Abstract
Purpose
To explore the brain microstructural and functional changes in patients with postherpetic neuralgia (PHN).
Materials and methods
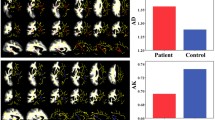
12 PHN patients and 12 healthy volunteers were enrolled. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and resting-state functional MRI (rfMRI) sequences were scanned by a 3T MR scanner. Fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) t-maps were obtained following DTI data processing. The amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) and fractional ALFF (fALFF) were obtained following rfMRI data processing. A two sample t-test was performed to compare the FA, MD, ALFF and fALFF differences between the PHN patients and healthy controls.
Results
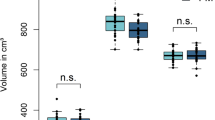
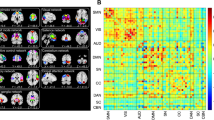
No significant differences were noted with regard to the parameters gender, age and education years between the two groups. FA, MD, ALFF and/or fALFF indicated significant alterations in specific pain or pain-related brain regions, such as brainstem, cerebellum, parietal lobe, precuneus, frontal lobe, temporal lobe, postcentral and precentral gyrus, corpus callosum, cingulate gyrus, putamen and insula.
Conclusion
Multi-local alterations of spontaneous brain activity could form a network related to chronic pain, sensory discrimination, emotion and cognition, suggesting complicated central mechanisms of PHN. The combined-action of brain microstructure and function may play a critical role in comprehension of neurological mechanisms of PHN-induced pain.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tontodonati M, Ursini T, Polilli E, Vadini F, Di Masi F, Volpone D, et al. Post-herpetic neuralgia. Int J Gen Med. 2012;5:861–71.
Kim W, Chivukula S, Hauptman J, Pouratian N. Diffusion tensor imaging-based thalamic segmentation in deep brain stimulation for chronic pain conditions. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2016;94(4):225–34.
Ceko M, Shir Y, Ouellet JA, Ware MA, Stone LS, Seminowicz DA. Partial recovery of abnormal insula and dorsolateral prefrontal connectivity to cognitive networks in chronic low back pain after treatment. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015;36(6):2075–92.
Lieberman G, Shpaner M, Watts R, Andrews T, Filippi CG, Davis M, et al. White matter involvement in chronic musculoskeletal pain. J Pain. 2014;15(11):1110–9.
Cao S, Song G, Zhang Y, Xie P, Tu Y, Li Y, et al. Abnormal local brain activity beyond the pain matrix in postherpetic neuralgia patients: a resting-state functional MRI study. Pain Physician. 2017;20(2):E303–E314314.
Chen F, Chen F, Shang Z, Shui Y, Wu G, Liu C, et al. White matter microstructure degenerates in patients with postherpetic neuralgia. Neurosci Lett. 2017;656:152–7.
Zhang Y, Yu T, Qin B, Li Y, Song G, Yu B. Microstructural abnormalities in gray matter of patients with postherpetic neuralgia: a diffusional kurtosis imaging study. Pain Physician. 2016;19(4):E601–E611611.
Van Hecke W, Leemans A, De Backer S, Jeurissen B, Parizel PM, Sijbers J. Comparing isotropic and anisotropic smoothing for voxel-based DTI analyses: a simulation study. Hum Brain Mapp. 2010;31(1):98–114.
Cao S, Li Y, Deng W, Qin B, Zhang Y, Xie P, et al. Local Brain activity differences between herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia patients: a resting-state functional MRI study. Pain Physician. 2017;20(5):E687–E699699.
Castarlenas E, Jensen MP, von Baeyer CL, Miro J. Psychometric properties of the numerical rating scale to assess self-reported pain intensity in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Clin J Pain. 2017;33(4):376–83.
Cui Z, Zhong S, Xu P, He Y, Gong G. PANDA: a pipeline toolbox for analyzing brain diffusion images. Front Hum Neurosci. 2013;7:42.
Song XW, Dong ZY, Long XY, Li SF, Zuo XN, Zhu CZ, et al. REST: a toolkit for resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data processing. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(9):e25031.
Chen X, Lu B, Yan CG. Reproducibility of R-fMRI metrics on the impact of different strategies for multiple comparison correction and sample sizes. Hum Brain Mapp. 2018;39(1):300–18.
Surjya Prasad U, Shiv Pratap R, Mishra S, Bhatnagar S. Successful treatment of an intractable postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) using peripheral nerve field stimulation (PNFS). Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2010;27(1):59–62.
Dai H, Yin D, Hu C, Morelli JN, Hu S, Yan X, et al. Whole-brain voxel-based analysis of diffusion tensor MRI parameters in patients with primary open angle glaucoma and correlation with clinical glaucoma stage. Neuroradiology. 2013;55(2):233–43.
Zou QH, Zhu CZ, Yang Y, Zuo XN, Long XY, Cao QJ, et al. An improved approach to detection of amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) for resting-state fMRI: fractional ALFF. J Neurosci Methods. 2008;172(1):137–41.
Habas C, Kamdar N, Nguyen D, Prater K, Beckmann CF, Menon V, et al. Distinct cerebellar contributions to intrinsic connectivity networks. J Neurosci. 2009;29(26):8586–94.
Moulton EA, Schmahmann JD, Becerra L, Borsook D. The cerebellum and pain: passive integrator or active participator? Brain Res Rev. 2010;65(1):14–27.
Restuccia D, Marca GD, Valeriani M, Leggio MG, Molinari M. Cerebellar damage impairs detection of somatosensory input changes. A somatosensory mismatch-negativity study. Brain J Neurol. 2007;130(Pt 1):276–87.
Seifert F, Maihofner C. Representation of cold allodynia in the human brain—a functional MRI study. NeuroImage. 2007;35(3):1168–80.
Valet M, Sprenger T, Boecker H, Willoch F, Rummeny E, Conrad B, et al. Distraction modulates connectivity of the cingulo-frontal cortex and the midbrain during pain—an fMRI analysis. Pain. 2004;109(3):399–408.
Bogdanov VB, Vigano A, Noirhomme Q, Bogdanova OV, Guy N, Laureys S, et al. Cerebral responses and role of the prefrontal cortex in conditioned pain modulation: an fMRI study in healthy subjects. Behav Brain Res. 2015;281:187–98.
Wu GR, Marinazzo D. Point-process deconvolution of fMRI BOLD signal reveals effective connectivity alterations in chronic pain patients. Brain Topogr. 2015;28(4):541–7.
Lopez-Sola M, Pujol J, Wager TD, Garcia-Fontanals A, Blanco-Hinojo L, Garcia-Blanco S, et al. Altered functional magnetic resonance imaging responses to nonpainful sensory stimulation in fibromyalgia patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(11):3200–9.
Fritz HC, McAuley JH, Wittfeld K, Hegenscheid K, Schmidt CO, Langner S, et al. Chronic back pain is associated with decreased prefrontal and anterior insular gray matter: results from a population-based cohort study. J Pain. 2016;17(1):111–8.
Liu J, Hao Y, Du M, Wang X, Zhang J, Manor B, et al. Quantitative cerebral blood flow mapping and functional connectivity of postherpetic neuralgia pain: a perfusion fMRI study. Pain. 2013;154(1):110–8.
Funding
This work was mainly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers 81971573, 81671743, 81201079, 81471136, 81701098), Jiangsu Provincial Medical Youth Talent (Grant numbers QNRC2016709, QNRC2016740), Special Technical Project of Diagnosis and Treatment of Key Clinical Diseases of Suzhou (Grant number LCZX201801), and the "Six-one Project" for High-level Health Talents in Jiangsu Province (Grant number LGY2016035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Ethical statement
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, H., Jiang, C., Wu, G. et al. A combined DTI and resting state functional MRI study in patients with postherpetic neuralgia. Jpn J Radiol 38, 440–450 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-020-00926-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-020-00926-4