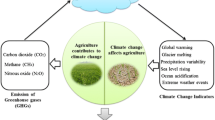
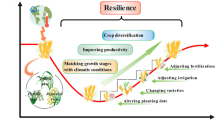
Abstract
Potato has been recognized as a crop of importance in developing countries for ensuring human nutrition and food security. The dwindling natural resources, low fertility of soils, the incidence of pests and diseases, climate change and lack of strategic planning pose major constraints for potato production in these countries. Crop models are efficient tools for assisting research and development efforts towards achieving maximum production potential in these areas as it predicts the phenology and yield of crop taking into consideration the factors affecting growth and development. A well-validated model can be used for quantification of adaptation domains, optimization and efficient utilization of resources, forecasting of pest and diseases, mitigating climate changes, yield gap analysis, a pre-harvest judgment of production and accordingly market surveillance and formulation of monitory policies. The multifaceted application of simulation models presents futuristic opportunities for developing decision supporting systems and agro-advisory services for scheduling best management practices for attaining sustained potato production. This review summarizes comprehensive information on the crop models being used along with their applications in the different aspects of potato production system towards a precision as well as smart agriculture.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adavi Z, Moradi R, Saeidnejada AH, Tadayonc MZ, Mansourid H (2018) Assessment of potato response to climate change and adaptation strategies. Sci Hortic-Amsterdam 228:91–102
Afshar A, Neshat A (2013) Evaluation of Aqua Crop computer model in the potato under irrigation management of continuity plan of Jiroft region Kerman Iran. Int J Adv Biol Biom Res 1(12):1669–1678
Aggarwal PK (2002) Crop growth modeling in India: past present and future. In: Paul Khurana SM, Shekhawat GS, Pandey SK, Singh BP (eds) Potato Global Research and Development. Indian Potato Research Association Shimla, India, pp 788–795
Aggarwal PK, Kropff MJ, Teng PS, Khush GS (1997) The challenge of integrating systems approaches in plant breeding: opportunities accomplishments and limitations. In: Teng PS, Aggarwal PK, Bouma Jvan Laar HH (eds) Kropff MJ. Applications of Systems Approaches at the Field Level, Kluwer Dordrecht The Netherlands, pp 1–13
Alexandrov VA, Eitzinger J (2005) The potential effect of climate change and elevated air carbon dioxide on agricultural crop production in central and southeastern Europe. J Crop Improv 13(1–2):291–231
Alva AK, Marcos J, Stockle C, Reddy VR, Timlin D (2010) A crop simulation model for predicting yield and fate of nitrogen in irrigated potato rotation cropping system. J Crop Improv 24(2):142–152
Andrare-Piedra JL, Forbes GA, Shtienberg D, Grunwald NJ, Taipe MV, Hijmans RJ, Fry WE (2005) Qualification of a plant disease simulation model: performance of the LATEBLIGHT model across a broad range of environments. Phytopathol 95:1412–1422
Angulo C, Rötter RP, Lock R, Enders A, Fronzek S, Ewert F (2013) Implication of crop model calibration strategies for assessing regional impacts of climate change in Europe. Agric For Meteorol 170:32–46
Araya A, Habtu S, Hadgu KM, Kebede A, Dejene T (2010) Test of AquaCrop model in simulating biomass and yield of water deficient and irrigated barley (Hordeum vulgare). Agric Water Manag 97:1838–1846
Arora RK, Ahmad I, Singh BP (2012) Forecasting late blight of potato in Punjab using JHULSACAST model. Potato J 39(2):173–176
Arora VK, Nath JC, Singh CB (2013) Analyzing potato response to irrigation and nitrogen regimes in a sub-tropical environment using SUBSTOR-potato model. Agric Water Manag 124:69–76
Asseng S, Ewert F, Martre P, Rotter RP, Lobell DB, Cammarano D, White JW (2015) Rising temperatures reduce global wheat production. Nat Clim 5(2):143–147
Badini O, Stockle CO, Franz EH (1997) Application of crop simulation modeling and GIS to agroclimatic assessment in Burkina Faso. Agric Ecosyst Environ 64:233–244
Barrios-Peres C, Villegas JR, Heinemann AB (2017) Linking crop simulation models with artificial neural networks for characterization of target population of environments (TPEs) and abiotic stresses in lowland rice. In: The 243rd Meeting of The Crop Sciences Society of Japan University of Tokyo Japan. https://doi.org/10.14829/jcsproc.243.0_119
Basso B, Ritchie JT, Pierce FJ, Braga RP, Jones JW (2001) Spatial validation of crop models for precision agriculture. Agric Syst 68:97–112
Basso B, Cammarano D, Chen D, Cafiero G, Amato M, Bitella G, Rossi R, Basso F (2009) Landscape position and precipitation effects on spatial variability of wheat yield and grain protein in Southern Italy. J Agron Crop Sci 195:301–312
Berntsen J, Hauggard-Nielsen H, Olesen JE, Petersen BM, Jensen ES, Thomsen A (2004) Modelling dry matter production and resource use in intercrops of pea and barley. Field Crops Res 88:69–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr2003.11.012
Biggs JS, Thorburn PJ, Crimp S, Masters B, Attard SJ (2013) Interactions between climate change and sugarcane management systems for improving water quality leaving farms in the Mackay Whitsunday region Australia. Agri Ecosyst Environ 180:79–89
Boggess WG, Amerling CB (1983) A bioeconomic simulation analysis of irrigation environments. S J Agric Econ 15:85–91
Boogaard HL, Van Diepen CA, Rotter RP, Cabrera JMCA, Van Laar H (1998) WOFOST 7.1; User’s guide for the WOFOST 7.1 crop growth simulation model and WOFOST Control Center 1.5. Wageningen (Netherlands) DLO Win and Staring Centre. Technical Document:137
Borus D, Parsons D, Boersma M, Brown H, Mohammed C (2018) Improving the prediction of potato productivity: APSIM-Potato model parameterization and evaluation in Tasmania Australia. Aust J Crop Sci 12(1):32–43
Boryan C, Yang Z, Mueller R, Craig M (2011) Monitoring US agriculture: the US department of agriculture national agricultural statistics service cropland data layer program. Geocarto Int 26:341–358
Bouman BAM, van Keulen H, van Laar HH, Rabbinge R (1996) The ‘School of de Wit’ crop growth simulation models: a pedigree and historical overview. Agric Syst 52(2–3):171–198
Bouman BAM, Van Diepen CA, Vossen P, Van Der Val T (1997) Simulation and systems analysis tools for crop yield forecasting. In: Teng PS (ed) Applications of systems approaches at the farm and regional levels. Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Nederland, pp 325–340
Bowen WT, Thornton TK, Hoogenboom G (1998) The simlulation of cropping sequence with DSSAT. In: Tsuji GY, Hoogenboom G, Thornton PK (eds) Potato global Research and Development. Kluwer Academic Publishers Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 317–331
Bowen W, Cabrera H, Barrera V, Baigorria G (1999) Simulating the response of potato to applied nitrogen. In: CIP program report 1997–1998. International Potato Center, Lima, Peru, pp 381–386
Bowen WT, Lal SS, Govindakrishnan PM (2002) Simulation of potato based cropping system. In: Paul Khurana SM, Shekhawat GS, Pandey SK, Singh BP (eds) Understanding options for agricultural production. Malhotra Publishing House, New Delhi, pp 776–787
Brisson N, Bussiere F, Ozier-Lafontaine H, Tournebize R, Sinoquet H (2004) Adaptation of the crop model STICS to intercropping. Theoretical basis and parameterisation. Agronomie 24:409–421. https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2004031
Brown HE, Huth N, Holzworth D (2011) A potato model built using the APSIM plant. NET framework. 19th International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Perth Australia, pp 961-967
Bruhn JA, Fry WE (1981) Analysis of potato late blight epidemiology by simulation modeling. Phytopathol 71:612–616
Ceglar A, Kajfež-Bogataj L (2012) Simulation of maize yield in current and changed climatic conditions: addressing modelling uncertainties and the importance of bias correction in climate model simulations. Eur J Agron 37(1):83–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2011.11.005
Chakrabarti SK, Pandey NK, Tiwari JK, Kumar R, Raigond P, Mankar P, Kharumnuid P, Buckseth T, Dalamu (2019) Annual Report 2018-19 ICAR-Central Potato Research Institute, Shimla, Himachal Pradesh, India, pp. 63. Available at: https://cpri.icar.gov.in/WriteReadData/LINKS/AnnualReport_2018_19-compressedf65d210a-0507-4775-97a9-a801e69b3563.pdf. Accessed 11 Sept 2020
Chakraborty A, Singh BP, Ahmad I, Sharma S (2015) Forecasting late blight of potato in plains of West Bengal using JHULSACAST model. Potato J 42(1):50–57
Chimonyo VGP, Modi AT, Mabhaudhi T (2015) Perspective on crop modelling in the management of intercropping systems. Arch Agron Soil Sci 61:1511–1529. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2015.1017816
Condori B, Hijmans RJ, Francois LJ, Quiroz R (2014) Managing potato biodiversity to cope with frost risk in the High Andes: a modeling perspective. PLoS One 9(1):e81510. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0081510
Confalonieri R, Acutis M, Bellocchi G, Cerrani I, Tarantola S, Donatelli M, Genovese G (2006) Exploratory sensitivity analysis of CROPSYST WARM and WOFOST: a case-study with rice biomass simulations. Ital J Agrometeorol 3:17–25
Contina JB, Dandurand LM, Knudsen GR (2018) A spatial analysis of the potato cyst nematode Globodera pallida in Idaho. Phytopathol 108:988–1001
Cosmo PS, Raffaele C, Stefano P, Fabio C, Hao Y, Guijun Y (2016) Spatialized application of remotely sensed data assimilation methods for farmland drought monitoring using two different crop models. In: Ouwehand L (ed) Proceedings of Dragon 3 Final Results and Dragon 4 Kick-Off Wuhan China
Costa R, Fraga H, Malheiro AC, Santos JA (2015) Application of crop modelling to Portuguese viticulture: implementation and added-values for strategic planning. Ciencia Tec Vitiv 30(1):29–42
Dadrasi A, Torabi Rahimi A, Soltani A, Zeinali E (2020) Parameterization and evaluation of a Simple Simulation Model (SSM-iCrop2) for potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) growth and yield in Iran. Potato Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11540-020-09456-y
de la Casa A, Ovando G, Bressanini L, Martínez J (2013) Aquacrop model calibration in potato and its use to estimate yield variability under field conditions. Atmospheric Clim Sci 3:397–407
de Wit CT, Goudriaan J (1978) Simulation of assimilation respiration and transpiration of crops. Simulation monograph. PUDOC Wageningen, The Netherlands, p 138
de Wit AJW, van Diepen CA (2007) Crop model data assimilation with the Ensemble Kalman filter for improving regional crop yield forecasts. Agric Forest Meteorol 146:38–56
Dewlle GA (1964) Forecasting crop infection by the potato blight fungus. A fundamental approach to the ecology of a parasite–host relationship. Koninklijk Ned. Meteorol. Inst Mededelingen en Verhandelingen 82:1–144
Domínguez A, de Juan JA, Tarjuelo JM, Martínez RS, Martínez-Romero A (2012) Determination of optimal regulated deficit irrigation strategies for maize in a semi-arid environment. Agric Water Manag 110:67–77
Doorenbos J, Kassam A (1979) Yield response to water. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Irrigation and Drainage Paper 33:257
Dua VK, Singh BP, Govindakrishnan PM, Kumar S, Lal SS (2013) Impact of climate change on potato productivity in Punjab – a simulation study. Curr Sci 105(6):787–794
Dua VK, Govindakrishnan PM, Singh BP (2014) Calibration of WOFOST model for potato in India. Potato J 41(2):105–112
Dwelle RB, Kleinkopf GE, Steinhorst RK, Pavek JJ, Hurley PJ (1981) The influence of physiological process on tuber yield of potato genotypes (Solanum tuberosum L.): stomatal diffusive resistance stomatal conductance gross photosynthetic rate leaf canopy tissue nutrient levels and tuber enzymes. Potato Res 24:33–47
Eva P, Petr H, Jozef T, Zdenek Z, Miroslav T (2015) Calibration and validation of the crop growth model DAISY for spring barley in Czech Republic. Acta Univ Agric et Silvic Mendelianae Brun 63(4):1177–1186
Fagodia RK, Nareshkuar S, Harit R (2017) Impacts of short-term sequential stresses on maize (Zea mays L.) and its simulation using info crop-maize model. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 6(12):911–921
Faivre R, Leenhardt D, Voltz M, Benoit M, Papy F, Dedieu G, Wallach D (2004) Spatialising crop models. Agronomie 24:205–217
FAOSTAT (2018) FAO statistical pocketbook. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Rome. Available at http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#search/potato. Accessed 11 Sept 2020
Fischer RA (2015) Definitions and determination of crop yield gaps and of rates of change. Field Crops Res 182:9–18
Forrer HR, Gujer HU, Fried PM (1993) PhytoPRE- a comprehensive information and decision support system for late blight of potatoes. SP- Report Danish Inst Plant Soil Sci 7:173–181
Franke AC, Haverkort AJ, Steyn JM (2013) Climate change and potato production in contrasting South African agro-ecosystems 2. Assessing risks and opportunities of adaptation strategies. Potato Res 56:51–66
Fry WE, Shtienberg D (1990) Integration of host resistance and fungicide to manage potato disease. Can J Plant Pathol 12(1):111–116
Garcia-Vila M, Fereres E (2012) Combining the simulation crop model AquaCrop with an economic model for the optimization of irrigation management at farm level. Eur J Agron 36:21–31
Garcia-Vila M, Fereres E, Mateos L, Orgaz F, Steduto P (2008) Deficit irrigation optimization of cotton with AquaCrop. Agron J 101:477–487
Gaudio N, Gutierrez AJE, Casadebaig P, Evers JB, Gerard F, Louarn G, Colbach N, Munz S, Launay M, Marrou H, Barillot R, Hinsinger P, Bergez J-E, Combes D, Durand J-L, Frak E, Pagès L, Pradal C, Saint-Jean S, Van Der Werf W, Justes E (2019) Current knowledge and future research opportunities for modeling annual crop mixtures-a review. Agron Sustain Dev 39:20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-019-0562-6
Gayler S, Wang E, Priesack E, Schaaf T, Maid FX (2002) Modeling biomass growth N-uptake and phenological development of potato crop. Geoderma 105:367–383
Gobin A (2010) Modelling climate impacts on crop yields in Belgium. Clim Res 44:55–68
Gordon R, Brown D, Dixon MA (1996) Evaluation of a cultivar sensitive soil water model for the potato crop. Can J Soil Sci 76:275–283
Goswami B, Hussain R, Kumar PV, Saikia US, Banarjee S (2018) Impact assessment of climate change on potato productivity in Assam using SUBSTOR-potato model. J Agrometrol 20(2):105–109
Govindakrishnan PM, Singh JP, Lal SS, Panigrahy S (2007) A methodology for pre-harvest prediction of mean potato yield at regional scale using INFOCROP-POTATO model. Potato J 34:125–126
Griffin TS, Johnson BS, Ritchie JT (1995) A simulation model for potato growth and development: SUBSTOR-Potato version 2.0. IBSNAT Research Support series 02. Department of Agronomy and Soil Science University of Hawaii Honolulu HI USA
Gutsche V (1993) PROGEB- a model aided forecasting service for pest management in cereals and potatoes. EPPO Bull 23:577–581
Hansen JW, Challinor A, Ines A, Wheeler T, Moron V (2006) Translating climate forecasts into agricultural terms: advances and challenges. Clim Res 33:27–41
Haris AA, Chabra V, Bhatt BP, Sikka AK (2015) Yield and duration of potato crop in Bihar under projected climate scenarios. J Agrometeorol 17(1):67–73
Haverkort AJ, Grashoff C (2004) IDEOTYPING POTATO: a modelling approach to genotype performance. In: MacKerron DKL, Haverkort AJ (eds) Decision support systems in potato production: bringing models to practice. Wageningen Academic Publishers, Wageningen, pp 198–211
Haverkort AJ, Kooman PL (1997) The use of systems analysis and modelling of growth and development in potato ideotyping under conditions affecting yields. Euphytica 94:191–200
Haverkort AJ, van Haren RJF (1998) The application of modeling in the potato production chain. Acta Horti 476:13–20
Haverkort AJ, Verhagen A, Grashoff C, Uithol PWJ (2003) Potato zoning: a decision support system on expanding the potato industry through agro ecological zoning using the LINTUL simulation approach. In: Mac Kerron DKL, Haverkort AJ (eds) International potato modeling conference: decision support system in potato production. Bringing model to practice. Wageningen Academic Publishers, Wageningen, pp 28–45
Haverkort AJ, Franke AC, Engelbrecht FA, Steyn JM (2013) Climate change and potato production in contrasting South African agro-ecosystems 1. Effects on land and water use efficiencies. Potato Res 56:31–50
Heidmann T, Tofteng C, Abrahamsen P, Plauborg F, Hansen S, Battilani A, Coutinho J, Dolezal F, Mazurczyk W, Ruiz JDR, Takac J, Vacek J (2008) Calibration procedure for a potato crop growth model using information from across. Eur Ecol Model 211:209–223
Hijmans JR (2003) The effect of climate change on global potato production. Amer J Potato Res 80:271–280
Hijmans RJ, Condori B, Carrillo R, Kropff M (2003) A quantitative and constraint specific method to assess the potential impact of new agricultural technology: the case of frost resistant potato for the Altiplano (Peru and Bolivia). Agric Syst 76:895–911
Holzworth DP, Huth NI, deVoil PG, Zurcher EJ, Herrmann NI, McLean G, Chenu K, van Oosterom EJ, Snow V, Murphy C, Moore AD, Brown H, Whish JPM, Verrall S, Fainges J, Bell LW, Peake AS, Poulton PL, Hochman Z, Thorburn PJ, Gaydon DS, DalglieshNP RD, Cox H, Chapman S, Doherty A, Teixeira E, Sharp J, Cichota R, Vogeler I, Li FY, Wang E, Hammer GL, Robertson MJ, Dimes JP, Whitbread AM, Hunt J, van Rees H, McClelland T, Carberry PS, Hargreaves JNG, MacLeod N, McDonald C, Harsdorf J, Wedgwood S, Keating BA (2014) APSIM – evolution towards a new generation of agricultural systems simulation. Environ Model Softw 62:327–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.07.009
Hoogenboom GJ, White JW, Messina CD (2004) From genome to crop: integration through simulation modeling. Field Crops Res 90:145–150
Hoogenboon G (2000) Contribution of agrometeorology to the simulation of crop production and its applications. Agril For Meteorol 103:137–157
Hsiao TC (1973) Plant responses to water stress. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 24:519–570
Hunt LA (1993) Designing improved plant types: a breeder’s view point. In: Penning de Vries FWT, Teng PS, Metselaar K (eds) Systems approaches for sustainable agricultural development. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 3–17
Hunt LA, Reynolds MP, Rajaram S, Whte JW, Yan W (2003) Crop modeling and the identification of stable coefficients that may reflect significant groups of genes. Agron J 95:20–31
Hyre RA (1954) Progress in forecasting late blight of potato and tomato. Plant Dis Reptr 38:245–253
Ines AVM, Mohanty BP (2009) Near-surface soil moisture assimilation for quantifying effective soil hydraulic properties using genetic algorithms: 2. Using airborne remote sensing during SGP97 and SMEX02. Water Resour Res 45:W01408. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR007022
Ines AVM, Honda K, Gupta AD, Droogers P, Clemente R (2006) Combining remote sensing-simulation modeling and genetic algorithm optimization to explore water management options in irrigated agriculture. Agric Water Manag 83(3):221–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2005.12.006
Ines AVM, Das NN, Hansen JW, Njoku EG (2013) Assimilation of remotely sensed soil moisture and vegetation with a crop simulation model for maize yield prediction. Remote Sens Environ 138:149–164
IPCC (2007) Summary for policymakers. In: Parry ML, Canziani OF, Palutikof JP, van der Linden PJ, Hanson CE (eds) Climate Change 2007: Impacts Adaptation and Vulnerability, Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press UK, Cambridge, pp 7–78
Jagyasi B, Kumar V, Pande A, Singh BP, Lal M, Ahmad I, Lohia P (2015) Validation of JHULSACAST model using human participatory sensing and wireless sensor networks. Potato J 42(1):44–49
Jamieson PD, Zyskowski RF, Sinton SM, Brown HE, Butler RC (2006) The potato calculator: a tool for scheduling nitrogen fertilizer applications. Agron NZ 36:49–53
Jego G, Martinez M, Antiguedad I, Launayc M, Sanchez-Pereza JM, Justes E (2008) Evaluation of the impact of various agricultural practices on nitrate leaching under the root zone of potato and sugar beet using the STICS soil–crop model. Sci Total Environ 394:207–221
Jia HC, Wang J, Yue Y, Zhou H, Li R, Gao T, Bai Y (2009) Construction and application of index system of winter wheat drought risk assessment-a preliminary cognition based on fieldwork of spring drought in North China. J Catastrophol 4:20–25
Jones JT, Tsuji JW, Hoogenboom G, Hunt L, Thornton PK, Wilkens P, Singh U (1998) Decision support system for agrotechnology transfer: DSSAT v3 understanding options for agricultural production. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 157–177
Jones JW, Hoogenboom G, Porter CH, Boote KJ, Batchelor WD, Hunt LA, Wilkens PW, Singh U, Gijsman AJ, Ritchie JT (2003) The DSSAT cropping system model. Eur J Agron 18:235–265
Karvonen T, Kleemola J (1995) CROPWATN: prediction of water and nitrogen limited potato production. In: Kabat P, Marshall B, van den Broek BJ, Vos JKH (eds) Modelling and parameterization of the soil-plant-atmosphere system; A Comparison of Potato Growth Models. Wageningen Pers, Wageningen, pp 335–369
Keating BN, Carberry PS, Smith CJ (2003) An overview of APSIM a model Design for Farming Systems Simulation. Eur J Agron 18:267–272
Keating BA, Herraro M, Carberry PS, Garden J, Cole MB (2014) Food wedges: framing the global food demand and supply challenge towards 2050. Glob Food Secur 3(3–4):125–132
Khaembah EN, Brown H, Sharp J, Zyskowski R (2015) Soil nitrogen and soil water dynamics in crop rotations: estimation with the multiple crop single purpose model. In: Conference: moving farm systems to improved attenuation at: fertilizer and lime research Centre Massey University. Palmerston, North New Zealand, pp 1–10
Khan MS, Yin X, van der Putten PEL, Struik PC (2013) An ecophysiological model analysis of yield differences within a set of contrasting cultivars and an F1 segregating population of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) grown under diverse environments. Ecol Model 290:146–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2013.11.015
Kleinhenz B, Falke K, Kakau J, Rossberg D (2007) SIMBLIGHT1 - a new model to predict first occurrence of potato late blight. EPPO Bull 37:339–343
Kleinwechter U, Asseng S, Gastelo M, Ritchie J, Nelson GC (2013) Virtual crop modelling for technology impact assessment - lessons from a potato crop growth model. In: Tielkes E (ed) Agricultural development within the rural urban continuum. Book of abstracts. Tropentag International Research on Food Security, Natural Resource Management and Rural Development, University of Hohenheim, Germany, p 367
Kleinwechter U, Gastelo M, Ritchie J, Nelson G, Asseng S (2016) Simulating cultivar variations in potato yields for contrasting environments. Agric Syst 145:51–63
Kooman PL, Haverkort AJ (1995) Modelling development and growth of the potato crop influenced by temperature and daylength: LINTUL-POTATO. In: Haverkort AJ, MacKerron DKL (eds) Potato ecology and modelling of crops under conditions limiting growth. Kluwer Academic Publication, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 41–59
Kooman PL, Fahem M, Tegera P, Haverkort AJ (1996) Effects of climate on different potato genotypes 1. Radiation interception total and tuber dry matter production. Eur J Agron 5:193–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1161-0301(96)02031
Krause RA, Massie LB, Hyre RA (1975) BLITECAST: a computerized forecast of potato late blight. Plant Dis Reptr 59:95–98
Kropff MJ, Haverkort AJ, Aggarwal PK, Kooman PL (1995) Using systems approaches to design and evaluate ideotypes for specific environments. In: Bouma J, Kuyvenhoven A, Bouman BAM, Luyten JC, Zandstra HG (eds) Eco-regional approaches for sustainable land use and food production. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 417–135
Kropff MJ, Teng PS, Aggarwal PK, Bouman B, Bouma J, Van Laar HH (1996) Applications of system approaches at field level volume 2. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands, p 45
Kroschel J, Sporleder M (2006) Ecological approaches to Integrated Pest Management of the Potato Tuber Moth Phthorimaea operculella Zeller (Lepidoptera: Gelechidae). Proceedings of the 45th Annual Washington State Potato Conference, 7-9 February 2006, Moses Lake Washington, pp 85-94
Lawrence RL, Ripple WJ (1998) Comparisons among vegetation index and bandwise regression in a highly disturbed heterogenous landscape. Washington. Remote Sens Environ 64:91–102
Leinonen I, Grant OM, Tagliavia CPP, Chaves MM, Jones HG (2006) Estimating stomatal conductance with thermal imagery. Plant Cell Environ 29:1508–1518
Leinonen I, Chen H, Taylor JA (2018) Modelling potato growth. In: Wale S (ed) Achieving sustainable cultivation of potatoes: Volume 2: production and Storage, Production and Sustainability (Vol. 2). Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing Limited: Series in Agricultural Science
Lenz-Wiedemann VIS, Klar CW, Schneider K (2010) Development and test of a crop growth model for application within a global change decision support system. Ecol Model 221:314–329
Levy Y, Cohen Y, Benderly M (1991) Disease development and buildup of resistance to oxadixyl in potato crops inoculated with Phytophthora infestans as affected by oxadixyl and oxadixyl mixtures. Experimental and Simulation Studies. J Phytopathol 132:219–229
Li X, Takahashi T, Suzuki N, Kaiser HM (2011) The impact of climate change on maize yields in the United States and China. Agric Syst 104:348–353
Lipper L, Thornton P, Campbel BM, Baedeker T, Braimoh A, Bwalya M (2014) Climate-smart agriculture for food security. Nat Clim Chang 4:1068–1072
Lisson SN, Cotching WE (2011) Modelling the fate of water and nitrogen in the mixed vegetable farming systems of northern Tasmania Australia. Agric Syst 104:600–608
Lobell DB, Gourdji SM (2012) The influence of climate change on global crop productivity. Plant Physiol 160:1686–1697. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.208298
Luo Q, Bellotti W, Williams M, Wang E (2009) Adaptation to climate change of wheat growing in South Australia: analysis of management and breeding strategies. Agric Ecosyst Environ 129:261–267
Mac Hardy WE (1979) A simplified non-computerized programme for forecasting potato late blight. Plant Dis Reptr 63(1):21–25
Machakaire ATB, Steyn JM, Caldiz DO, Haverkort A. J (2016) Forecasting yield and tuber size of processing potatoes in South Africa using the LINTUL-Potato-DSS Model. Potato Res 59:195–206
MacHardy WE (1979) A simplified non-computerized program for forecasting potato late blight. Plant Dis Reptr 63:21–25
Mahdian MH, Gallichand J (1995) Validation of the SUBSTOR model for simulating soil water content. Trans ASAE 38:513–520. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.27860
Malkia R, Hartani T, Dechmi F (2016) Evaluation of DSSAT model for sprinkler irrigated potato: a case study of Northeast Algeria. African J Agric Res 11(29):2589–2598
Manorama K, Govindakrishnan PM, Ravichandran G, Singh BP (2015) Development of a decision support system for potato crop scheduling in Nilgiri hills of Western Ghats. J Agrometeorol 17(2):219–222
McCown RL, Hammer GL, Hargreaves GJN, Holzworth DP, Freebairn DM (1996) APSIM: a novel software system for model development model testing and simulation in agricultural systems research. Agric Syst 50:255–271
Mehraban A (2013) Simulation of wheat yield by AquaCrop model. Int J Farm Allied Sci 2:939–943
Mhatre PH, Karthik C, Kadirvelu K, Divya KL, Venkatasalam EP, Srinivasan S, Ramakumar G, Saranya C, Shanmuganathan R (2019a) Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR): a potential alternative tool for nematodes bio-control. Biocatalyst Agric Biotechnol 17:119–128
Mhatre PH, Divya KL, Venkatasalam EP, Bairawa A, Sudha R, Berliner J (2019b) Potato cyst nematode: a hidden enemy of potato cultivation in hills. Bhartiy Krishi Anusandhan Patrika 34(1):50–53
Mhatre PH, Divya KL, Venkatasalam EP, Bairwa A, Sharma S (2020a) Management of the late blight (Phytophthora infestans) disease of potato in the southern hills of India. J Phytopathol. https://doi.org/10.1111/jph.12958
Mhatre PH, Patil J, Rangasamy V, Divya KL, Tadigiri S, Chawla G, Bairwa A, Venkatasalam EP (2020b) Biocontrol potential of Steinernema cholashanense (Nguyen) on larval and pupal stages of potato tuber moth Phthorimaea operculella (Zeller). J Helminthol 94:e188. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X20000723
Mishra T, Raigond P, Thakur N, Dutt S, Singh B (2020) Recent updates on healthy phytoconstituents in potato: a nutritional depository. Potato Res 63:323–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11540-019-09442-z
Mohabir G, John P (1988) Effect of temperature on starch synthesis in potato tissue and in amyloplasts. Plant Physio 88:1222–1228
Molitor D, Caffarra A, Sinigoj P, Pertot I, Hoffmann L, Junk J (2014) Late frost damage risk for viticulture under future climate conditions: a case study for the Luxembourgish wine growing region. Aust J Grape Wine Res 20(1):160–168
Montoya F, Camargo D, Ortega J, Córcoles J, Domínguez A (2016) Evaluation of Aquacrop model for a potato crop under different irrigation conditions. Agric Water Manag 164:267–280
Montoya F, Camargo D, Córcoles JI, Domínguez A, Ortega JF (2020) Analysis of deficit irrigation strategies by using SUBSTOR-Potato model in a semi-arid area. J Agri Sci 157:578–591. https://doi.org/10.1017/S002185961900090X
Moran MS, Inoue Y, Barnes EM (1997) Opportunities and limitations for image-based remote sensing in precision crop management. Remote Sens Environ 61(3):319–346
Morissette R, Jego G, Belanger G, Cambouris AN, Nyiraneza J, Zebarth BJ (2016) Simulating potato growth and nitrogen uptake in Eastern Canada with the STICS model. Agron J 108:1853–1868
Muli MN, Onwonga RN, Karuku GN, Kathumo VM, Nandukule MO (2015) Simulating soil moisture under different tillage practices cropping systems and organic fertilizers using cropsyst model in Matuu Division Kenya. J Agric Sci 7(2):26–40
Müller C, Elliott J, Chryssanthacopoulos J, Arneth A, Balkovic J, Ciais P, Deryng D, Folberth C, Glotter M, Hoek S, Iizumi T, Izaurralde RC, Jones C, Khabarov N, Lawrence P, Liu W, Olin S, Pugh TAM, Ray DK, Reddy A, Rosenzweig C, Ruane AC, Sakurai G, Schmid E, Skalsky R, Song CX, Wang X, de Wit A, Yang H (2017) Global gridded crop model evaluation: benchmarking skills deficiencies and implications. Geosci Model Dev 10:1403–1422
Nagamani K, Mariappan VEN (2017) Remote sensing GIS and crop simulation models -a review. Int J Curr Res Biosci Plant Biol 4(8):80–92
Nian AS, Kresbaum KC, Dadhwal VK (2012) Linking crop simulation model and remote sensing for wheat yield forecast. J Agrometeorol 14:482–490
Oerke EC, Dehne HW, Schonbeck F, Weber A (1994) Crop production and CropProtection-estimated losses in major food and cash crops. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Olesen JE, Bindi M (2002) Consequences of climate change for European agricultural productivity land use and policy. Eur J Agron 16:239–262
Osakabe Y, Osakabe K, Shinozaki K, Tran L-SP (2014) Response of plants to water stress. Front Plant Sci 5:86
Oteng-Darko P, Yeboah S, Addy SNT, Amponsah S, Danquah EO (2013) Crop modeling: a tool for agricultural research – a review. J Agric Res Dev 2(1):1–6
Palanisamy S, Penning de Vries FWT, Mohandas S, Thiyagarajan TM, Kareem AA (1993) Simulation in pre-testing of rice genotypes in Tamil Nadu. In: de Vries FWT P, Teng PS, Metselaar K (eds) Systems approaches for agricultural development. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 63–75
Palanisamy S, Aggarwal PK, Thiyagarajan TM, Ranganathan TBR (1995) Simulating yield and ranking of rice genotypes in multi-location trials. In: Aggarwal PK, Matthews RB, Kropff MJ, Van Laar HH (eds) Applications of systems approach in plant breeding. SARP Research Proceedings International Rice Research Institute, Manila Philippines, pp 91–95
Park SJ, Hwang CS, Vlek PLG (2005) Comparison of adaptive techniques to predict crop yield response under varying soil and land management conditions. Agric Syst 85(1):59–70
Patel N, Kumar P, Singh N (2011) Performance evaluation of AquaCrop in simulating potato yield under varying water availability conditions. Water Technology Centre Indian Agricultural Research Institute, pp 1–13
Peacock L, Worner S (2006) Using analogous climates and global insect pest distribution data to identify potential sources of new invasive insect pests in New Zealand. New Zealand J Zool 33:141–145
Peng B, Guan K, Tang J, Ainsworth EA, Asseng S, Bernacchi CJ, Cooper M, Delucia EH, Elliott JW, Ewert F, Grant RF, Gustafson DI, Hammer GL, Jin Z, Jones JW, Kimm H, Lawrence DM, Li Y, Lombardozzi DL, Marshall-Colon A, Messina CD, Ort DR, Schnable JC, Vallejos CE, Wu A, Yin X, Zhou W (2020) Towards a multiscale crop modelling framework for climate change adaptation assessment. Nat Plants 6:338–348
Penning de Vries FWT, Jansen DM, Ten Berge HFM, Bakema AH (1989) Simulation of ecophysiological processes in several crops. In: Simulation Monograph. PUDOC Wageningen, The Netherlands, p 271
Place RE, Brown DM (1987) Modelling corn yields from soil moisture estimates: description sensitivity analysis and validation. Agric Forest Meteorol 41:36–56
Pollak ML, Corbett JD (1993) Using GIS datasets to classify maize-growing regions in Mexico and Central America. Agron J 85:1133–1139
Pongratz J, Dolman H, Don A, Erb K-H, Fuchs R, Herold M, Jones C, Kuemmerle T, Luyssaert S, Meyfroidt P, Naudts K (2017) Models meet data: challenges and opportunities in implementing land management in Earth system models. Glob Change Biol 24:1470–1487
Prasad R, Hochmuth GJ, Boote KJ (2015) Estimation of nitrogen pools in irrigated potato production on sandy soil using the Model SUBSTOR. PLoS One 10(1):e0117891
Pundhir VS, Singh BP, Ahmad I, Sharma S, Kushwaha HS, Singh VK, Joshi V (2014) Forecasting late blight of potato in Tarai region of Uttarakhand using JHULSACAST model. Potato J 41(2):95–104
Quiroz R, Loayza H, Barreda C, Gavilán C, Posadas A, Ramírez DA (2017) Linking process-based potato models with light reflectance data: does model complexity enhance yield prediction accuracy? Eur J Agron 82:104–112
Raes D, Steduto P, Hsiao TC, Fereres E (2009) AquaCrop–the FAO crop model to simulate yield response to water: II. Main algorithms and software description. Agron J 101:438–447
Raes D, Steduto P, Hsiao TC, Fereres E (2012) AquaCrop Reference Manual AquaCrop version 4.0. http://www.fao.org/nr/water/aquacrop.html. Accessed 9 May 2020
Rahman A, Mojid MA, Banu S (2018) Climate change impact assessment on three major crops in the north-central region of Bangladesh using DSSAT. Int J Agric Biol Eng 11(4):135–143
Rana A, Dua VK, Chauhan S, Sharma J (2020) Climate change and potato productivity in punjab—impacts and adaptation. Potato Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11540-020-09460-2
Raymundo R, Asseng S, Cammarano D, Quiroz R (2014a) Potato sweet potato and yam models for climate change: a review. Field Crops Res 166:173–185
Raymundo, R., Kleinwechter, U., & Asseng, S. (2014b, January 20). Virtual potato crop modeling: A comparison of genetic coefficients of the DSSAT-SUBSTOR potato model with breeding goals for developing countries. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7687
Raymundo R, Asseng S, Prasad R, Kleinwechter U, Concha J, Condoric B, Bowen W, Wolf J, Olesen JE, Dong Q, Zotarellia L, Gastelo M, Alva A, Travasso M, Quirozc R, Arorai V, Grahama W, Porter C (2017) Performance of the SUBSTOR- Potato model across contrasting growing conditions. Field Crops Res 202:57–76
Razzaghi F, Zhou Z, Andersen MN, Plauborg F (2017) Simulation of potato yield in temperate condition by the AquaCrop model. Agric Water Manag 191:113–123
Resop JP, Fleisher DH, Timlin D, Reddy VR (2011) Evaluating county-level potential production capacity of potatoes for Maine using the crop model SPUDSIM. ASABE Annual Int Meeting 5:3871–3889. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.37346
Ritchie JT, Godwin DC, Otter-Nacke S (1985) CERES-wheat. A Simulation Model of Wheat Growth and Development. US Department of Agriculture, Washington DC, pp 159–175
Ritchie JT, Griffin TS, Johnson BS (1995) SUBSTOR: functional model of potato growth development and yield. In: Kabat P, Marshall B, van den Broek BJ, Vos J, van Kuelen H (eds) Modeling and parameterization of soil-plant-atmosphere system: a comparison potato growth models. Wageningen, Pres Wageningen, pp 401–435
Rondeux G, Steven M, Baret F (1996) Optimization of soil adjusted vegetation indices. Remote Sens Environ 55:95–107
Rotter R, Veeneklaas FR, Van Diepen CA (1995) Impacts of changes in climate and socio-economic factors on land use in the Rhine basin: projections for the decade 2040-49. In: Zwerver S, van Rompaey SAR, Kok TJ, Berk MM (eds) Climate Change Research: Evaluation and Policy Implications. Studies in Environmental Science. Elsevier Science BV, Amsterdam, pp 947–950
Rötter RP, Tao F, Höhn JG, Palosuo T (2015) Use of crop simulation modelling to aid ideotype design of future cereal cultivars. J Exp Bot 66:3456–3476
Sarimento L, Bowen W (2002) Growth of an Andigenum potato variety in the Venezuelan Andes and its simulation by the SUBSTOR model. Ecotropicos 15(1):111–122
Satchithanantham S, Ranjan RS (2015) Evaluation of DRAINMOD for potato crop under cold conditions. Trans ASABE 58(2):307–317
Sedegui M, Carroll RB, Morehart AL, Arifi A, Lakhadar R, Belarbi A (1999) Forecasting potato late blight in Morocco. Al-Awamia 97:9–15
Semenov MA, Doblas-Reyes FJ (2007) Utility of dynamical seasonal forecasts in predicting crop yield. Clim Res 34(1):71–81
Semenov MA, Martre P, Jamieson PD (2009) Quantifying effects of simple wheat traits on yield in water-limited environments using a modelling approach. Agric Forest Meteorol 149(6–7):1095–1104
Semenov MA, Stratonovitch P, Alghabari F, Gooding MJ (2014) Adapting wheat in Europe for climate change. J Cereal Sci 59:245–256
Sharkawy MM, Abd El Hady Arafat SM, Aggag AM (2013) Precision farming using remote sensing and GIS to improve soil and potato crop management. J Agric Environ Sci 2(1):8–16
Shtienberg D, Raposo R, Bergeron SN, Legard DE, Dyer AT, Fry WE (1994) Incorporation of cultivar resistance in a reduced sprays strategy to suppress early and late blight on potato. Plant Dis 78:23–26
Siebert S, Ewert F, Rezaei EE, Kage H, Graβ R (2014) Impact of heat stress on crop yield—on the importance of considering canopy temperature. Environ Res Lett 9:044012
Singh BP, Ahmed I, Sharma VC, Shekhawat GS (2000) JHULSACAST: a computerized forecast of potato late blight in Western Uttar Pradesh. J Indian Potato Assoc 27:25–34
Singh JP, Govindakrishnan PM, Lal SS, Aggarwal PK (2005) Increasing the efficiency of agronomic experiments in potato using INFOCROP- POTATO model. Potato Res 48:131–152
Singh JP, Govindakrishnan PM, Lal SS, Aggarwal PK (2008) INFOCROP-POTATO a model for simulating growth and yield of potato in the sub-tropics. Technical Bulletin-87, CPRI, Shimla, India, pp. 30
Singh JP, Lal SS, Govindakrishnan PM, Dua VK, Pandey SK (2010) Impact of climate change on potato in India. In: Singh HP, Singh JP, Lal SS (eds) Challenges of climate change: Indian horticulture. Westville Publishers, New Delhi, India, pp 90–99
Singh AK, Goyal V, Mishra AK, Parihar SS (2013a) Validation of CropSyst simulation model for direct seeded rice-wheat cropping system. Curr Sci 104:1324–1331
Singh VK, Shailbala, Pundhir VS (2013b) Forecasting models for potato late blight management - a review. Agric Rev 34(2):87–96
Singh BP, Govindakrishnan PM, Ahmad I, Rawat S, Sharma S, Sreekumar J (2016) INDO-BLIGHTCAST-a model for forecasting late blight across agroecologies. Int J Pest Manag 62(4):360–367
Skaggs RW, Youssef MA, Chescheir GM (2012) DRAINMOD: model use calibration and validation. Trans ASABE 55(4):1509–1522
Song Y, Elisabeth S, Chen D, Dong W (2005) Influence of climate change on winter wheat growth in north China during 1950-2000. Acta Meteorol Sinica 19:501–510
Song Y, Chen D, Dong W (2006) Influence of climate on winter wheat productivity in different climate regions of China. Clim Res 32:219–227
Spitters CJT (1990) Crop growth models: their usefulness and limitations. Acta Hort 267:349–368
Spitters CJT, Schapendonk AHCM (1990) Evaluation of breeding strategies for drought tolerance in potato by means of crop growth simulation. Plant Soil 123(2):193–203
Sporleder M, Kroschel J (2008) The potato tuber moth granulovirus (PoGV): use limitations and possibilities for field applications. In: Kroschel J, Lacey L (eds) Integrated Pest Management for the Potato Tuber Moth, Phthorimaea operculella Zeller – a potato Pest of global importance. Tropical agriculture 20 advances in crop research 10. Margraf Publishers, Weikersheim, Germany, pp 49–71
Stasna M, Toman F, Dufkova J (2010) Usage of SUBSTOR model in potato yield prediction. Agric Water Manag 97:286–290
Steduto P, Hsiao TC, Raes D, Fereres E (2009) AquaCrop-the FAO crop model tosimulate yield response to water: I. concepts and underlying principles. Agron J 101:426–437
Steinbauer MJ, Yonow T, Reid IA, Cant R (2002) Ecological biogeography of species of Gelonus Acantholybas and Amorbus in Australia. Austral Ecol 27:1–25
Stevenson WR (1993) IPM for potatoes: a multifaceted approach to disease management and information delivery. Plant Dis 77:309–311
Stockle CO, Martin S, Campbell GS (1994) CropSyst a cropping systems model: water/nitrogen budgets and crop yield. Agric Syst 46:335–359
Stockle CO, Donatelli M, Nelson R (2003) CropSyst a cropping systems simulation model. Eur J Agron 18:289–307
Struik PC (2007) Responses of the potato plant to temperature. In: Vreugdenhil D, Bradshaw J, Gebhardt C, Govers F, MacKerron DKL, Taylor MA, Ross H (eds) Potato biology and biotechnology: advances and perspectives: advances and perspectives. Elsevier Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp 367–393
Struik PC, Ewing EE (1995) Crop physiology of potato (Solanum tuberosum): responses to photoperiod and temperature relevant to crop modelling. In: Haverkort AJ, MacKerron DKL (eds) Potato Ecology and Modelling of Cropsunder Conditions Limiting Growth. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 19–41
Sudha R, Mhatre PH, Divya KL, Venkatasalam EP, Bairawa A, Bharadwaj V, Dalamu SR (2019) Phenotypic and molecular characterization of potato germplasm for potato cyst nematode resistance. Indian J Genet Plant Breed 79(2):394–403
Sun H, Su Z, Lv J, Li L, Wang Y (2017) Dynamic drought risk assessment using crop model and remote sensing techniques IOP Conference Series: earth and environmental science. China. 57:012012. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/57/1/012012
Sutherst RW, Maywald GF (1991) Climate modelling and pest establishment. Climate-matching for quarantine using CLIMEX. Plant Prot Quarterly 6:3–7
Tao F, Rotter RP, Palosuo T, Díaz-Ambrona CGH, Mínguez MI, Semenov MA, Schulman AH (2017) Designing future barley ideotypes using a crop model ensemble. Eur J Agron 82:144–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2016.10.012
Travasso MI, Caldiz DO, Saluzzo JA (1997) Yield prediction using the SUBSTOR-Potato under Argentenina conditions. Potato Res 39:305–312
Trnka M, Rotter RP, Ruiz-Ramos M, Kersebaum KC, Olesen JE, Zalud Z, Semenov MA (2014) Adverse weather conditions for European wheat production will become more frequent with climate change. Nat Clim Chang 4:637–643
Tubiello FN, Ewert F (2002) Simulating the effects of elevated CO2 on crops: approaches and applications for climate change. Eur J Agron 18:57–74
Van Delden A, Schroder JJ, Kropff MJ, Grashoff C, Booij R (2003) Simulated potato yield and crop and soil nitrogen dynamics under different organic nitrogen management strategies in the Netherlands. Agric Ecosyst Environ 96:77–95
Van Haren RJF, van Oijen M, Leffelaar PA, Haverkort AH (1998) Application and description of the LINTUL-potato crop growth model in information technology as a tool to assess land use options in space and time. In: Stoorvogel JJ, Bouma J, Bowen WT (eds) Proceedings of an international workshop 28th September – 4th October, 1997. International Centre of Potato, Lima Peru, pp. 43–57
Van Keulen H, Stol W (1995) Agro ecological zonation for potato production. In: Haverkort AJ, MacKerron DKL (eds) Potato ecology and modeling of crops under conditions limiting growth. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 357–371
Van Keulen H, Wolf J (1986) Modelling of agricultural production: weather soils and crops. Simulation Monographs. PUDOC Wageningen, The Netherlands, p 478
Van Oijen M (1992) Selection and use of a mathematical model to evaluate components of resistance to Phytophthora infestans in potato. Netherlands J Plant Path 98:192–202
Vanuytrecht E, Raes D, Willems P (2011) Considering sink strength to model crop production under elevated atmospheric CO2. Agric Forest Meteorol 151:1753–1762
Vanuytrecht E, Raes D, Willems P (2016) Regional and global climate projections increase midcentury yield variability and crop productivity in Belgium. Reg Environ Chang 16:659–672
Vazifedoust M, Van Dam JC, Bastiaanssen WGM, Feddes RA (2009) Assimilation of satellite data into agrohydrological models to improve crop yield forecasts. Int J Remote Sens 30:2523–2545
Vos J, Haverkort AJ (2007) Water availability and potato crop performance. In: Vreugdenhil (ed) Potato biology and biotechnology advances and perspectives, Elsevier B.V Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp. 333–438
Waggoner PE (1968) Weather and rise and fall of fungi. Oregon State Corvallis USA, pp 45–66
Wallach DJWJ, Makowski D, Brun F (2006) Working with dynamic crop models. In: Wallach JWJD, Makowski D (eds) Evaluation Analysis Parameterization and Applications. Elsevier Science, p 462
Wallin JR (1962) Summary of recent progress in predicting late blight epidemics in United States and Canada. Am Potato J 39:306–312
Wellens J, Raes D, Traore F, Denis A, Djaby B, Tychon B (2013) Performance assessment of the FAO AquaCrop model for irrigated cabbage on farmer plots in a semi-arid environment. Agric Water Manag 127:40–47
Wharton PS, Kirk WW, Baker KM, Uynslager L (2008) A web-based interactive system for risk management of potato late blight in Michigan. Comput Electron Agr 61:136–148
Wheeler T, von Braun J (2013) Climate change impacts on global food security. Sci 341:508–513. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1239402
Wheeler RM, Seffen KL, Tibbitts TW, Palta JP (1986) Utilization of potatoes for life support systems. II: the effects of temperature under 24-h and 12-hphotoperiods. Am Potato J 63:639–647
Wijesinha-Bettoni R, Mouillé B (2019) The contribution of potatoes to global food security, nutrition and healthy diets. Am J Potato Res 96:139–149
Wilhite DA (2011) Quantification of agricultural drought for effective drought mitigation and preparedness: key issues and challenges. Drought Mitigation Center Faculty Publications Paper, 82
Winstel K (1993) Kraut-und-knollenfaule der kartoffel eine eeue prognosemoglichkeit-sowie bekampfungsstrategien. Med Fac Landbouww, Univ Gent 58(3b):1477–1489
Wolday K, Hruy G (2015) A review on: performance evaluation of crop simulation model (APSIM) in prediction crop growth development and yield in semi-arid tropics. J Natural Sci Res 5:21
Wolf J (2002) Comparison of two potato simulation models under climate change. II. Application of climate change scenarios. Clim Res 21:187–198
Wolf J, Van Oijen M (2003) Model simulation of effects of changes in climate and atmospheric CO2 and O3 on tuber yield potential of potato (cv Bintje) in the European Union. Agric Ecosyst Environ 94:141–157
Wolf J, Mandryk M, Kanellopoulos A, Oort PV, Schaap BF, Reidsma P, Van Ittersum MK (2011) Integrated assessment of adaptation to climate change in Flevoland at the farm and regional level. AgriAdapt report 4&5. Wageningen University and Research Centre, Wageningen, The Netherlands, p 137
Woli P, Hoogenboom G, Alva A (2016) Simulation of potato yield nitrate leaching and profit margins as influenced by irrigation and nitrogen management in different soils and production regions. Agric Water Manag 171:120–130
Wu A, Hammer GL, Doherty A, von Caemmerer S, Farquhar GD (2019) Quantifying impacts of enhancing photosynthesis on crop yield. Nat Plants 5:380–388
Xie Y, Lark TJ, Brown JF, Gibbs HK (2019) Mapping irrigated cropland extent across the conterminous United States at 30 m resolution using a semi-automatic training approach on Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J Photogramm 155:136–149
Yang W, Duan L, Chen G, Xiong L, Liu Q (2013) Plant phenomics and high throughput phenotyping: accelerating rice functional genomics using multidisciplinary technologies. Curr Opin Plant Biol 16:180–187
Zinyengere N, Crespo O, Hachigonta S, Tadross M (2015) Crop model usefulness in drylands of southern Africa: an application of DSSAT. South African J Plant Soil 32(2):95–104
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Divya KL: conceptualization and writing original draft. Priyank Hanuman Mhatre: conceptualization, writing, review and editing the original draft. Venkatasalam EP: review and editing. Sudha R: review and editing. All authors read and approved manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Statement
This review paper has not been considered in this or any other form for publication elsewhere. No ethics have been violated in compiling this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Divya, K.L., Mhatre, P.H., Venkatasalam, E.P. et al. Crop Simulation Models as Decision-Supporting Tools for Sustainable Potato Production: a Review. Potato Res. 64, 387–419 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11540-020-09483-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11540-020-09483-9