Abstract
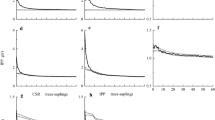
Abies georgei var. smithii is an important plant species in Southeast Tibet, China. It has high ecological value in terms of biodiversity protection, as well as soil and water conservation. We analyzed the spatial pattern and associations of A. georgei var. smithii populations at different growth stages by using Ripley’s L function for point pattern analysis. The diameter structure was a nearly reverse ‘J’ shape. The amount of saplings and medium-sized trees accounts for a large part of the entire population, suggesting a high regeneration rate and an expanding population. In the transition from saplings to medium trees or to large trees, saplings show a significant aggregation distribution at small scales, while medium trees and large trees show a random distribution. There are significant inverse associations between saplings and medium trees and large trees at small scales, while there are no obvious associations between medium trees and large trees. The natural regeneration was affected by interspecific competition, and it was also affected by intraspecific competition. The joint effects of biological characteristics and environmental factors contribute to the spatial distribution pattern and associations of this A. georgei var. smithii population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhavan R, Sagheb-Talebi K, Zenner EK, et al. (2012) Spatial patterns in different forest development stages of an intact old-growth Oriental beech forest in the Caspian region of Iran. European Journal of Forest Research 131: 1355–1366. DOI: 10.1007/s10342-012-0603-z
Cheng XQ, Han HR, Kang FF, et al. (2014) Point pattern analysis of different life stages of Quercus liaotungensis in Lingkong Mountain, Shanxi Province, China. Journal of Plant Interactions 9: 233–240. DOI: 10.1080/17429145.2013. 818167
Condit R, Ashton PS, Baker P, et al. (2000) Spatial patterns in the distribution of tropical tree species. Science 288: 1414–1418. DOI: 10.1126/science.288.5470.1414
Connell JH (1971) On the role of natural enemies in preventing competitive exclusion in some marine animals and in rain forest trees. In: Boer PJD, Gradwell GR, eds. Dynamics of numbers in populations. Wageningen, Netherlands: Centre for Agricultural Publication and Documentation. pp 298–312.
Crawley MJ (1986) Plant Ecology. Blackwell Scientific Publications. pp 97–185.
Cullen LE, Stewart GH, Duncan RP (2001) Disturbance and climate warming influences on New Zealand Nothofagus tree-line population dynamics. Journal of Ecology 89: 1061–1071. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2745.2001.00628.x
Dale MRT (1999) Spatial pattern analysis in plant ecology. Cambridge University Press. p 119.
Da LJ, Yang YC, Song YC (2004) Population structure and regeneration types of dominant species in an evergreen broadleaved forest in Tiantong National Forest Park, Zhejiang Province, Eastern China. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica 28: 376–384. (In Chinese)
Damgaard C, Borksted B, Kjaer C (2005) Herbivory and plant community dynamics: Competitive interactions between an insect-resistant and an insect-susceptible Arabidopsis thaliana genotype. Journal of Plant Interactions 1: 83–91. DOI: 10.1080/17429140500364527
Deng JM, Ran JZ, Wang ZQ, et al. (2012) Models and tests of optimal density and maximal yield for crop plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 109: 15823–15828. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1210955109
Fajardo A, Goodburn JM, Graham J (2006) Spatial patterns of regeneration in managed uneven-aged ponderosa pine/Douglas-fir forests of Western Montana, USA. Forest Ecology and Management 223: 255–266. DOI: 10.1016/j.foreco.2005.11.022
Fan JS (2007) Chinese fir forest. China Forestry Publishing House. pp 169–172. (In Chinese)
Frost I, Rydin H (2000) Spatial pattern and size distribution of the animal-dispersed tree Quercus robur in two spruce-dominated forests. Ecoscience 7: 38–44.
Ge LW, Pan G, Ren DZ, et al. (2013) Forest carbon storage, carbon density, and their distribution characteristics in Linzhi area of Tibet, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 24: 319–325. DOI: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.2013.0162 (In Chinese)
Genet M, Li MC, Luo TX, et al. (2011) Linking carbon supply to root cell-wall chemistry and mechanics at high altitudes in Abies georgei. Annals of Botany 107: 311–320. DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcq237
Getzin S, Wiegand T, Wiegand K, et al. (2008) Heterogeneity influences spatial patterns and demographics in forest stands. Journal of Ecology 96: 807–820. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2745.2008.01377.x
Greig-Smith P (1983) Quantitative plant ecology. Blackwell Scientific Publication. pp 54–60.
Grubb PJ (1977) The maintenance of species-richness in plant communities: the importance of the regeneration niche. Biological Reviews 52: 107–145. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.1977.tb01347.x
Guo QQ, Zhang WH (2015) Sap flow of Abies georgei var. smithii and its relationship with the environment factors in the Tibetan subalpine region, China. Journal of Mountain Science 12: 1373–1382. DOI: 10.1007/s11629-015-3618-3
Guo YX, Hu YN, Li G, et al. (2014) Spatial pattern and spatial association of Betula albosinensis at different developmental stages at Taibai Mountain. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 50: 9–14. (In Chinese)
Hall JS, McKenna JJ, Ashton PMS, et al. (2004) Habitat characterizations underestimate the role of edaphic factors controlling the distribution of Entandrophragma. Ecology 85: 2171–2183. DOI: 10.1890/03-0043
Hammond DS, Brown VK, Zagt R (1999) Spatial and temporal patterns of seed attack and germination in a large-seeded neotropical tree species. Oecologia 119: 208–218. DOI: 10.1007/s004420050778
Harms KE, Wright SJ, Calderón O (2000) Pervasive density-dependent recruitment enhances seedling diversity in a tropical forest. Nature 404: 493–495. DOI: 10.1038/35006630
He FL, Legendre P, LaFrankie JV (1997) Distribution patterns of tree species in a Malaysian tropical rain forest. Journal of Vegetation Science 8: 105–114. DOI: 10.2307/3237248
He JC, Luo TX, Xu YQ (2010) Composition and partition of biomass in a smith fir (Abies georgei var. smithii) timberline forest on the Sergyemla Mountain, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Forestry Studies in China 12: 131–136. DOI: 10.1007/s11632-010-0304-y
Hou JH, Mi XC, Liu CR, et al. (2004) Spatial patterns and associations in a Quercus-Betula forest in northern China. Journal of Vegetation Science 15: 407–414. DOI: 10.1111/j.1654-1103.2004.tb02278.x
Hubbell SP (1979) Tree dispersion, abundance, and diversity in a tropical dry forest. Science 203: 1299–1309. DOI: 10.1126/science.203.4387.1299
Janzen DH (1970) Herbivores and the number of tree species in tropical forests. The American Naturalist 104: 501–528. DOI: 10.1086/282687
Kato K, Yamamoto SI (2001) Effects of canopy heterogeneity on the sapling bank dynamics of a subalpine old-growth forest, central Japan. Ecoscience 8: 96–104. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6114-2_10
King DA, Wright SJ, Connell JH (2006) The contribution of interspecific variation in maximum tree height to tropical and temperate diversity. Journal of Tropical Ecology 22: 11–24. DOI: 10.1017/S0266467405002774
Kohyama T, Suzuki E, Hotta M, et al. (1994) Spatial distribution pattern of representative tree species in a foothill rain forest in West Sumatra. Tropics 4: 1–15. DOI: 10.3759/tropics.4.1
Kollmann J, Schill HP (1996) Spatial patterns of dispersal, seed predation and germination during colonization of abandoned grassland by Quercus petrea and Corylus avellana. Vegetatio 125: 193–205. DOI: 10.1007/BF00044651
Koukoulas S, Blackburn GA (2005) Spatial relationships between tree species and gap characteristics in broad-leaved deciduous woodland. Journal of Vegetation Science 16: 587–596. DOI: 10.1111/j.1654-1103.2005.tb02400.x
Lan GY, Getzin S, Wiegand T, et al. (2012) Spatial distribution and interspecific associations of tree species in a tropical seasonal rain forest of China. PLoS ONE 7: e46074. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046074
Liang EY, Wang YF, Xu Y, et al. (2010) Growth variation in Abies georgei var. smithii along altitudinal gradients in the Sygera Mountains, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Trees 24: 363–373. DOI: 10.1007/s00468-009-0406-0
Liebhold AM, Gurevitch J (2002) Integrating the statistical analysis of spatial data in ecology. Ecography 25: 553–557. DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-0587.2002.250505.x
Luo DQ, Guo QS, Xue HY, et al. (2002) Characteristics and disturbance status of gaps in subalpine fir forest in Southeast Tibet. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 13: 777–780. DOI: 10.13287/j.1001-9932.2002.0185 (In Chinese)
Luo DQ, Wang JH, Ren YH, et al. (2010) Fruiting characteristics of Abies georgei var. smithii forest on the eastern slope of the Sejila Mountain in Tibet. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 46: 30–35. (In Chinese)
Luo DQ, Zhang XJ, Ren DZ (2014) Comparative research on microclimate between forest gaps and non-gaps of Smith fir forests in the Sejila Mountains, southeastern Tibet. Journal of Beijing Forestry University 36: 48–53. DOI: 10.13332/j.cnki.jbfu.2014.06.011 (In Chinese)
Myster RW (2012) The role of seed predation in the maintenance of the cross timbers ecotone of Oklahoma, USA. Journal of Plant Interactions 8: 134–139. DOI: 10.1080/17429145.2012.707234
Nathan R (2006) Long-distance dispersal of plants. Science 313: 786–788. DOI: 10.1126/science.1124975
Nicotra AB, Chazdon RL, Iriarte SVB (1999) Spatial heterogeneity of light and woody seedling regeneration in tropical wet forests. Ecology 80: 1908–1926. DOI: 10.1890/0012-9658(1999)080
Perry GLM, Miller BP, Enright NJ (2006) A comparison of methods for the statistical analysis of spatial point patterns in plant ecology. Plant Ecology 187: 59–82. DOI: 10.1007/s11258-006-9133-4
Perry JN, Liebhold AM, Rosenberg MS, et al. (2002) Illustrations and guidelines for selecting statistical methods for quantifying spatial pattern in ecological data. Ecography 25: 578–600. DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-0587.2002.250507.x
Pielou EC (1969) An introduction to mathematical ecology. Bioscience 78: 7–12. DOI: 10.2307/3799632
Ren QS, Yang XL, Cui GF, et al. (2007) Smith fir population structure and dynamics in the timberline ecotone of the Sejila Mountain, Tibet, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica 27: 2669–2677. (In Chinese)
Ripley BD (1977) Modelling spatial patterns. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society 39: 172–212.
Salas C, LeMay V, Núñez P, et al. (2006) Spatial patterns in an old-growth Nothofagus obliqua forest in south-central Chile. Forest Ecology and Management 231: 38–46. DOI: 10.1016/j.foreco.2006.04.037
Sterner RW, Ribic CA, Schatz GE (1986) Testing for life historical changes in spatial patterns of four tropical tree species. The Journal of Ecology 74: 621–633. DOI: 10.2307/2260386
Stoyan D, Stoyan H (1996) Fractals, random shapes, and point fields: methods of geometrical statistics. Journal of Applied Statistics 23: 559–567. DOI: 10.1080/02664769624107
Taylor AH, Qin ZS, Liu J (1996) Structure and dynamics of subalpine forests in the Wang Lang Natural Reserve, Sichuan, China. Vegetatio 124: 25–38. DOI: 10.1007/BF00045141
Thioulouse J, Chessel D, Doledec S, et al. (1997) Ade-4: A multivariate analysis and graphical display software. Statistics and Computing 7: 75–83. DOI: 10.1023/A:1018513530268
Veblen TT, Donoso C, Schlegel FM, et al. (1981) Forest dynamics in south-central Chile. Journal of Biogeography 8: 211–247. DOI: 10.2307/2844678
Wang BY, Yu SX (2005) Multi-scale analyses of population distribution patterns. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica 29: 235–241. (In Chinese)
Wang L, Sun QW, Hao CY, et al. (2010) Point pattern analysis of different age-class Taxus chinensis var. mairei individuals in mountainous area of southern Anhui Province. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 21: 272–278. DOI: 10.13287/j. 1001-9332.2010.0028 (In Chinese)
Wiegand T, Gunatilleke S, Gunatilleke N (2007) Species associations in a heterogeneous Sri Lankan dipterocarp forest. The American Naturalist 170: E77–95. DOI: 10.1086/521240
Wiegand T, Moloney KA (2004) Rings, circles, and null-models for point pattern analysis in ecology. Oikos 104: 209–229. DOI: 10.1111/j.0030-1299.2004.12497.x
Wu XP, Zheng Y, Ma KP (2002) Population distribution and dynamics of Quercus liaotungensis, Fraxinus rhynchophylla and Acer mono in Dongling Mountain, Beijing. Acta Botanica Sinica 44: 212–223.
You HZ, Liu XL, Miao N, et al. (2010) Individual association and scale effect of spatial pattern of Quercus aquifolioides populations along the elevation gradients. Acta Ecologica Sinica 30: 4004–4011. (In Chinese)
Yuan YL, Si GC, Wang J, et al. (2015) Effects of microclimate on soil bacterial communities across two contrasting timberline ecotones in southeast Tibet. European Journal of Soil Science 66: 1033–1043. DOI: 10.1111/ejss.12292
Zhang L, Luo TX, Liu XS, et al. (2010) Altitudinal variations in seedling and sapling density and age structure of timberline tree species in the Sergyemla Mountains, southeast Tibet. Acta Ecologica Sinica 30: 76–80. DOI: 10.1016/j.chnaes.2010.03.005
Zhang JT (1998) Point pattern analysis of spatial distribution of the plant population. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica 22: 344–349. (In Chinese)
Zhang XJ, Luo DQ (2013) Community structure and species diversity of Abies georgei var. smithii forest near the timberline. Journal of Northwest Forestry University 28: 1–7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2013.02.01 (In Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Key Technology Support Program (2013BAC04B01). Thanks to all those who provided helpful suggestions and critical comments on the manuscript. We also thank GAO San, WU Jing-jing, YU Xiao-ya for providing a critical revision of English. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6767-0282
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0749-5072
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6354-3836
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3460-7540
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Zq., Lu, J., Hua, M. et al. Spatial pattern analysis and associations of different growth stages of populations of Abies georgei var. smithii in Southeast Tibet, China. J. Mt. Sci. 13, 2170–2181 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-016-3849-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-016-3849-y