Abstract
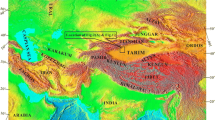
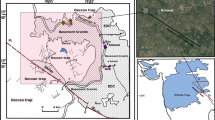
The regional geologic and geomorphic observations show that an active arcuate normal fault constitutes the main boundary fault of the Haba-Yulong Snow Mountains (HYSM). This fault is called eastern piedmont fault of Haba-Yulong Snow Mountains (HYPF). The fault consists of two segments with differential trend; the northern segment is NW-trending and NE-dipping and the southern section is S-N trending and E-dipping. Three sets of fault scarps cutting late Quaternary landforms and their dating results indicate that the fault is a prominent Holocene active fault and its throw rates are 0.3–1.4 mm/a during late Quaternary. The geometry and kinematics of the fault suggest that the arcuate normal faulting or rifting are typical surface deformation pattern at the two tips of the Z-shaped rift zone of northwestern Yunnan, which is related to regional east-west extension accompanying clockwise rotation of micro-block.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tapponnier P, Molnar P. Active faulting and tectonics in China. J Geophys Res, 1977, 82(20): 2905–2930
Liu G X, Li F Q, Li G R. Active tectonics and state of stress in seismic region of north-west Yunnan Province, China (in Chinese with English abstract). Seismol Geol, 1986, 8(1): 1–10
Holt W E, Ni J F, Wallace T C, et al. The active tectonics of the eastern Himalayan syntaxis and surrounding regions. J Geophys Res, 1991, 96(B9): 14595–14632
Burchfiel B C. New technology: New geological challenges. GSA Today, 2004, 14(2): 4–9, doi: 10.1130/1052-5173(2004)014<0004:NTNGC>2.0.CO:2
Chen Z, Burchfiel B C, Liu Y, et al. Global positioning system measurements from eastern Tibet and their implications for India/Eurasia intercontinental deformation. J Geophys Res, 2000, 105(B7): 16215–16227
Socquet A, Pubellier M. Cenozoic deformation in western Yunnan (China-Myanmar border). J Asian Earth Sci, 2005, 24: 495–515, doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.03.006
Wang E, Burchfiel B C, Royden L H, et al. Late Cenozoic Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang Red River, and Dali fault systems of southwestern Sichuan and central Yunnan, China. Geol Soc Amer Spec Paper, 1998, 327: 108
Wu D N, Deng Q D. The basic taphrogenic feature in north-western Yunnan and its formation mechanism. In: Institute of Geology State Seismological Bureau, ed. Research on Recent Crustal Movement (1), Continental Rifts and Deep Internal Processes (in Chinese). Beijing: Seismological Press, 1985. 118–132
Institute of Geology, State Seismological Bureau and Seismological Bureau of Yunnan Province. Active Faults in Northwestern Yunnan Region (in Chinese). Beijing: Seismological Press, 1990. 321
Guo S M, Li X G, Xiang H F, et al. Kinematic model for extensional tip area of Honghe strike-slip fault Yunnan Province. In: Institute of Geology State Seismological Bureau, ed. Research on Recent Crustal Movement (5) (in Chinese). Beijing: Seismological Press, 1991. 1–12
Mao Y P, Han X M. Research on Strong Earthquakes of M⩾6.0 in Yunnan Province (in Chinese). Kunming: Technological Press of Yunnan, 2003. 302
Xu X W, Wen X, Zheng R, et al. Pattern of latest tectonic motion and its dynamics for active blocks in Sichuan-Yunnan region, China. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 2003, 46(Suppl): 210–226
Xiang H F, Han Z J, Guo S M, et al. Large-scale dextral strike-slip movement and associated tectonic deformation along the red-river fault zone (in Chinese with English abstract). Seismol Geol, 2004, 26(4): 597–610
Shen J, Ren J W, Wang Y P, et al. The Quaternary right lateral strike slipping Deqin-Zhongdian-Daju fault in Yunnan, China. In: Ma Z J, Wang Y P, Zhang Y P, eds. Study on the Recent Deformation and Dynamics of the Lithosphere of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau (in Chinese with English abstract). Beijing: Seismologica Press, 2001. 123–135
Han Z J, Xing H F, Guo S M. Sinistral shear and extension of the northern section of Lijiang Basin in northwestern Yunnan in Quaternary. Chin Sci Bull, 2005, 50(5): 452–459
Han Z J, Guo S M, Xing H F, et al. Seismotectonic environment of occurring the February 3, 1996 Lijiang M=7.0 earthquake, Yunnan Province. Acta Seismol Sin, 2004, 26(4): 410–418
Lacassin R, Scharer U, Leloup P H, et al. Tertiary deformation and metamorphism of SE Tibet: The folded Tiger-leap decollement of NW Yunnan, China. Tectonics, 1996, 15(2): 605–622
Seismological Bureau of Yunnan Province and Western Yunnan Earthquake Prediction Study Area. The 1996 Lijiang Earthquake (in Chinese). Beijing: Seismological Press, 1998. 188
Fan C, Wang G, Wang S, et al. Structural interpretation of extensional deformation along the Dali fault system, southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Int Geol Rev, 2006, 48: 1–24
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Yunnan Province. Regional Geology of Yunnan Province (in Chinese with English abstract). Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1990. 728
Kan Y J, Zhang S C, Yan F T, et al. Present tectonic stress field and its relation to the characteristics of recent tectonic activity in Southwestern China (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Geophy Sin, 1977, 20(2): 96–107
Wang S J, Long X F, Luo S J. The focal mechanism, seismogenic stress field and rupture characteristics of the Lijiang earthquake sequence (in Chinese with English abstract). J Seismol Res, 1997, 20(1): 26–34
Zhao X T, Zhang Y S, Hu D G, et al. Discovery of early Pleistocene gravels of the Jinsha river in the Daju basin, Yunnan, China, and its significance (in Chinese with English abstract). Geol Bull Chin, 2006, 25(12): 1381–1386
Masek J G, Isacks B L, Fielding E J, et al. Rift-flank uplift in Tibet: Evidence for a viscous lower crust. Tectonics, 1994, 13: 659–667
Zhao X T, Qu Y X, Li T S. Pleistocene Glaciations along the eastern foot of Yulong Mountains (in Chinese with English abstract). J Glaciol Geocryol, 1999, 21(3): 242–248
Xu Y, Masayuki K, Su Y J. Body waveform inversion for the source process of the February 3, 1996 Lijiang, Yunnan earthquake. Acta Seismol Sin, 1998, 20(2): 2–7
Ji F J, Zheng R Z, Li J P, et al. The chronological study on the surfaces of lower terraces in significant river in east and west Yunnan (in Chinese with English abstract). Seismol Geol, 2000, 22(3): 265–266
Wallace R E. Grouping and migration of surface faulting and variation in slip rates on faults in the Great Basin Province. Bull Seismol Soc Amer, 1987, 77: 868–877
Allen C R, Gillespie A R, Han Y, et al. Red River and associated faults, Yunnan Province, China: Quaternary geology, slip rate and seismic hazard. Geol Soc Am Bull, 1984, 95: 686–700
Guo S M, Xiang H F, Ji F J, et al. A study on the relation between Quaternary right-lateral slip and tip extension along the Honghe fault (in Chinese with English abstract). Seismol Geol, 1996, 18(4): 301–309
Lacassin R, Replumaz A, Leloup P H. Hairpin river loops and slip-sense inversion on southeast Asian strike-slip faults. Geology, 1998, 26(8): 703–706
Zhang P Z, Wang Q, Ma Z J. GPS velocity field and active crustal deformation in and around the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (in Chinese with English abstract). Earth Sci Front, 2002, 9(2): 442–450
Zhang P Z, Shen Z K, Wang M, et al. Continuous deformation of the Tibetan Plateau from global positioning system data. Geology, 2004, 32: 809–812, doi: 10.1130/G20554.1
Meltzer S A, Burgmann R, Van der hilst R D, et al. Geodynamics of the southeastern Tibetan Plateau from seismic anisotropy and geodesy. Geology, 2007, 35(6): 563–566, doi: 10.1130/G23408A.1
Lev E, Long M D, Van der Hilst R D. Seismic anisotropy in eastern Tibet from shear wave splitting reveals changes in lithospheric deformation. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 2006, 251: 293–304, doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2006.09.018
Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, King R W, et al. Surface deformation and lower crustal flow in eastern Tibet. Science, 1997, 276: 788–790
Shen Z K, Lu J, Wang M, et al. Contemporary crustal deformation around the southeast borderland of the Tibetan Plateau. J Geophys Res, 2005, 110: B11409, doi: 1029/2004JB003421
Schoenbohm L M, Burchfiel B C, Chen L, et al. Miocene to present activity along the Red River fault, China, in the context of continental extrusion, upper-crustal rotation, and lower-crustal flow. Geol Soc Am Bull, 2006, 118(5–6): 672–688, doi: 10.1130/ B25816.1
Molnar P, England P. Late Cenozoic uplift of mountain ranges and global climate change: Chicken or egg? Nature, 1990, 346: 29–34
Zhang P Z, Molnar P, Downs W. Increased sedimentation rates and grain sizes 2-4 Myr ago due to the influence of climate change on erosion rates. Nature, 2001, 410: 891–897, doi: 10.1038/35073504
Clark M K, Schoenbohm M L, Royden L H, et al. Surface uplift, tectonics, and erosion of eastern Tibet from large-scale drainage patterns. Tectonics, 2004, 23: TC1006, doi: 10.1029/2002TC001402
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Department of International Cooperation of Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2006DFA21320), China Geological Survey of Ministry of Land and Resources (Grant No. 1212010541404) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 40501006)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Zhang, Y., Hu, D. et al. Late Quaternary normal faulting and its kinematic mechanism of eastern piedmont fault of the Haba-Yulong Snow Mountains in northwestern Yunnan, China. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 52, 1470–1484 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-009-0148-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-009-0148-2