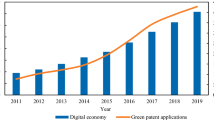
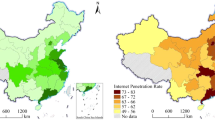
Abstract
In the epoch of the digital economy, technological innovation and energy conservation are significantly facilitated by digital infrastructure, leading to substantial improvements in green innovation efficiency at the provincial level. This study employed the feasible generalized least square (FGLS) method to examine the effects of digital infrastructure on the green innovation efficiency across 30 provinces in the Chinese mainland, utilizing panel data from 2011 to 2020. Additionally, this investigation delves into the intervening role of industrial structure upgrading and the amplifying effects of environmental regulation and human capital on the process. Findings indicate that, to begin with, digital infrastructure contributes to the meaningful enhancement of green innovation efficiency within provinces. Subsequently, the industrial structure upgrading partially mediates the impact of digital infrastructure on the efficiency of provincial green innovation. Lastly, both human capital and environmental regulations amplify the beneficial influence of digital infrastructure on the effectiveness of green innovation at the provincial level. This study provides valuable insights into the mechanisms through which digital infrastructure boosts green innovation efficiency, aiding policymakers in formulating appropriate policies to augment digital infrastructure, thereby promoting provincial green innovation efficiency.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Apergis N, Eleftheriou S, Payne JE (2013) The relationship between international financial reporting standards, carbon emissions, and R&D expenditures: evidence from European manufacturing firms. Ecol Econ 88:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2012.12.024
Benhabib J, Spiegel M (1994) The role of human capital in economic development evidence from aggregate cross-country data. J Monet Econ 34(2):143–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3932(94)90047-7
Bian YC, Wu LH, Bai JH (2019) Does high-speed rail improve regional innovation in China? J Financial Res 6:132–149. https://doi.org/10.1111/pirs.12641
Borsatto JM, Amui LB (2019) Green innovation: unfolding the relation with environmental regulations and competitiveness. Resour Conserv Recycl 149:445–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.06.005
Bozkus K (2021) Digital devices and student achievement: the relationship in PISA 2018 data. Int Online J Educ Teach 8(3):1560–1579. https://iojet.org/index.php/IOJET/article/view/1255
Chakrabortya P, Chatterjee C (2017) Does environmental regulation indirectly induce upstream innovation? New evidence from India. Res Policy 46(5):939–955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2017.03.004
Chen Z, Haynes KE (2017) Impact of high-speed rail on regional economic disparity in China. J Transp Geogr 65:80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2017.08.003
Chen H, Hao Y, Li J et al (2018) The impact of environmental regulation, shadow economy, and corruption on environmental quality: theory and empirical evidence from China. J Clean Prod 195(10):200–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.206
Chen X, Liu X, Gong Z et al (2021) Three-stage super-efficiency DEA models based on the cooperative game and its application on the R&D green innovation of the Chinese high-tech industry. Comput Ind Eng 156:107234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2021.107234
Cravo TA, Gourlay A, Becker B (2012) SMEs and regional economic growth in Brazil. Small Bus Econ 38(2):217–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-010-9261-z
Darnall N, Henriques I, Sadorsky P (2010) Adopting proactive environmental strategy: the influence of stakeholders and firm size. J Manage Stud 47(6):1072–1094. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6486.2009.00873.x
Du JL, Liu Y, Diao WX (2019) Assessing regional differences in green innovation efficiency of industrial enterprises in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(6):940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16060940
Fang Z, Bai H, Bilan YE (2020) Evaluation research of green innovation efficiency in China’s heavy polluting industries. Sustainability (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010146
Fichman RG, Dos Santos BL, Zheng Z (2014) Digital innovation as a fundamental and powerful concept in the information systems curriculum. MIS Q 38(2):329–343. https://doi.org/10.25300/misq/2014/38.2.01
Gao Y, Tsai SB, Xue X et al (2018) An empirical study on green innovation efficiency in the green institutional environment. Sustainability 10(3):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10030724
Granell C, Havlik D, Schade S et al (2016) Future internet technologies for environmental applications. Environ Model Softw 78:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.12.015
Guan J, Chen K (2010) Measuring the innovation production process: a cross-region empirical study of China’s high-tech innovations. Technovation 30(5–6):348–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2010.02.001
Guo H, Xie Z, Wu R (2021) Evaluating green innovation efficiency and its socioeconomic factors using a slack-based measure with environmental undesirable outputs. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:12880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182412880
Han J (2012) Research on green innovation efficiency in China’s region. Res Financial Econ Issues 11:130–137. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010146
Han M, Zhou Y (2022) The impact of high-tech product export trade on regional carbon performance in China: the mediating roles of industrial structure supererogation, low-carbon technological innovation, and human capital accumulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:31148–31163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17252-5
Han H, Hai C, Wu T, Zhou N (2023) How does digital infrastructure affect residents’ healthcare expenditures? Evidence from Chinese microdata. Front Public Health 11:1122718. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2023.1122718
He Z, Xing W, Chen Y (2021) Marketization, industrial structure upgrading, and energy efficiency. Energy Res Lett 2(2):25725. https://doi.org/10.46557/001c.25725
He Z, Chen H, Hu J, Zhang Y (2022) The impact of digital inclusive finance on provincial green development efficiency: empirical evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(60):90404–90418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22071-3
Henfridsson O, Bygstad B (2013) The generative mechanisms of digital infrastructure evolution. MIS Q 37(3):907–931. https://doi.org/10.25300/misq/2013/37.3.11
Henfridsson O, Mathiassen L, Svahn F (2013) Managing technological change in the digital age: the role of architectural frames. J Inf Technol 29(1):27–43. https://doi.org/10.1057/jit.2013.30
Horbach J, Rammer C, Rennings K (2012) Determinants of eco-innovations by type of environmental impact—the role of regulatory push/pull, technology push and market pull. Ecol Econ 78:112–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2012.04.005
Hu B, Zhu Y (2021) From spatial production to production space: a study on the economic spatial logic of the new development pattern of double cycle. Econ Syst Reform: 53–58. https://doi.org/10.33049/11.052718.5
Huang Y, Wang Y (2020) How does high-speed railway affect green innovation efficiency? A perspective of innovation factor mobility. J Clean Prod 265:121623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121623
Jiang M, Luo S, Zhou G (2020) Financial development, OFDI spillovers and upgrading of industrial structure. Technol Forcast Soc Change 155:119974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.119974
Lahouel BB, Taleb L, Zaied YB et al (2021) Does ICT change the relationship between total factor productivity and CO2 emissions? Evidence based on a nonlinear model. Energy Econ 101:105406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105406
Li W, Xi YQ (2017) Is innovation driving low-carbon development? An empirical study from the dual perspective of fundamental heterogeneity and environmental regulation. Sci Technol Manag 38(5):14–26. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095381
Li X, Liu J, Ni P (2021) The impact of the digital economy on CO2 emissions: a theoretical and empirical analysis. Sustainability 13(13):7267. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137267
Li G, Wang P, Pal R (2022a) Measuring sustainable technology R&D innovation in China: a unified approach using DEA-SBM and projection analysis. Expert Syst Appl 209:118393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118393
Li X, Lu Y, Rafique MZ et al (2022b) The effect of fiscal decentralization, environmental regulation, and economic development on haze pollution: empirical evidence for 270 Chinese cities during 2007–2016. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:20318–20332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17175-1
Li GQ, Li XG, He LZ (2023) Digital economy, spatial spillover and industrial green innovation efficiency: empirical evidence from China. Heliyon 9(1):12875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e12875
Lin J (2021) The impact of digital infrastructure, Internet use on the quality of employment. Dissertation: Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences
Lin S, Xiao L, Wang X (2021) Does air pollution hinder technological innovation in China? A perspective of innovation value chain. J Clean Prod 278:123326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123326
Lyytinen K, Yoo Y (2002) Research commentary: The next wave of nomadic computing. Inf Syst Res 13(4):377–388. https://doi.org/10.1287/isre.13.4.377.75
Ma T, Liu C (2021) Identification of driving factors of scientific and technological innovation in the new material industry based on the theory of complex adaptive system: taking the construction of green innovation system as an example. Complexity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5537789
Merem E, Robinson B, Wesley JM et al (2010) Using GIS in ecological management: green assessment of the impacts of petroleum activities in the State of Texas. Int J Environ Res Public Health 7(5):2101–2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7052101
Ndubuisi G, Otioma C, Tetteh GK (2021) Digital infrastructure and employment in services: evidence from Sub-Saharan African countries. Telecommunications Policy 5(8):102153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2021.102153
Peneder M (2003) Industrial structure and aggregate growth. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 14(4):427–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0954-349X(02)00052-8
Porter M (1991) America’s green strategy. Sci Am 264(4):193–246. https://doi.org/10.1038/scientificamerican0491-168
Qiu Y, Wang H, Wu J (2023) Impact of industrial structure upgrading on green innovation: evidence from Chinese cities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:3887–3900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22162-1
Romer PM (1986) Increasing returns and long-run growth. J Polit Econ 94(5):1002–1037. https://doi.org/10.1086/261420
Romer P, Review AE, Duflo E (1990) Are nonconvexities important for understanding growth? Am Econ Rev 80:97–103. https://doi.org/10.2307/2006550
Salahuddin M, Alam K (2015) Internet usage, electricity consumption and economic growth in Australia: a time series evidence. Telematics Inform 32(4):862–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2015.04.011
Sassi S, Goaied M (2013) Financial development, ICT diffusion and economic growth: lessons from MENA region. Telecomm Policy 37(4–5):252–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2012.12.004
Schade P, Schuhmacher MC (2022) Digital infrastructure and entrepreneurial action-formation: a multilevel study. J Bus Ventur 37(5):106232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2022.106232
Schultz TW (1961) Investment in human capital. Am Econ Rev 51(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789814335027_0004
Shao X, Liu S, Ran R, Liu Y (2022) Environmental regulation, market demand, and green innovation: spatial perspective evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:63859–63885. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20313-y
Song Y, Zhang X, Zhang M (2021) The influence of environmental regulation on industrial structure upgrading: based on the strategic interaction behavior of environmental regulation among local governments. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 170(9):120930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120930
Spagnoletti P, Ceci F, Bygstad B (2022) Online black-markets: an investigation of a digital infrastructure in the dark. Inf Syst Front 24(6):1811–1826. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-021-10187-9
Star SL, Ruhleder K (1996) Steps toward an ecology of infrastructure: design and access for large information spaces. Inf Syst Res 7(1):111–134. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781452231266.n11
Takalo SK, Tooranloo HS (2021) Green innovation: a systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 279:122474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122474
Tan HF, Zhang SF (2023) Digital new infrastructure, financial resource allocation and high quality economic development. Yunnan Univ Natl (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.): 134–142. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010216
Tang K, Yang G (2022) Does digital infrastructure cut carbon emissions in Chinese cities? Sustain Prod Consump 35:431–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2022.11.022
Tilson D, Lyytinen K, Sørensen C (2010) Research commentary-Digital infrastructures: the missing is research agenda. Inf Syst Res 21(4):748–759. https://doi.org/10.1287/isre.1100.0318
Tone K, Tsutsui M (2010) Dynamic DEA: a slacks-based measure approach. Omega 38(3–4):145–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2009.07.003
Träskman TI, Skoog M (2021) Performing openness: how the interplay between knowledge sharing and digital infrastructure creates multiple accountabilities. J Strateg Manag 15(2):194–219. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSMA-12-2020-0359
Wang Q, Zhang F, Li R (2022) Do environmental regulation and urbanization help decouple economic growth from water consumption at national and subnational scales in China? Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:19473–19495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16667-4
Wen H, Dai J (2020) Trade openness, environmental regulation, and human capital in China: based on ARDL cointegration and Granger causality analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:1789–1799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06808-1
Wen C, Tan J, Li Y, Zhao S (2021) Research on the emission reduction effect of new infrastructure construction and its mechanism of action. Ind Technol Econ 40:122–130. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4202306
Yu YG, Xu ZZ, Shen PY, Zhang LN, Ni TH (2022) Efficiency evaluation and influencing factors of green innovation in Chinese resource-based cities: based on SBM-undesirable and spatial Durbin model. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19:13772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192113772
Yu H, Zhu Q (2022) Impact and mechanism of digital economy on China’s carbon emissions: from the perspective of spatial heterogeneity. Environ Sci Pollut Res: 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22552-5
Zhang HM, Zhu ZS, Fan YG (2018) The impact of environmental regulation on the coordinated development of environment and economy in China. Nat Hazards 91:473–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-3137-3
Zhang J, Kang L, Li H, Ballesteros-Pérez P, Skitmore M, Zuo J (2020) The impact of environmental regulations on urban green innovation efficiency: the case of Xi’an. Sustain Cities Soc 57:102123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102123
Zheng W, Lu YQ (2019) The spillover effect of innovation drive on industrial structure upgrading and its decay boundary. Sci Technol Manag 40(9):75–87. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.963960
Funding
The General Program of the National Social Science Fund of China “A Study on the Impact of Reverse Internationalization on the Innovation Performance of Chinese Export-oriented Enterprise” (20BGL049). This work was supported by the General Program of the National Social Science Foundation of China “A Study on the Impact of Institutional Gap on the Social Responsibility of Chinese Overseas Investment Enterprise” (Grant No. 18BGL026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JH: material preparation, conceptualization, writing, and revising. HC: funding acquisition, investigation, writing—reviewing, and supervision. JF: methodology, modeling, and software. ZH: data collection, validation, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, J., Chen, H., Fan, J. et al. The impact of digital infrastructure on provincial green innovation efficiency—empirical evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 9795–9810 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31757-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31757-1