Abstract
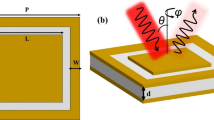
In this study, a periodic array of square bar-shaped nickel (Ni) metal is presented as a straightforward and cost-effective broadband absorber spanning the visible to mid-infrared spectrum. The proposed square bar-shaped nanoabsorber (SBNA) holds a simple and single-layer design topology, which contains plasmonic metal at the top and bottom side of the middle dielectric spacer. The metallic layers are composed of plasmonic Ni, while a dielectric spacer, aluminum nitride (AlN), is employed. The absorption characteristics of the proposed SBNA are evaluated using the full-wave simulation software CST Studio. The SBNA exhibits a broad absorption bandwidth spanning from 200 to 3500 nm, encompassing the ultraviolet (UV) to the short-infrared spectrum. Moreover, an angular stability analysis of the designed SBNA is conducted by considering both the excitation modes (TE and TM). The absorption properties of the SBNA remain the same under the variation of polarization angle; it is owing to the fourfold symmetric configuration of the absorber. The effective engineering of design parameters, including the length of the square-shaped nano-bar, spacer thickness, and periodicity of the unit cell, significantly influences the absorption window. In conclusion, the designed SBNA holds significant potential for diverse applications such as energy harvesting, optical emission, and thermal photonics.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Groever B, Chen WT, Capasso F (2017) Meta-lens doublet in the visible region. Nano Lett 17(8):4902–4907
Khorasaninejad M et al (2016) Multispectral chiral imaging with a metalens. Nano Lett 16(7):4595–4600
Chau Y-F et al (2013) Structurally and materially sensitive hybrid surface plasmon modes in periodic silver-shell nanopearl and its dimer arrays. J Nanopart Res 15:1–13
Yang W, Lin Y-S (2020) Tunable metamaterial filter for optical communication in the terahertz frequency range. Opt Express 28(12):17620–17629
Landy N, Smith DR (2013) A full-parameter unidirectional metamaterial cloak for microwaves. Nat Mater 12(1):25–28
Miscuglio M et al (2021) Approximate analog computing with metatronic circuits. Commun Phys 4(1):196
Naveed MA, Bilal RMH, Baqir MA, Bashir MM, Ali MM, Rahim AA (2021) Ultrawideband fractal metamaterial absorber made of nickel operating in the UV to IR spectrum. Opt Express 29(26):42911–42923
Engheta N, Ziolkowski RW (2006) Metamaterials: physics and engineering explorations. John Wiley & Sons
Shalaev VM (2007) Optical negative-index metamaterials. Nat Photonics 1(1):41–48
Naveed MA et al (2021) Optical spin-symmetry breaking for high-efficiency directional helicity-multiplexed metaholograms. Microsyst Nanoeng 7(1):5
Naveed MA et al (2022) Novel spin-decoupling strategy in liquid crystal-integrated metasurfaces for interactive metadisplays. Adv Opt Mater 10(13):2200196
Alsulami QA, Wageh S, Al-Ghamdi AA, Bilal RMH, Saeed MA (2022) A tunable and wearable dual-band metamaterial absorber based on polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate for sensing applications. Polymers 14(21):4503
Chau Y-F, Yeh H-H, Tsai DP (2010) A new type of optical antenna: plasmonics nanoshell bowtie antenna with dielectric hole. J Electromagn Waves Appl 24(11–12):1621–1632
Bilal R et al (2021) A novel omega shaped microwave absorber with wideband negative refractive index for C-band applications. Optik 242:167278
He Y, Gao Z, Jia D, Zhang W, Du B, Chen ZN (2017) Dielectric metamaterial-based impedance-matched elements for broadband reflectarray. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 65(12):7019–7028
Zetterstrom O, Hamarneh R, Quevedo-Teruel O (2021) Experimental validation of a metasurface Luneburg lens antenna implemented with glide-symmetric substrate-integrated holes. IEEE Antennas Wirel Propag Lett 20(5):698–702
Ahmad T et al (2022) Ultrawideband cross-polarization converter using anisotropic reflective metasurface. Electronics 11(3):487
Costa F, Borgese M (2021) Electromagnetic model of reflective intelligent surfaces. IEEE Open J Commun Soc 2:1577–1589
Chau Y-F, Tsai DP (2007) Three-dimensional analysis of silver nano-particles doping effects on super resolution near-field structure. Opt Commun 269(2):389–394
Bilal RMH, Baqir MA, Hameed M, Naqvi SA, Ali MM (2022) Triangular metallic ring-shaped broadband polarization-insensitive and wide-angle metamaterial absorber for visible regime. JOSA A 39(1):136–142
Genovesi S, Costa F, Monorchio A (2012) Low-profile array with reduced radar cross section by using hybrid frequency selective surfaces. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 60(5):2327–2335
Sabaruddin NR et al (2024) Designing a broadband terahertz metamaterial absorber through bi-layer hybridization of metal and graphene. Plasmonics 1–14
Sabaruddin NR, Tan YM, Chou Chao C-T, Kooh MRR, Chou Chau Y-F (2023) High sensitivity of metasurface-based five-band terahertz absorber. Plasmonics 1–13
Chao C-TC, Kooh MRR, Lim CM, Thotagamuge R, Mahadi AH, Chau Y-FC (2023) Visible-range multiple-channel metal-shell rod-shaped narrowband plasmonic metamaterial absorber for refractive index and temperature sensing. Micromachines 14(2):340
Grant J, Kenney M, Shah YD, Escorcia-Carranza I, Cumming DR (2018) CMOS compatible metamaterial absorbers for hyperspectral medium wave infrared imaging and sensing applications. Opt Express 26(8):10408–10420
Garg P, Jain P (2019) Isolation improvement of MIMO antenna using a novel flower shaped metamaterial absorber at 5.5 GHz WiMAX band. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs 67(4):675–679
Tak J, Jeong E, Choi J (2017) Metamaterial absorbers for 24-GHz automotive radar applications. J Electromagn Waves Appl 31(6):577–593
Chou Chao C-T, Chen S-H, Huang HJ, Chou Chau Y-F (2023) Near-and mid-infrared quintuple-band plasmonic metamaterial absorber. Plasmonics 18(4):1581–1591
Xiong H, Hong J-S, Luo C-M, Zhong L-L (2013) An ultrathin and broadband metamaterial absorber using multi-layer structures. J Appl Phys 114(6)
Park JW et al (2013) Multi-band metamaterial absorber based on the arrangement of donut-type resonators. Opt Express 21(8):9691–9702
Bilal R, Naveed M, Baqir M, Ali M, Rahim A (2020) Design of a wideband terahertz metamaterial absorber based on Pythagorean-tree fractal geometry. Opt Mater Express 10(12):3007–3020
Bilal RMH, Rahim AA, Maab H, Ali MM (2018) Modified wang shaped ultra-wideband (UWB) fractal patch antenna for millimetre-wave applications. In 2018 Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS-Toyama). IEEE 280–284
Yang C, Chang H, Xiao L, Qu Y (2022) Visible and NIR transparent broadband microwave absorption metamaterial based on silver nanowires. Opt Mater 131:112464
Tuan TS, Hoa NTQ (2019) Numerical study of an efficient broadband metamaterial absorber in visible light region. IEEE Photonics J 11(3):1–10
Bilal R et al (2020) Elliptical metallic rings-shaped fractal metamaterial absorber in the visible regime. Sci Rep 10(1):14035
Bilal RMH, Zakir S, Naveed MA, Zubair M, Mehmood MQ, Massoud Y (2023) Nanoengineered nickel-based ultrathin metamaterial absorber for the visible and short-infrared spectrum. Opt Mater Express 13(1):28–40
Qian Q, Yan Y, Wang C (2018) Flexible metasurface black nickel with stepped nanopillars. Opt Lett 43(6):1231–1234
Zhou Y, Luo M, Shen S, Zhang H, Pu D, Chen L (2018) Cost-effective near-perfect absorber at visible frequency based on homogenous meta-surface nickel with two-dimension cylinder array. Opt Express 26(21):27482–27491
Hakim ML et al (2022) Ultrawideband polarization-independent nanoarchitectonics: a perfect metamaterial absorber for visible and infrared optical window applications. Nanomaterials 12(16):2849
Mehrabi S, Bilal RMH, Naveed MA, Ali MM (2022) Ultra-broadband nanostructured metamaterial absorber based on stacked square-layers of TiN/TiO 2. Opt Mater Express 12(6):2199–2211
Sheta E, Choudhury P, Ibrahim A-BM (2022) Polarization-insensitive ultra-wideband metamaterial absorber comprising different forms of ZrN structures at the metasurface. Opt Mater 133:112990
Wang W et al (2021) Broadband thin-film and metamaterial absorbers using refractory vanadium nitride and their thermal stability. Opt Express 29(21):33456–33466
Bilal RMH et al (2021) Wideband microwave absorber comprising metallic split-ring resonators surrounded with E-shaped fractal metamaterial. IEEE Access 9:5670–5677
Liu C et al (2019) Angular dependent strong coupling between localized waveguide resonance and surface plasmon resonance in complementary metamaterials. J Phys Condens Matter 31(8)
Naveed MA, Bilal RMH, Rahim AA, Baqir MA, Ali MM (2021) Polarization-insensitive dual-wideband fractal meta-absorber for terahertz applications. Appl Opt 60(29):9160–9166
Vu DQ et al (2018) Broadening the absorption bandwidth of metamaterial absorber by coupling three dipole resonances. Physica B 532:90–94
Wang B-X (2016) Quad-band terahertz metamaterial absorber based on the combining of the dipole and quadrupole resonances of two SRRs. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 23(4):1–7
Mehmood MQ, Shah AR, Naveed MA, Mahmood N, Zubair M, Massoud Y (2023) MXene-based polarization-insensitive UV-VIS-NIR meta-absorber. IEEE Access 11:130287–130295
Hoa NTQ, Lam PH, Tung PD, Tuan TS, Nguyen H (2019) Numerical study of a wide-angle and polarization-insensitive ultrabroadband metamaterial absorber in visible and near-infrared region. IEEE Photonics J 11(1):1–8
Luo F, Li C, He X (2023) Ultra-wideband and wide-angle metamaterial absorber for solar energy harvesting from ultraviolet to near infrared. Phys Scr 98(12):125504
Kumar R, Singh BK, Pandey PC (2023) Cone-shaped resonator-based highly efficient broadband metamaterial absorber. Opt Quant Electron 55(7):579
Liu Z, Liu G, Huang Z, Liu X, Fu G (2018) Ultra-broadband perfect solar absorber by an ultra-thin refractory titanium nitride meta-surface. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 179:346–352
Wu P, Dai S, Zeng X, Su N, Cui L, Yang H (2023) Design of ultra-high absorptivity solar absorber based on Ti and TiN multilayer ring structure. Int J Therm Sci 183:107890
Funding
There is no associated funding with this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z. Gao is the single author of this article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Z. Design and Analysis of Plasmonic Solar Absorber for Visible and Infrared Spectrum. Plasmonics (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-024-02297-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-024-02297-2