-8
Silva LOB, da Silva DG, Leao DJ, Matos GD, Ferreira SLC (2012) Slurry sampling for the determination of mercury in rice using cold vapor atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Anal Methods 5:1289–1295. doi:10.1007/s12161-012-9371-0
Stein ED, Cohen Y, Winer AM (1996) Environmental distribution and transformation of mercury compounds. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 26:1–43
Swain EB, Engstrom DR, Brigham ME, Henning TA, Brezonik PL (1992) Increasing rates of atmospheric mercury deposition in midcontinental North-America. Science 257:784–787. doi:10.1126/science.257.5071.784
US EPA (2001a) Method 1630: Methyl mercury in water by distillation, aqueous ethylation, purge and trap, and CVAFS. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
US EPA (2001b) Method 1631, revision E: mercury in water by oxidation, purge & trap, and cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectrometry. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Wan Q, Feng XB, Lu JL, Zheng W, Song XJ, Han SJ, Xu H (2009) Atmospheric mercury in Changbai Mountain area, northeastern China I. The seasonal distribution pattern of total gaseous mercury and its potential sources. Environ Res 109:201–206. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2008.12.001
Wang SF, Feng XB, Qiu GL, Fu XW, Wei ZQ (2007) Characteristics of mercury exchange flux between soil and air in the heavily air-polluted area, eastern Guizhou, China. Atmos Environ 41:5584–5594. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.03.002
Windham-Myers L et al (2014) Mercury cycling in agricultural and managed wetlands of California, USA: seasonal influences of vegetation on mercury methylation, storage, and transport. Sci Total Environ 484:308–318. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.05.027
Zhang L, Jin YQ, Lu JL, Zhang CX (2009) Concentration, distribution and bioaccumulation of mercury in the Xunyang mercury mining area, Shaanxi Province, China. Appl Geochem 24:950–956. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.02.027
Zhang H, Feng XB, Larssen T, Qiu GL, Vogt RD (2010) In inland China, rice, rather than fish, is the major pathway for methylmercury exposure. Environ Health Perspect 118:1183–1188. doi:10.1289/ehp.1001915
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by National Key Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2013CB430004); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41273152; 41473123); CAS Youth Innovation Promotion Association, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. 2011280). The authors wish to thank Cynthia Lin from the McKetta Department of Chemical Engineering, the University of Texas at Austin, USA, for the English revision to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ao, M., Meng, B., Sapkota, A. et al. The influence of atmospheric Hg on Hg contaminations in rice and paddy soil in the Xunyang Hg mining district, China. Acta Geochim 36, 181–189 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-017-0142-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-017-0142-x