Abstract
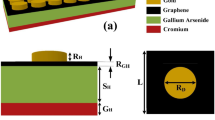
Early in history, societies utilize renewable energy sources in response to technical developments and external factors, which resulted in the development of hydropower, wind turbines, and solar PV, as well as their support through policies and agreements. The double ring covered disk resonator solar absorber (DRCDRSA) structures are examined over the spectral range of wavelength 0.2 µm to 2.5 µm (UV-FIR) with the help of finite element method (FEM) in this study. This design achieved effective solar absorption, surpassing 99% over the 0.46 µm band, 95% over 2.05 µm wideband, and 90% over the entire observed spectral range, with an overall average absorbance of 96.38%. In addition, the maximum absorbance is 99.9% with three pick values at the wavelengths of 0.34 µm, 1.35 µm, and 1.51 µm. This research includes a parameter optimization as well as the electric field strength and magnetic field intensity distribution over a three-dimensional solar absorber construction. The structure’s angle-polarization study shows it is polarization independent, handles diverse angles, and maintains even absorption up to 60° across all wavelengths. This study explores effective solar heaters for air and water systems, offering promising prospects for maximizing solar energy utilization.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The data supporting the findings in this work are available from the corresponding author with reasonable request.
References
Alsalman O, Wekalao J, Arun Kumar U, Agravat D, Parmar J, Patel SK (2023) Design of split ring resonator graphene metasurface sensor for efficient detection of brain tumor. Plasmonics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02002-9
Aliqab K, Wekalao J, Alsharari M, Armghan A, Agravat D, Patel SK (2023) Designing a graphene metasurface organic material sensor for detection of organic compounds in wastewater. Biosensors 13(8):759. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13080759
Szunerits S, Maalouli N, Wijaya E, Vilcot JP, Boukherroub R (2013) Recent advances in the development of graphene-based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) interfaces. Anal Bioanal Chem 405(5):1435–1443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6624-0
Rangasamy S, Khansadurai AM, Venugopal G, Udayakumar AK (2023) Graphene-based O-shaped metamaterial absorber design with broad response for solar energy absorption. Opt Quantum Electron 55:1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-04315-1
Dharmaraj SK, Ramasubbu H, Rajendran V, Ravichandran P (2023) Effect of graphene nanopaint on performance of solar air heater attached with inclined and winglet baffles. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28646-y
Almawgani AHM, Htay MM, Al-Athwary AAH, Patel SK (2023) Perfect and broadband slotted Zr thin film solar absorber backed by Ti layer for visible and infrared spectrum. Opt Quantum Electron 55(8):722. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05021-2
Almawgani AHM et al (2023) Structural investigation of ultra – Broadband disk-shaped resonator solar absorber structure based on CNT – TiC composites for solar energy harvesting. Int J Therm Sci 192:108414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2023.108414
Almawgani AHM, Han BB, Anushkannan NK, Armghan A, Alzahrani A, Patel SK (2023) Solar thermal energy harvesting using graphene-based plus-shaped Cr–InSb–Cr multilayer structure. Int J Therm Sci 193:108501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2023.108501
Patel SK et al (2023) Design of a broadband solar absorber based on Fe2O3/CuO thin film absorption structure. Opt Quantum Electron 55:5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-04706-y
Patel SK, Charola S, Parmar J, Ladumor M, Ngo QM, Dhasarathan V (2020) Broadband and efficient graphene solar absorber using periodical array of C-shaped metasurface. Opt Quantum Electron 52:5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02379-5
Hoque A, Islam MT (2020) Numerical analysis of single negative broadband metamaterial absorber based on Tri thin layer material in visible spectrum for solar cell energy harvesting. Plasmonics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01132-8
Zhou F et al (2021) Ultra-wideband and wide-angle perfect solar energy absorber based on Ti nanorings surface plasmon resonance. Phys Chem Chem Phys 23(31):17041–17048. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1cp03036a
Zhuo S et al (2022) THz broadband and dual-channel perfect absorbers based on patterned graphene and vanadium dioxide metamaterials. Opt Express 30(26):47647. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.476858
Liu Z et al (2022) Double narrowband induced perfect absorption photonic sensor based on graphene–dielectric–gold hybrid metamaterial. Nanoscale Res Lett 17:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-022-03724-1
Agravat D, Patel SK, Almawgani AHM, Irfan M, Armghan A, Taya SA (2023) Graphite-based surface plasmon resonance structure using Al2O3-TiO2-ZrO2 materials for solar thermal absorption. Plasmonics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01986-8
Kalogirou SA (2004) Solar thermal collectors and applications. Prog Energy Combust Sci 30(3):231–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2004.02.001
COMSOL Multiphysics® v. 6.0
Falkovsky LA (2008) Optical properties of graphene. J Phys Conf Ser 129. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/129/1/012004
Hu B, Yao M, Xiao R, Chen J, Yao X (2014) Optical properties of amorphous Al2O3 thin films prepared by a sol-gel process. Ceram Int 40(9):14133–14139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.05.148
Evtushenko YM, Romashkin SV, Trofimov NS, Chekhlova TK (2015) Optical properties of TiO2 thin films. Phys Procedia 73:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2015.09.128
Lye RG, Logothetis EM (1966) Optical properties and band structure of titanium carbide. Phys Rev 147(2):622–635. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.147.622
Marques L, Pinto HM, Fernandes AC, Banakh O, Vaz F, Ramos MMD (2009) Optical properties of titanium oxycarbide thin films. Appl Surf Sci 255(10):5615–5619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.08.022
Qing F, Hou Y, Stehle R, Li X (2019) Chemical vapor deposition synthesis of graphene films. APL Mater 7(2). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5078551
Xu S, Zhang L, Wang B, Ruoff RS (2021) Chemical vapor deposition of graphene on thin-metal films. Cell Rep Phys Sci 2(3). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrp.2021.100372
Singh RS, Bhushan S, Singh AK, Deo SR (2011) Characterization and optical properties of Cdse nano-crystalline thin films. Dig J Nanomater Biostructures 6(2):403–412
Agarwal S, Prajapati YK (2019) Multifunctional metamaterial surface for absorbing and sensing applications. Opt Commun 439:304–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2019.01.020
Demiryont H, Thompson LR, Collins GJ (1986) Optical properties of aluminum oxynitrides deposited by laser-assisted CVD. Appl Opt 25(8):1311. https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.25.001311
Hanson GW (2008) Dyadic Green’s functions and guided surface waves for a surface conductivity model of graphene. J Appl Phys 103:6. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2891452
Air Mass 1.5 Spectrum, American society for testing and materials (ASTM)
Patel SK, Agravat D, Alsalman O, Surve J, Taya SA, Parmar J (2023) Numerical analysis of wideband solar absorber using thick film with glassy material, resonator and back reflector. Opt Quantum Electron 55(9):754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-04982-8
Liu Z et al (2019) Truncated titanium/semiconductor cones for wide-band solar absorbers. Nanotechnology 30:30. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab109d
Yu P et al (2019) A numerical research of wideband solar absorber based on refractory metal from visible to near infrared. Opt Mater (Amst) 97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2019.109400
Obaidullah M, Esat V, Sabah C (2021) Multi-band (9,4) chiral single-walled carbon nanotube based metamaterial absorber for solar cells. Opt Laser Technol 134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106623
Wu P, Dai S, Zeng X, Su N, Cui L, Yang H (2023) Design of ultra-high absorptivity solar absorber based on Ti and TiN multilayer ring structure. Int J Therm Sci 183:107890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2022.107890
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Deanship of Scientific Research at Najran University for funding this work under the Research Groups Funding program grant code (NU/RG/SERC/12/1).
Funding
The authors are thankful to the Deanship of Scientific Research at Najran University for funding this work under the Research Groups Funding program grant code (NU/RG/SERC/12/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Shobhit K. Patel; methodology: Abdulkarem H. M. Almawgani; software, Dhruvik Agravat and Shobhit K. Patel; validation: Abdulkarem H. M. Almawgani, Turki Alsuvian, Ammar Armghan, and Malek G. Daher; writing—original draft preparation: Dhruvik Agravat; writing—review and editing: Shobhit K. Patel; all authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Agravat, D., Patel, S.K., Almawgani, A.H.M. et al. Investigation of a Novel Graphene-Based Surface Plasmon Resonance Solar Absorber to Achieve High Absorption Efficiency Over a Wide Spectrum of Wavelengths, from Ultraviolet to Infrared. Plasmonics 19, 1071–1083 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02061-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02061-y