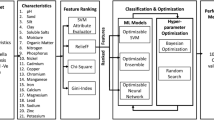
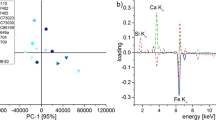
Abstract
With the extensive development of nuclear energy, soil uranium contamination has become an increasingly prominent problem. The development of evaluation systems for various uranium contamination levels and soil microhabitats is critical. In this study, the effects of uranium contamination on the carbon source metabolic capacity and microbial community structure of soil microbial communities were investigated using Biolog microplate technology and high-throughput sequencing, and the responses of soil biochemical properties to uranium were also analyzed. Then, ten key biological indicators as reliable input variables, including arylsulfatase, biomass nitrogen, metabolic entropy, microbial entropy, Simpson, Shannon, McIntosh, Nocardioides, Lysobacter, and Mycoleptodisus, were screened by random forest (RF), Boruta, and grey relational analysis (GRA). The optimal uranium-contaminated soil microbiological evaluation model was obtained by comparing the performance of three evaluation methods: partial least squares regression (PLS), support vector regression (SVR), and improved particle algorithm (IPSO-SVR). Consequently, partial least squares regression (PLS) has a higher R2 (0.932) and a lower RMSE value (0.214) compared to the other. This research provides a new evaluation method to describe the relationship between soil ecological effects and biological indicators under nuclear contamination.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad MB, Soomro U, Muqeet M, Ahmed Z (2020) Adsorption of Indigo Carmine dye onto the surface-modified adsorbent prepared from municipal waste and simulation using deep neural network. J Hazard Mater 408:124433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124433
Alla N, Guy JL, Oshri R, Gil E, Mikhail B (2022) Organic matter in aqueous soil extracts: prediction of compositional attributes from bulk soil mid-IR spectra using partial least square regressions. Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2021.115678
Bing K, Ying Y, Xiaoli Z, Yuxin K, Hui W, Tingqiao Y, Wenbing T (2024) Effect of soil organic matter-mediated electron transfer on heavy metal remediation: current status and perspectives. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.170451
Ćalasan M, Abdel Aleem SHE, Zobaa AF (2020) On the root mean square error (RMSE) calculation for parameter estimation of photovoltaic models: a novel exact analytical solution based on Lambert W function. Energy Convers Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2020.112716
Carvalho FP, Oliveira JM, Malta M (2016) Preliminary assessment of uranium mining legacy and environmental radioactivity levels in Sabugal region, Portugal. Int J Energy Environ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-016-0219-z
Chang D, Chen Y, He Z, Hu X, Wei J (2014) Geochemical characteristics of trace elements of Zoige 510–1 uranium deposit, Sichuan Province, China. Acta Geol Sin-Eng Edition. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.12381_3
Chen J, Sinsabaugh RL (2021) Linking microbial functional gene abundance and soil extracellular enzyme activity: implications for soil carbon dynamics. Glob Chang Biol. 27:1322–1325. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15506
Cong W, Qinggong M, Taiki M, Juan H, Hui M, Jiangming M, Xiankai L (2023) Resource allocation theory reveals sulfur shortage for microbes under phosphorus amendment in tropical forests with divergent land use history. Soil Biol Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2023.109126
Cuicui S, Yuanhua L, Xin C (2021) Water quality prediction model based on particle swarm optimization support vector regression. Information and Control 51:307–317. https://doi.org/10.13976/j.cnki.xk.2022.1125
De Paul Obade OV, Lal R (2016) Towards a standard technique for soil quality assessment. Geoderma 265(96–102):96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.11.023
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Reich PB, Trivedi C, Eldridge DJ, Abades S, Alfaro FD, Bastida F, Berhe AA, Cutler NA, Gallardo A, García-Velázquez L, Hart SC, Hayes PE, He J-Z, Hseu Z-Y, Hu H-W, Kirchmair M, Neuhauser S, Pérez CA, Reed SC, Santos F, Sullivan BW, Trivedi P, Wang J-T, Weber-Grullon L, Williams MA, Singh BK (2020) Multiple elements of soil biodiversity drive ecosystem functions across biomes. Nat Ecol Evol 4:210–220. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-019-1084-y
Duan C, Wang Y, Wang Q, Ju W, Zhang Z, Cui Y, Beiyuan J, Fan Q, Wei S, Li S, Fang L (2022) Microbial metabolic limitation of rhizosphere under heavy metal stress: evidence from soil ecoenzymatic stoichiometry. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.118978
Elberling B, Brandt KK (2003) Uncoupling of microbial CO2 production and release in frozen soil and its implications for field studies of arctic C cycling. Soil Biol Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0038-0717(02)00258-4
Feizi A, Nazemi A, Rabiei MR (2021) Solving the stochastic support vector regression with probabilistic constraints by a high-performance neural network model. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01214-5
Fernández-Calviño D, Rousk J, Bååth E, Bollmann UE, Bester K, Brandt KK (2017) Ecotoxicological assessment of propiconazole using soil bacterial and fungal growth assays. Appl Soil Ecol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.03.009
Firat MEO (2021) Experimental investigation on the thermal characteristics and grey correlation analysis of frost penetration depths for different subgrade soils. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09698-0
Frimpong JO, Ofori ESK, Yeboah S, Marri D, Offei BK, Apaatah F, Sintim JO, Ofori-Ayeh E, Osae M (2018) Evaluating the impact of synthetic herbicides on soil dwelling macrobes and the physical state of soil in an agro-ecosystem. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.034
Garland JL, Mills AL (1991) Classification and characterization of heterotrophic microbial communities on the basis of patterns of community-level sole-carbon-source utilization. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.57.8.2351-2359.1991
Gazzola G, Jeong MK (2019) Dependence-biased clustering for variable selection with random forests. Pattern Recognit. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2019.106980
Ge Y, Wang Q, Wang L, Liu W, Liu X, Huang Y, Christie P (2017) Response of soil enzymes and microbial communities to root extracts of the alien Alternanthera philoxeroides. Arch Agron Soil Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2017.1373186
Gibbons SM (2017) Microbial community ecology: function over phylogeny. Nat Ecol Evol 1:32. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-016-0032
Gil-García CJ, Rigol A, Vidal M (2011) Comparison of mechanistic and PLS-based regression models to predict radiocaesium distribution coefficients in soils. J Hazard Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.09.048
Gui H, Yang Q, Lu X, Wang H, Gu Q, Martín JD (2023) Spatial distribution, contamination characteristics and ecological-health risk assessment of toxic heavy metals in soils near a smelting area. Environ Res 222:115328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115328
Guo H, Nguyen H, Vu D-A, Bui X-N (2019) Forecasting mining capital cost for open-pit mining projects based on artificial neural network approach. Resour Policy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.101474
Haider I, Ali MA, Sanaullah M, Ahmed N, Hussain S, Shakeel MT, Naqvi SaH, Dar JS, Moustafa M, Alshaharni MO (2023) Unlocking the secrets of soil microbes: how decades-long contamination and heavy metals accumulation from sewage water and industrial effluents shape soil biological health. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.140193
Han M, Zhang R, Qiu T, Xu M, Ren W (2019) Multivariate chaotic time series prediction based on improved grey relational analysis. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern: Syst [J] 49:2144–2154. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2017.2758579
Han S, Wang X, Cheng Y, Wu G, Dong X, He X, Zhao G (2023) Multidimensional analysis reveals environmental factors that affect community dynamics of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in poplar roots. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1068527
Harpy NM, El Dabour SE, Sallam AM, Nada AA, El Aassy AE, El Feky MG (2019) Radiometric and environmental impacts of mill tailings at experimental plant processing unit, Allouga. Egypt Environ Forensics. https://doi.org/10.1080/15275922.2019.1695020
Hartmann M, Frey B, Mayer J, Mäder P, Widmer F (2015) Distinct soil microbial diversityunder long-term organic and conventional farming. The ISME Journal 9:1177–1194. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2014.210
Hasseim AA, Sudirman R, Khalid PI, Tabatabaey-Mashadi N (2013) Comparison of ANN and SVM to identify children handwriting difficulties. Engineering. https://doi.org/10.4236/eng.2013.55b001
He J, Zhang B, Wang YN, Chen S, Dong H (2023) Vanadate bio-detoxification driven by pyrrhotite with secondary mineral formation. Environ Sci Technol 57:1807–1818. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.2c06184
Hermans SM, Buckley HL, Case BS, Curran-Cournane F, Taylor M, Lear G (2020) Using soil bacterial communities to predict physico-chemical variables and soil quality. Microbiome. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-020-00858-1
Houfani AA, Větrovský T, Navarrete OU, Štursová M, Tláskal V, Beiko RG, Boucherba N, Baldrian P, Benallaoua S, Jorquera MA (2018) Cellulase-hemicellulase activities and bacterial community composition of different soils from Algerian ecosystems. Microb Ecol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-018-1251-8
Ioannidis JPA, Boyack K, Wouters PF (2016) Citation metrics: a primer on how (not) to normalize. PLOS Biol 14(9):e1002542. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1002542
Jiang R, Wang M, Chen W, Li X, Balseiro-Romero M, Baveye PC (2019) Ecological risk of combined pollution on soil ecosystem functions: insight from the functional sensitivity and stability. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113184
Jingming L, Fengmei L, Menghan T, Ze Z, Kailu X, Shuhai G (2024) Construction of an effective method combining in situ capping with electric field-enhanced biodegradation for treating PAH-contaminated soil at abandoned coking sites. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.171209
Karaca S, Dengiz O, Demirağ Turan İ, Özkan B, Dedeoğlu M, Gülser F, Sargin B, Demirkaya S, Ay A (2021) An assessment of pasture soils quality based on multi-indicator weighting approaches in semi-arid ecosystem. Ecol Indic 121:107001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107001
Kassim AM, Nawar S, Mouazen AM (2021) Potential of on-the-go gamma-ray spectrometry for estimation and management of soil potassium site specifically. Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020661
Katherine SR, Michael B, John MB, Alan KK, Chao L, Cotrufo MF (2023) Thirty years of increased precipitation modifies soil organic matter fractions but not bulk soil carbon and nitrogen in a mesic grassland. Soil Biol Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2023.109145
Khan A, Zhang G, Li T, He B (2023) Fertilization and cultivation management promotes soil phosphorus availability by enhancing soil P-cycling enzymes and the phosphatase encoding genes in bulk and rhizosphere soil of a maize crop in sloping cropland. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 264:11544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115441
Kong X, Wang C, Ji M (2013) Analysis of microbial metabolic characteristics in mesophilic and thermophilic biofilters using Biolog plate technique. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.073
Kumar M, Michael E, David S, Emily M, Becca M, Susan M (2022) Convolutional neural network for high-resolution wetland mapping with open data: variable selection and the challenges of a generalizable model. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160622
Kursa MB, Rudnicki WR (2010) Feature selection with Boruta Package. J Stat Softw 36:1–13. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v036.i11
Levakov I, Ronen Z, Siebner H, Dahan O (2021) Continuous in-situ measurement of free extracellular enzyme activity as direct indicator for soil biological activity. Soil Biol Biochem 163:108448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108448
Levi N, Karnieli A, Paz-Kagan T (2020) Using reflectance spectroscopy for detecting land-use effects on soil quality in drylands. Soil Tillage Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104571
Li S, Fang H, Liu X (2017) Parameter optimization of support vector regression based on sine cosine algorithm. Expert Syst Appl. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.08.038
Li Y, Wang Z, Tian H, Megharaj M, Jia H, He W (2023) Using soil enzyme Vmax as an indicator to evaluate the ecotoxicity of lower-ring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil: evidence from fluorescein diacetate hydrolase kinetics. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162521
Lin H, Liu C, Li B, Dong Y (2021) Trifolium repens L. regulated phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil by promoting soil enzyme activities and beneficial rhizosphere associated microorganisms. J Hazard Mater 402:123829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123829
Lin M, Zhixuan L, Guihua L, Wenzhi L (2022) Low-level cadmium alleviates the disturbance of doxycycline on nitrogen removal and N2O emissions in ditch wetlands by altering microbial community and enzymatic activity. J Clea Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135807
Liu M, Zhu J, Yang X, Fu Q, Hu H, Huang Q (2022) Mineralization of organic matter during the immobilization of heavy metals in polluted soil treated with minerals. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134794
Longfei X, Guiyin W, Shirong Z, Ting L, Xiaoxun X, Guoshu G, Wei Z, Yulin P, Yongxia J, Yun L, Lulu L (2024) Inhibition of high sulfur on functional microorganisms and genes in slightly contaminated soil by cadmium and chromium. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2024.123421
Lovatti BPO, Nascimento MHC, Neto ÁC, Castro EVR, Filgueiras PR (2019) Use of random forest in the identification of important variables. Microchem J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.12.028
Lu Z, Liu Z (2018) Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of uranium and heavy metals of agricultural soil around the uranium tailing reservoir in Southern China. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-6081-0
Lu Q, Tian S, Wei L (2022) Digital mapping of soil pH and carbonates at the European scale using environmental variables and machine learning. Sci Total Environ 856(Pt 2):159171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159171
Ma X, Tian H, Dai Y, Yang Y, Megharaj M, He W (2022) Respecting catalytic efficiency of soil arylsulfatase as soil Sb contamination bio-indicator by enzyme kinetic strategy. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23338-5
Maowei Z, Yongmeng L, Chuanzhi S, Xiaoming W, Jiubin T (2020) Precision measurement and evaluation of flatness error for the aero-engine rotor connection surface based on convex hull theory and an improved PSO algorithm. Meas Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6501/ab8170
Martín-Sanz JP, De Santiago-Martín A, Valverde-Asenjo I, Quintana-Nieto JR, González-Huecas C, López-Lafuente AL (2022) Comparison of soil quality indexes calculated by network and principal component analysis for carbonated soils under different uses. Ecol Indic 143:109374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109374
Mina M, Rezaei M, Sameni A, Moosavi AA, Ritsema C (2021a) Vis-NIR spectroscopy predicts threshold velocity of wind erosion in calcareous soils. Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2021.115163
Mina M, Rezaei M, Sameni A, Ostovari Y, Ritsema C (2021b) Predicting wind erosion rate using portable wind tunnel combined with machine learning algorithms in calcareous soils, southern Iran. J Environ Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114171
Moazenzadeh R, Mohammadi B (2019) Assessment of bio-inspired metaheuristic optimisation algorithms for estimating soil temperature. Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.06.028
Nakaji T, Oguma H, Nakamura M, Kachina P, Asanok L, Marod D, Aiba M, Kurokawa H, Kosugi Y, Kassim AR, Hiura T (2019) Estimation of six leaf traits of East Asian forest tree species by leaf spectroscopy and partial least square regression. Remote Sens Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111381
Napoletano P, Guezgouz N, Di Iorio E, Colombo C, Guerriero G, De Marco A (2022) Anthropic impact on soil heavy metal contamination in riparian ecosystems of northern Algeria. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137522
Neda K, Ataollah E, Esmaeil A (2023) Comparative analysis of random forest, exploratory regression, and structural equation modeling for screening key environmental variables in evaluating rangeland above-ground biomass. Ecol Inform. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2023.102251
Nie M, Wu C, Tang Y, Shi G, Wang X, Hu C, Cao J, Zhao X (2023) Selenium and Bacillus proteolyticus SES synergistically enhanced ryegrass to remediate Cu–Cd–Cr contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 323:121272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121272
Otto G (2021) Changing soil microbiomes. Nat Rev Microbiol 19:283–283. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-021-00544-5
Ouyang J, Liu Z, Ye T, Zhang L (2019) Uranium pollution status and speciation analysis in the farmland-rice system around a uranium tailings mine in southeastern China. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-019-06783-4
Palansooriya KN, Li J, Dissanayake PD, Suvarna M, Li L, Yuan X, Sarkar B, Tsang DCW, Rinklebe J, Wang X, Ok YS (2022) Prediction of soil heavy metal immobilization by biochar using machine learning. Environ Sci Technol 56:4187–4198. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c08302
Pan F, Zhang Q, Liu J, Li W, Gao Q (2014) Consensus analysis for a class of stochastic PSO algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 23:567–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2014.05.010
Paweł T, Aleksandra W, Barbara W, Agata S-P (2023) Assessment of heavy metal contamination of agricultural soils in Poland using contamination indicators. Ecol Indic. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111161
Phung VLH, Oka K, Hijioka Y, Ueda K, Sahani M, Wan Mahiyuddin WR (2022) Environmental variable importance for under-five mortality in Malaysia: a random forest approach. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157312
Qu J-H, Sun D-W, Cheng J-H, Pu H (2016) Mapping moisture contents in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) slices under different freeze drying periods by Vis-NIR hyperspectral imaging. LWT - Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.09.024
Sahoo M (2022) Winter soil temperature and its effect on soil nitrate status: a support vector regression-based approach on the projected impacts. CATENA 211:105958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2021.105958
Schneider AR, Gommeaux M, Duclercq J, Fanin N, Conreux A, Alahmad A, Lacoux J, Roger D, Spicher F, Ponthieu M, Cancès B, Morvan X, Marin B (2017) Response of bacterial communities to Pb smelter pollution in contrasting soils. Sci Total Environ 605–606:436–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.159
Selçuk D, Emrehan Kutlug S (2022) An investigation of feature selection methods for soil liquefaction prediction based on tree-based ensemble algorithms using AdaBoost, gradient boosting, and XGBoost. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07856-4
Shi X-Z, Zhou J, Wu B-B, Huang D, Wei W (2012) Support vector machines approach to mean particle size of rock fragmentation due to bench blasting prediction. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1003-6326(11)61195-3
Shi X, Tan W, Tang S, Ling Q, Tang C, Qin P, Luo S, Zhao Y, Yu F, Li Y (2023) Metagenomics reveals taxon-specific responses of soil nitrogen cycling under different fertilization regimes in heavy metal contaminated soil. J Environ Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118766
Shi ZH, Ai L, Li X, Huang XD, Wu GL, Liao W (2013) Partial least-squares regression for linking land-cover patterns to soil erosion and sediment yield in watersheds. J Hydrol 498:165–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.06.031
Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi R, Schmidt K, Toomanian N, Heung B, Behrens T, Mosavi A, Band SS, Amirian-Chakan A, Fathabadi A, Scholten T (2021) Improving the spatial prediction of soil salinity in arid regions using wavelet transformation and support vector regression models. Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114793
Wang S, Liu G, Gao M, Cao S, Guo A, Wang J (2020) Heterogeneous comprehensive learning and dynamic multi-swarm particle swarm optimizer with two mutation operators. Inform Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.06.027
Wilhelm RC, Cardenas E, Maas KR, Leung H, Mcneil L, Berch S, Chapman W, Hope G, Kranabetter JM, Dubé S, Busse M, Fleming R, Hazlett P, Webster KL, Morris D, Scott DA, Mohn WW (2017) Biogeography and organic matter removal shape long-term effects of timber harvesting on forest soil microbial communities. ISME J 11:2552–2568. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2017.109
Wold S, Sjöström M, Eriksson L (2001) PLS-regression: a basic tool of chemometrics. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-7439(01)00155-1
Wu B, Hou S, Peng D, Wang Y, Wang C, Xu F, Xu H (2018) Response of soil micro-ecology to different levels of cadmium in alkaline soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.076
Xian Y, Wang M, Chen W (2015) Quantitative assessment on soil enzyme activities of heavy metal contaminated soils with various soil properties. Chemosphere 139:604–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.12.060
Xiao Z, Duan C, Li S, Chen J, Peng C, Che R, Liu CE, Huang Y, Mei R, Xu L, Luo P, Yu Y (2023) The microbial mechanisms by which long-term heavy metal contamination affects soil organic carbon levels. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.139770
Xiping H, Chenchen Q, Hanzhi S, Peng C, Wenli C, Qiaoyun H (2023) Mineral-organic interactions drive the aging and stabilization of exogenous Pb in soils. Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2023.116588
Xu W, Yuan W (2017) Responses of microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen to experimental warming: a meta-analysis. Soil Biol Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.08.033
Yan J, Yilin H, Di W, Jie W, Hanyue W, Ya L, Jie P (2022) A nomogram for predicting the risk of mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis and Gram-negative bacilli infection. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.1032375
Yang J, Sun Y, Wang Z, Gong J, Gao J, Tang S, Ma S, Duan Z (2022) Heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils of a typical volcanic area: risk assessment and source appointment. Chemosphere 304:135340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135340
Zhang H, Zimmerman J, Nettleton D, Nordman DJ (2019) Random forest prediction intervals. Am Stat. https://doi.org/10.1080/00031305.2019.1585288
Zhang X, Xiong Z, Zhang S, Ge Y, Ma W, Yan L, Li D, Wang D, Deng S, Zhao Q, Wang W, Xing B (2020) Response of soil enzyme activity and bacterial community to black phosphorus nanosheets. Environ Sci: Nano. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9en00716d
Zhang M, Zhang T, Zhou L, Lou W, Zeng W, Liu T, Yin H, Liu H, Liu X, Mathivanan K, Praburaman L, Meng D (2022) Soil microbial community assembly model in response to heavy metal pollution. Environ Res 213:113576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113576
Funding
This work was supported by the Major Science and Technology Projects in Sichuan Province (2019ZDZX0003) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (12275227).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fanzhou Tang, Shiqi Xiao, and Xiaoming Chen have made substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work and analysis or interpretation of data for the work. Fanzhou Tang has drafted the work or revised it critically for important intellectual content. Jiali Huang, Jia hao Xue, Imran Ali, Wenkun Zhu, Hao Chen, and Min Huang performed all the experiments. All persons who have made substantial contributions to the work were reported in the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Agree.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Robert Duran
I have not submitted my manuscript to a preprint server before submitting it to Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, F., Xiao, S., Chen, X. et al. Preliminary construction of a microecological evaluation model for uranium-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 28775–28788 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33044-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33044-z