Abstract
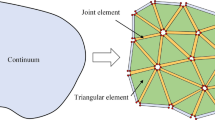
A novel two-dimensional mixed fracture–pore seepage model for fluid flow in fractured porous media is presented based on the computational framework of finite-discrete element method (FDEM). The model consists of a porous seepage model in triangular elements bonded by unbroken joint elements, as well as a fracture seepage model in broken joint elements. The principle for determining the fluid exchange coefficient of the unbroken joint element is provided to ensure numerical accuracy and efficiency. The mixed fracture–pore seepage model provides a simple but effective tool for solving fluid flow in fractured porous media. In this paper, examples of 1D and 2D seepage flow in porous media and porous media with a single fracture or multiple fractures are studied. The simulation results of the model match well with theoretical solutions or results obtained by commercial software, which verifies the correctness of the mixed fracture–pore seepage model. Furthermore, combining FDEM mechanical calculation and the mixed fracture–pore seepage model, a coupled hydromechanical model is built to simulate fluid-driven dynamic propagation of cracks in the porous media, as well as its influence on pore seepage and fracture seepage.





































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Areias P, Msekh MA, Rabczuk T (2016) Damage and fracture algorithm using the screened Poisson equation and local remeshing. Eng Fract Mech 158:116–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2015.10.042
Areias P, Reinoso J, Camanho PP, César de Sá J, Rabczuk T (2018) Effective 2D and 3D crack propagation with local mesh refinement and the screened Poisson equation. Eng Fract Mech 189:339–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2017.11.017
Baca RG, Arnett RC, Langford DW (1984) Modelling fluid flow in fractured-porous rock masses by finite-element techniques. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 4(4):337–348
Barenblatt GI, Zheltov IP, Kochina IN (1960) Basic concept in the theory of homogeneous liquids in fissured rocks. J Appl Math Mech 24(5):1286–1303
Bastian P, Chen Z, Ewing RE, Helmig R, Jakobs H, Reichenberger V (2000) Numerical simulation of multiphase flow in fractured porous media. Numerical treatment of multiphase flows in porous media. Springer, Berlin
Benedetto MF, Berrone S, Pieraccini S, Scialò S (2014) The virtual element method for discrete fracture network simulations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 280:135–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2014.07.016
Berkowitz B (2002) Characterizing flow and transport in fractured geological media: a review. Adv Water Resour 25(2002):861–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0309-1708(02)00042-8
Berrone S, Borio A, Vicini F (2019) Reliable a posteriori mesh adaptivity in Discrete Fracture Network flow simulations. Comput Method Appl Mech Eng 354:904–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2019.06.007
Bourbiaux B (2010) Fractured reservoir simulation: a challenging and rewarding issue. Oil Gas Sci Technol 65(2):227–238. https://doi.org/10.2516/ogst/2009063
COMSOL Multiphysics® v. 5.4 (2018). COMSOL AB, Stockholm, Sweden
Cipolla CL, Lolon EP, Erdle JC, Rubin B (2010) Reservoir modeling in shale-gas reservoirs. SPE Reserv Eval Eng 13(4):638–653
de Dreuzy JR, Méheust Y, Pichot G (2012) Influence of fracture scale heterogeneity on the flow properties of three-dimensional discrete fracture networks. J Geophys Res Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JB009461
Dverstorp B, Andersson J, Nordqvist W (1992) Discrete fracture network interpretation of field tracer migration in sparsely fractured rock. Water Resour Res 28(9):2327–2343
FLAC (2005) User’s guide. Itasca Consulting Group Inc, Minnesota
Farsi A, Bedi A, Latham JP, Bowers K (2019) Simulation of fracture propagation in fibre-reinforced concrete using FDEM: an application to tunnel linings. Comput Part Mech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40571-019-00305-5
Fukuda D, Mohammadnejad M, Liu H, Dehkhoda S, Chan A, Cho SH, Min GJ, Han H, Ji K, Fujii Y (2019) Development of a GPGPU-parallelized hybrid finite-discrete element method for modeling rock fracture. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.2934
Gan Q, Elsworth D (2016) A continuum model for coupled stress and fluid flow in discrete fracture networks. Geomech Geophys Geo-energy Geo-Resour 2(1):43–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-015-0020-0
Gläser D, Helmig R, Flemisch B, Class H (2017) A discrete fracture model for two-phase flow in fractured porous media. Adv Water Resour 110:335–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2017.10.031
Guo L, Latham J-P, Xiang J (2017) A numerical study of fracture spacing and through-going fracture formation in layered rocks. Int J Solids Struct 110–111(N):44–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2017.02.004
Hoteit H, Firoozabadi A (2008) An efficient numerical model for incompressible two-phase flow in fractured media. Adv Water Resour 31(6):891–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2008.02.004
Huang Z, Yan X, Yao J (2015) A two-phase flow simulation of discrete-fractured media using mimetic finite difference method. Commun Comput Phys 16(3):799–816. https://doi.org/10.4208/cicp.050413.170314a
Juanes R, Samper J, Molinero J (2002) A general and efficient formulation of fractures and boundary conditions in the finite element method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 54(12):1751–1774. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.491
Karimi-Fard M, Durlofsky LJ, Aziz K (2003) An efficient discrete fracture model applicable for general purpose reservoir simulators. SPE J 9(2):227–236
Kim JG, Deo MD (2000) Finite element, discrete-fracture model for multiphase flow in porous media. AIChE J 46(6):1120–1130
Lei Z, Rougier E, Munjiza A, Viswanathan H, Knight EE (2019) Simulation of discrete cracks driven by nearly incompressible fluid via 2D combined finite-discrete element method. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.2929
Li S, Zeng X, Ren B, Qian J, Zhang J, Jha AK (2012) An atomistic-based interphase zone model for crystalline solids. Comput Method Appl Methods 229–232:87–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2012.03.023
Lisjak A, Grasselli G, Vietor T (2014) Continuum–discontinuum analysis of failure mechanisms around unsupported circular excavations in anisotropic clay shales. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 65:96–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2013.10.006
Lisjak A, Tatone BSA, Mahabadi OK, Grasselli G, Marschall P, Lanyon GW, Rdl V, Shao H, Leung H, Nussbaum C (2016) Hybrid finite-discrete element simulation of the EDZ formation and mechanical sealing process around a microtunnel in Opalinus Clay. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(5):1849–1873. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0847-2
Long JCS, Remer JS, Wilson CR (1982) Porous media equivalents for networks of discontinuous fractures. Water Resour Res 18(3):645–658
Long JCS (1983) Investigation of equivalent porous medium permeability in networks of discontinuous fractures. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley
Mohajerani S, Baghbanan A, Wang G, Forouhandeh SF (2017) An efficient algorithm for simulating grout propagation in 2D discrete fracture networks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 98:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.07.015
Mohajerani S, Wang G, Huang D, Jalali SME, Torabi SR, Jin F (2019) An efficient computational model for simulating stress-dependent flow in three-dimensional discrete fracture networks. KSCE J Civ Eng 23(3):1384–1394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-019-0470-y
Moinfar A, Varavei A, Sepehrnoori K, Johns RT, (2013) Development of a coupled dual continuum and discrete fracture model for the simulation of unconventional reservoirs. SPE Reservoir Simulation Symposium. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Monteagudo JEP, Firoozabadi A (2004) Control-volume method for numerical simulation of two-phase immiscible flow in two- and three-dimensional discrete-fractured media. Water Resour Res 40(7):7405. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003wr002996
Munjiza A (2004) The combined finite-discrete element method. Wiley, London
Munjiza A (2011) Computational mechanics of discontinua. Wiley, London
Munjiza A, Andrews K, White J (1999) Combined single and smeared crack model in combined finite-discrete element analysis. Int J Numer Methods Eng 44(1):41–57
Munjiza A, Knight EE, Rougier E (2015) Large strain finite element method: a practical course. John Wiley & Sons
Noorishad J, Mehran M (1982) An upstream finite element method for solution of transient transport equation in fractured porous media. Water Resour Res 18(3):588–596
Paul B, Faivre M, Massin P, Giot R, Colombo D, Golfier F, Martin A (2018) 3D coupled HM–XFEM modeling with cohesive zone model and applications to non planar hydraulic fracture propagation and multiple hydraulic fractures interference. Comput Method Appl Methods 342:321–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2018.08.009
Rabczuk T, Belytschko T (2004) Cracking particles: a simplified meshfree method for arbitrary evolving cracks. Int J Numer Methods Eng 61(13):2316–2343. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.1151
Rabczuk T, Zi G, Bordas S, Nguyen-Xuan H (2010) A simple and robust three-dimensional cracking-particle method without enrichment. Comput Method Appl Mech Eng 199(37–40):2437–2455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2010.03.031
Rayudu NM, Tang X, Singh G (2019) Simulating three dimensional hydraulic fracture propagation using displacement correlation method. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 85:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2018.11.010
Ren H, Zhuang X, Cai Y, Rabczuk T (2016) Dual-horizon peridynamics. Int J Numer Methods Eng 108(12):1451–1476. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.5257
Ren H, Zhuang X, Rabczuk T (2017) Dual-horizon peridynamics: a stable solution to varying horizons. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 318:762–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2016.12.031
Rougier E, Knight EE, Broome ST, Sussman AJ, Munjiza A (2014) Validation of a three-dimensional Finite-Discrete Element Method using experimental results of the Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar test. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 70(N):101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.03.011
Sun Y, Liu Z, Tang X (2020) A hybrid FEMM-Phase field method for fluid-driven fracture propagation in three dimension. Eng Anal Bound Elem 113:40–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2019.12.018
Tang X, Rutqvist J, Hu M, Rayudu NM (2019) Modeling three-dimensional fluid-driven propagation of multiple fractures using TOUGH-FEMM. Rock Mech Rock Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1715-7
Tatomir A (2007) Numerical investigations of flow through fractured porous media. Master’s Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart
UDEC (2005) User’s guide. Itasca Consulting Group Inc, Minnesota
Wang Y, Li T, Chen Y, Ma G (2019) A three-dimensional thermo-hydro-mechanical coupled model for enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) embedded with discrete fracture networks. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 356:465–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2019.06.037
Wu YS, Haukwa C, Bodvarsson GS (1999) A site-scale model for fluid and heat flow in the unsaturated zone of Yucca Mountain, Nevada. J Contam Hydrol 38(1–3):185–215
Wu YS, Qin G (2009) A generalized numerical approach for modeling multiphase flow and transport in fractured porous media. Commun Comput Phys 6(1):85–108
Yan C, Fan H, Zheng Y, Zhao Y, Ning F (2020) Simulation of the thermal shock of brittle materials using the finite-discrete element method. Eng Anal Bound Elem 115:142–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2020.03.013
Yan C, Jiao Y-Y (2018) A 2D fully coupled hydro-mechanical finite-discrete element model with real pore seepage for simulating the deformation and fracture of porous medium driven by fluid. Comput Struct 196:311–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2017.10.005
Yan C, Jiao Y-Y (2019) A 2D discrete heat transfer model considering the thermal resistance effect of fractures for simulating the thermal cracking of brittle materials. Acta Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-019-00821-x
Yan C, Jiao YY (2019) FDEM-TH3D: a three-dimensional coupled hydrothermal model for fractured rock. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 43:415–444. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.2869
Yan C, Jiao Y-Y, Yang S (2019) A 2D coupled hydro-thermal model for the combined finite-discrete element method. Acta Geotech 14(2):403–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-018-0653-6
Yan C, Jiao Y-Y, Zheng H (2018) A fully coupled three-dimensional hydro-mechanical finite discrete element approach with real porous seepage for simulating 3D hydraulic fracturing. Comput Geotech 96:73–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2017.10.008
Yan C, Jiao YY, Zheng H (2019) A three-dimensional heat transfer and thermal cracking model considering the effect of cracks on heat transfer. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.2937
Yan C, Ren Y, Yang Y (2019) A 3D thermal cracking model for rockbased on the combined finite–discrete element method. Comput Part Mech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40571-019-00281-w
Yan C, Zheng H (2016) A two-dimensional coupled hydro-mechanical finite-discrete model considering porous media flow for simulating hydraulic fracturing. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 88:115–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.07.019
Yan C, Zheng H (2016) A two-dimensional coupled hydro-mechanical finite-discrete model considering porous media flow for simulating hydraulic fracturing. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 88(2016):115–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.07.019
Yan C, Zheng H (2017) A coupled thermo-mechanical model based on the combined finite-discrete element method for simulating thermal cracking of rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 91:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.11.023
Yan C, Zheng H (2017) Three-dimensional hydromechanical model of hydraulic fracturing with arbitrarily discrete fracture networks using finite-discrete element method. Int J Geomech 17(6):04016133
Yan C, Zheng H (2017) FDEM-flow3D: a 3D hydro-mechanical coupled model considering the pore seepage of rock matrix for simulating three-dimensional hydraulic fracturing. Comput Geotech 81:212–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.08.014
Yan C, Zheng H (2017) FDEM-flow3D: a 3D hydro-mechanical coupled model considering the pore seepage of rock matrix for simulating three-dimensional hydraulic fracturing. Comput Geotech 81(2017):212–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.08.014
Yan CZ, Zheng H (2017) A new potential function for the calculation of contact forces in the combined finite-discrete element method. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 41(2):265–283. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.2559
Yan C, Zheng Y, Huang D, Wang G (2021) A coupled contact heat transfer and thermal cracking model for discontinuous and granular media. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2020.113587
Yan C, Zheng H, Sun G, Ge X (2016) Combined finite-discrete element method for simulation of hydraulic fracturing. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(4):1389–1410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0816-9
Yang Y, Tang X, Zheng H, Liu Q, Liu Z (2018) Hydraulic fracturing modeling using the enriched numerical manifold method. Appl Math Model 53:462–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2017.09.024
Zeng X, Li S (2010) A multiscale cohesive zone model and simulations of fractures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199(9–12):547–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2009.10.008
Zeng Q, Yao J, Shao J (2020) An extended finite element solution for hydraulic fracturing with thermo-hydro-elastic-plastic coupling. Comput Method Appl Methods 364:112967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2020.112967
Zhang K, Woodbury AD (2002) A Krylov finite element approach for multi-species contaminant transport in discretely fractured porous media. Adv Water Resour 25(7):705–721
Zhao Q, Lisjak A, Mahabadi O, Liu Q, Grasselli G (2014) Numerical simulation of hydraulic fracturing and associated microseismicity using finite-discrete element method. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 6(6):574–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2014.10.003
Zhou S, Zhuang X, Rabczuk T (2018) A phase-field modeling approach of fracture propagation in poroelastic media. Eng Geol 240:189–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.04.008
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Numbers 11872340, 11602006; the Hong Kong Scholars Program (XJ2019040, HKSP19EG04) from China National Postdoctoral Council; Hong Kong Research Grants Council grant number N_HKUST621/18; the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) (CUG170657, CUGGC09); and State Key Laboratory of Hydroscience and Engineering Grant 2019-KY-02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, C., Fan, H., Huang, D. et al. A 2D mixed fracture–pore seepage model and hydromechanical coupling for fractured porous media. Acta Geotech. 16, 3061–3086 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-021-01183-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-021-01183-z