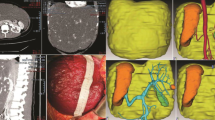
Abstract
The management of symptomatic giant hepatic hemangiomas (> 10 cm) varies in the literature. Multiple interventional approaches have been described including surveillance, embolization, enucleation, and resection based on tumor size, location, relationship to vascular and biliary structures, and the quality and quantity of the functional liver remnant. Resection is often performed as a last resort due to the risk of major hemorrhage. Preoperative arterial embolization is an option; however, many patients will experience severe pain, fever, transaminitis, acidosis, recanalization, and collateral inflow that limit its utility. Furthermore, patients require post-procedure inpatient observation, and there is no consensus on the appropriate time interval between procedures. We present and demonstrate a technique in the video that utilizes a hybrid operating room with on-table angiogram capabilities to perform hemangioma inflow embolization and immediate hepatic resection under the same anesthesia in a single procedure. Combining on-table embolization with immediate resection avoids many of the pitfalls of preoperative embolization, while enhancing the safety of the resection by decreasing the size of the tumor, enabling compressibility, and facilitating exposure of the vascular inflow and outflow. It is an efficient use of hospital resources and eliminates an intervening hospital admission. We have found it to be a preferred approach to enhance the safety and feasibility of resection for massive hepatic hemangiomas with minimal intraoperative blood loss and reduced risk.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu X, Yang Z, Tan H, et al. Long-term result of transcatheter arterial embolization for liver hemangioma. Medicine 2017;96:e9029.
Allison DJ, Jordan H, Hennessy O. Therapeutic embolisation of the hepatic artery: a review of 75 procedures. Lancet (London, England) 1985;1:595-9.
Srivastava DN, Gandhi D, Seith A, Pande GK, Sahni P. Transcatheter arterial embolization in the treatment of symptomatic cavernous hemangiomas of the liver: a prospective study. Abdominal imaging 2001;26:510-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study was conceived by AVM, and data collected, procedure performed, and video/submission drafted by AVM, DAR, and NP.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Patient Consent Statement
Patient consent was obtained prior to publication.
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts or disclosures. Presented at the Americas Hepatopancreatobiliary Association 2020, Miami, FL. Funded in part by the National Institutes of Health K08CA190855
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maker, A.V., Al Rameni, D. & Prabhakar, N. Combining On-Table Embolization with Immediate Resection to Safely Excise Giant Hepatic Hemangiomas. J Gastrointest Surg 25, 1651–1653 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-021-04957-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-021-04957-8