Abstract
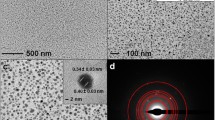
Incorporating silver nanoparticles (NPs) into a host material has been recognized to limit the release of Ag+ ions, yet their efficacy in neutralizing nearby microorganisms remains uncertain. This study aims to compare the toxicity of Ag+ ions versus the plasmonic effect of Ag NPs within a glass matrix, assessing their respective killing efficiency and mechanisms against microorganisms. To achieve this objective, a simple ion exchange technique was employed to embed glass with silver ions, nanoclusters (NCs), or NPs, which was confirmed by UV–Vis-NIR spectrometer, photoluminescence (PL), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The biocidal action of these Ag species on model Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria was investigated in the absence and presence of visible light. The findings revealed that in the absence of light, plasmonic Ag NPs were less toxic to E. coli compared to Ag+ ions due to the predominant release of Ag+ ions dictating the antibacterial effect. However, exposure to visible light triggered the plasmonic effect in Ag NPs to disintegrate 100% E. coli in 1 h compared to Ag+ ions (68%) owing to the localized heating around the Ag NPs, facilitated by surface plasmon resonance relaxation. The cell morphology investigated by Bio-AFM assisted in unraveling the mechanism leading to bacterial cell damage. Overall, this study demonstrates the sustained disinfection capability of Ag NPs embedded in glass without significant leaching, emphasizing their potential in prolonged antimicrobial applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Kim JS, Kuk E, Yu KN et al (2007) Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 3:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2006.12.001
Rai M, Yadav A, Gade A (2009) Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol Adv 27:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.09.002
Ravindran A, Chandran P, Khan SS (2013) Biofunctionalized silver nanoparticles: advances and prospects. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 105:342–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.07.036
Jiao Y, Li X, Zhang X et al (2023) Silver antibacterial surface adjusted by hierarchical structure on 3D printed porous titanium alloy. Appl Surf Sci 610:155519. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APSUSC.2022.155519
Hamad A, Khashan KS, Hadi A (2020) Silver nanoparticles and silver ions as potential antibacterial agents. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 30:4811–4828. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10904-020-01744-X/TABLES/4
Panáček A, Kvítek L, Prucek R et al (2006) Silver colloid nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and their antibacterial activity. J Phys Chem B 110:16248–16253. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp063826h
Franci G, Falanga A, Galdiero S et al (2015) Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 20:8856–8874. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20058856
Kunz JN, Voronine DV, Lu W et al (2017) Aluminum plasmonic nanoshielding in ultraviolet inactivation of bacteria. Sci Rep 7:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08593-8
Gamage McEvoy J, Zhang Z (2014) Antimicrobial and photocatalytic disinfection mechanisms in silver-modified photocatalysts under dark and light conditions. J Photochem Photobiol, C 19:62–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2014.01.001
Shi H, Li G, Sun H et al (2014) Visible-light-driven photocatalytic inactivation of E. coli by Ag/AgX-CNTs (X=Cl, Br, I) plasmonic photocatalysts: bacterial performance and deactivation mechanism. Appl Catal B 158–159:301–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.04.033
Evanoff DD, Chumanov G (2005) Synthesis and optical properties of silver nanoparticles and arrays. ChemPhysChem 6:1221–1231. https://doi.org/10.1002/CPHC.200500113
Evanoff DD, Chumanov G (2004) Size-controlled synthesis of nanoparticles. 2. Measurement of extinction, scattering, and absorption cross sections. J Phys Chem B 108:13957–13962. https://doi.org/10.1021/JP0475640
Romdoni Y, Kadja GTM, Kitamoto Y, Khalil M (2023) Synthesis of multifunctional Fe3O4@SiO2-Ag nanocomposite for antibacterial and anticancer drug delivery. Appl Surf Sci 610:155610. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APSUSC.2022.155610
Wang P, Song Y, Mei Q et al (2022) Sliver nanoparticles@carbon dots for synergistic antibacterial activity. Appl Surf Sci 600:154125. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APSUSC.2022.154125
Candreva A, De Rose R, Perrotta ID et al (2023) Light-induced clusterization of gold nanoparticles: a new photo-triggered antibacterial against E. coli proliferation. Nanomaterials 13:746. https://doi.org/10.3390/NANO13040746/S1
Guglielmelli A, D’Aquila P, Palermo G et al (2023) Role of the human serum albumin protein corona in the antimicrobial and photothermal activity of metallic nanoparticles against Escherichia coli bacteria. ACS Omega 8:31333–31343. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSOMEGA.3C03774/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/AO3C03774_0009.JPEG
Taye MB (2022) Biomedical applications of ion-doped bioactive glass: a review. Applied Nanoscience 12(12):3797–3812. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13204-022-02672-7
Hussein EA, Zagho MM, Nasrallah GK, Elzatahry AA (2018) Recent advances in functional nanostructures as cancer photothermal therapy. Int J Nanomedicine 13:2897–2906. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S161031
Varma RS, Kothari DC, Tewari R (2009) Nano-composite soda lime silicate glass prepared using silver ion exchange. J Non Cryst Solids 355:1246–1251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2009.05.001
Berneschi S, Righini GC, Pelli S (2021) Towards a glass new world: the role of ion-exchange in modern technology. Applied Sciences 11:4610. https://doi.org/10.3390/APP11104610
Guldiren D, Aydin S (2016) Characterization and antimicrobial properties of soda lime glass prepared by silver/sodium ion exchange. Mater Sci Eng, C 67:144–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEC.2016.04.109
Guldiren D, Aydın S (2017) Antimicrobial property of silver, silver-zinc and silver-copper incorporated soda lime glass prepared by ion exchange. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 78:826–832. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEC.2017.04.134
Zhang J, Dong W, Qiao L et al (2007) Silver nanocluster formation in soda-lime silicate glass by X-ray irradiation and annealing. J Cryst Growth 305:278–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCRYSGRO.2007.04.026
Varma RS, Kothari DC, Mallik AK et al (2015) Optical properties of ion exchanged and swift heavy ion beam treated silicate glasses. Adv Mater Lett 6:425–431. https://doi.org/10.5185/AMLETT.2015.5724
Fuertes G, Sánchez-Muñoz OL, Pedrueza E et al (2011) Switchable bactericidal effects from novel silica-coated silver nanoparticles mediated by light irradiation. Langmuir 27:2826–2833. https://doi.org/10.1021/la1045282
Sarkar D, Khare D, Kaushal A et al (2019) Green and scalable synthesis of nanosilver loaded silica microparticles by spray-drying: application as antibacterial agent, catalyst and SERS substrate. Applied Nanoscience (Switzerland) 9:1925–1937. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13204-019-01031-3/METRICS
Yallappa S, Manjanna J, Dhananjaya BL et al (2016) Phytochemically functionalized cu and ag nanoparticles embedded in MWCNTs for enhanced antimicrobial and anticancer properties. Nanomicro Lett 8:120–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-015-0066-0
Bing W, Chen Z, Sun H et al (2015) Visible-light-driven enhanced antibacterial and biofilm elimination activity of graphitic carbon nitride by embedded Ag nanoparticles. Nano Res 8:1648–1658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0654-1
Song J, Kang H, Lee C et al (2012) Aqueous synthesis of silver nanoparticle embedded cationic polymer nanofibers and their antibacterial activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:460–465. https://doi.org/10.1021/am201563t
Kędziora A, Wieczorek R, Speruda M et al (2021) Comparison of antibacterial mode of action of silver ions and silver nanoformulations with different physico-chemical properties: experimental and computational studies. Front Microbiol 12:1707. https://doi.org/10.3389/FMICB.2021.659614/BIBTEX
Kędziora A, Speruda M, Krzyżewska E et al (2018) Similarities and differences between silver ions and silver in nanoforms as antibacterial agents. Int J Mol Sci 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS19020444
Manikandan D, Mohan S, Nair KGM (2003) Absorption and luminescence of silver nanocomposite soda-lime glass formed by Ag+-Na+ ion-exchange. Mater Res Bull 38:1545–1550. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-5408(03)00165-X
Dubiel M, Haug J, Kruth H et al (2009) Temperature dependence of EXAFS cumulants of Ag nanoparticles in glass. J Phys Conf Ser 190:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/190/1/012123
Simo A, Polte J, Pfänder N et al (2012) Formation mechanism of silver nanoparticles stabilized in glassy matrices. J Am Chem Soc 134:18824–18833. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja309034n
Yu C, Schira R, Brune H et al (2018) Optical properties of size selected neutral Ag clusters: electronic shell structures and the surface plasmon resonance. Nanoscale 10:20821–20827. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr04861d
Cattaruzza E, Mardegan M, Trave E et al (2011) Modifications in silver-doped silicate glasses induced by ns laser beams. Appl Surf Sci 257:5434–5438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.11.099
Mooradian A (1969) Photoluminescence of metals. Phys Rev Lett 22:185–187. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.22.185
Mekki A, Holland D, McConville CF, Salim M (1996) An XPS study of iron sodium silicate glass surfaces. J Non Cryst Solids 208:267–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(96)00523-6
Singh P, Garg A, Pandit S et al (2018) Antimicrobial effects of biogenic nanoparticles Nanomaterials 8:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8121009
Xiu ZM, Zhang QB, Puppala HL et al (2012) Negligible particle-specific antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. Nano Lett 12:4271–4275. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl301934w
Jain PK, Huang X, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2008) Noble metals on the nanoscale: optical and photothermal properties and some applications in imaging, sensing, biology, and medicine. Acc Chem Res 41:1578–1586. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar7002804
Acknowledgements
Ranjana Varma thanks WOS-A scheme (SR/WOS-A/PM-5/2017) for providing financial support. The authors are grateful to Prof. D C Kothari, University of Mumbai, India for fruitful discussion and useful suggestions. Nainesh Patel thanks CHRIST University for providing SEED funding (SMSS-2107).
Funding
Department of Science and technology, India, WOS-A scheme (SR/WOS-A/PM-5/2017) for providing financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NT: performed the experiments and prepared the initial draft of manuscript. RV: analysis of data. KD: performed AFM and analyzed the data. VKM: performed antibacterial test. BMB: writing the manuscript. RP: performed the XPS and analyzed data. NP: supervising the complete work and preparing the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Thorat, N., Varma, R., Date, K. et al. Ag Ions Versus Ag Nanoparticle-Embedded Glass for Antimicrobial Activity Under Light. Plasmonics (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-024-02233-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-024-02233-4