Abstract
Purpose
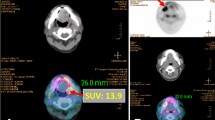
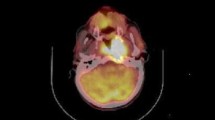
Our aim was to determine whether the maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) of the primary lesion demonstrated by [18F]-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG-PET/CT) is associated with the prognosis of maxillary sinus cancer.
Materials and methods
The relationships of clinicopathological factors including age, T stage, N stage, histologic type, treatment strategy, and primary tumor SUVmax with progression-free (PFS) and overall (OS) survival were evaluated using the log-rank test and Cox method in 31 patients with maxillary sinus cancer before combined superselective intra-arterial chemotherapy using high-dose cisplatin with concurrent radiotherapy, or radiotherapy alone.
Results
The median duration of follow-up was 55.4 (range 9.7–72.6) months. PFS and OS of patients exhibiting a high SUVmax (≥16 and ≥17, respectively) for the primary tumor were significantly lower than those of patients for whom the primary tumor SUVmax was low (p = 0.0010 and p = 0.033, respectively). Multivariate analyses showed that T stage (p = 0.0049) and primary tumor SUVmax (p = 0.026) were independently prognostic of poorer PFS and that only primary tumor SUVmax (p = 0.049) was independently prognostic of poorer OS.
Conclusion
SUVmax of the primary tumor determined by FDG-PET/CT before treatment could be a good surrogate marker for prognostication of maxillary sinus cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Myers LL, Nussenbaum B, Bradford CR, Teknos TN, Esclamado RM, Wolf GT. Paranasal sinus malignancies: an 18-year single institution experience. Laryngoscope. 2002;112:1964–9.
Davies A, Tan C, Paschalides C, Barrington SF, O’Doherty M, Utley M, et al. FDG-PET maximum standardised uptake value is associated with variation in survival: analysis of 498 lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer. 2007;55:75–8.
Kato H, Nakajima M, Sohda M, Tanaka N, Inose T, Miyazaki T, et al. The clinical application of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography to predict survival in patients with operable esophageal cancer. Cancer. 2009;115:3196–203.
Kidd EA, Siegel BA, Dehdashti F, Grigsby PW. The standardized uptake value for F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose is a sensitive predictive biomarker for cervical cancer treatment response and survival. Cancer. 2007;110:1738–44.
Xie P, Li M, Zhao H, Sun X, Fu Z, Yu J, et al. 18F-FDG PET or PET–CT to evaluate prognosis for head and neck cancer: a metaanalysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011;137:1085–93.
Muir CS, Nectoux J. Descriptive epidemiology of malignant neoplasms of nose, nasal cavities, middle ear and accessory sinuses. Clin Otolatyngol. 1980;5:195–211.
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A. Cancer staging handbooh from AJCC cancer staging mannual. 7th ed. New York: Springer; 2010. p. 39–126.
Samant S, Robbins KT, Vang M, Wan J, Robertson J. Intra-arterial cisplatin and concomitant radiation therapy followed by surgery for advanced paranasal sinus cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;130:948–55.
Kanoto M, Oda A, Hosoya T, Nemoto K, Ishida A, Nasu T, Koike S, Aoyagi M. Impact of superselective transarterial infusion therapy of high-dose cisplatin on maxillary cancer with orbital invasion. Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31:1390–4.
Homma A, Sakashita T, Yoshida D, Onimaru R, Tsuchiya K, Suzuki F, et al. Superselective intra-arterial cisplatin infusion and concomitant radiotherapy for maxillary sinus cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;109:2980–6.
Allal AS, Slosman DO, Kebdani T, Allaoua M, Lehmann W, Dulguerov P. Prediction of outcome in head-and-neck cancer patients using the standardized uptake value of 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;59:1295–300.
Tang C, Murphy JD, Khong B, La TH, Kong C, Fischbein NJ, et al. Validation that metabolic tumor volume predicts outcome in head-and-neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;83:1514–20.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) Grant Number 25861134.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare no financial support or relationship that may pose conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Doi, H., Kitajima, K., Fukushima, K. et al. SUVmax on FDG-PET is a predictor of prognosis in patients with maxillary sinus cancer. Jpn J Radiol 34, 349–355 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-016-0531-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-016-0531-9