Abstract
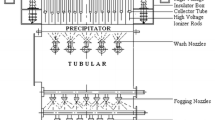
Heavy metal pollutants such as Hg, As, Pb, Cr, and Cd emitted from coal and waste combustion have received widespread attention. In this study, we systematically investigated the emission characteristics of heavy metals in waste incineration and coal-fired flue gases, focused on testing the removal effect of self-made cold electrode electrostatic precipitator (CE-ESP) on heavy metals in flue gas, and made a comparative analysis with the existing air pollution control devices (APCDs). Test results from waste incineration power plant showed that each APCD showed a certain effect on the removal of heavy metals in condensable particulate matter (CPM), with an average removal efficiency of bag filter was 86%, but its effect on Hg removal was slightly worse. Under the coupled field with electrified cold electrode plate operation mode, the average removal efficiency of CE-ESP on heavy metals in CPM was as high as 93%, including 76% for Hg. The removal efficiency of heavy metals (especially Hg) in CPM increased with the increase of flue gas temperature difference between inlet and outlet of CE-ESP. Test results from this coal-fired power plant showed that heavy metals were enriched in fly ash to a higher degree than in slag, the synergistic control of heavy metals in submicron particulate matter by the dust remover was not obvious, and there was a significant correlation between each heavy metal emission factor and its content in coal. Under the temperature field with non-electric cold electrode plate operation mode, the overall effect of CE-ESP on the removal of gaseous heavy metals was better than that of particulate heavy metals. Under the conventional electric field operation mode, CE-ESP was less effective in removing particulate Cr and gaseous Hg0. Under the coupled field with electrified cold electrode plate operation mode, the average removal efficiencies of CE-ESP for particulate and gaseous heavy metals were 82.37% and 76.16%, respectively.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Carey TR, Hargrove OW, Richardson CF, Chang R, Meserole FB (1998) Factors affecting mercury control in utility flue gas using activated carbon. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 48(12):1166–1174. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6701(00)95306-2
Chen C, Shen A, Duan YF, Meng JL, Hu B, Tan HZ, Ruan RH, Liu XS, Liu M (2022) Removal characteristics of particulate matters and hazardous trace elements in a 660 MW ultra-low emission coal-fired power plant. Fuel 311:122535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122535
Deng S, Shi YJ, Liu Y (2014) Emission characteristics of Cd, Pb and Mn from coal combustion: field study at coal-fired power plants in China. Fuel Process Technol 126(10):469–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.06.009
Gu YZ, Wei SZ (2023) Synergistic emission reduction and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in ultra-low emission coal-fired units. J China Coal Sci 48(8):3252–3262. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2023.0232
Lu JY, Zhang SW, Liu WT (2019) A cold electrode electrostatic precipitation process for agglomerating and trapping condensable particulate matter. Application Publication Number:CN110102406A
Meij R (1994) Trace element behavior in coal-fired power plants. Fuel Process Technol 39(1):199–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-3820(94)90180-5
Peng Y, Shi N, Wang JW, Wang T, Pan WP (2021) Mercury speciation and size-specific distribution in filterable and condensable particulate matter from coal combustion. Sci Total Environ 787:147597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147597
Peng Y (2021) Study on the migration and transformation of mercury in filterable and condensable particulate matter for coal combustion. North China University of Electric Power. https://doi.org/10.27140/d.cnki.ghbbu.2021.000016
Reddy MS, Basha S, Joshi HV, Jha B (2005) Evaluation of the emission characteristics of trace metals from coal and fuel oil fired power plants and their fate during combustion. J Hazard Mater 123(1–3):242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.04.008
Romay FJ, Takagaki SS, Pui DYH, Liu BYH (1998) Thermophoretic deposition of aerosol particles in turbulent pipe flow. J Aerosol Sci 29(8). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-8502(98)00004-4
Ruan R, Xu X, Tan H, Zhang S, Lu X, Zhang P, Han R, Xiong X (2019) Emission characteristics of particulate matter from two ultralow-emission coal-fired industrial boilers in Xi’an, China. Energy Fuels 33(3):1944–1954. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b04069
Sui Z, Zhang Y, Peng Y, Norris P, Cao Y, Pan WP (2016) Fine particulate matter emission and size distribution characteristics in an ultra-low emission power plant. Fuel 185:863–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.08.051
Tang J, Xia H, Aljerf L, Wang DD, Ukaogo PO (2022) Prediction of dioxin emission from municipal solid waste incineration based on expansion, interpolation, and selection for small samples. J Environ Chem Eng 10(5):108314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108314
Tang J, Xia H, Aljerf L, Cui CL, Gao BY, Ukaogo PO (2023a) Dioxin emission modeling using feature selection and simplified DFR with residual error fitting for the grate-based MSWI process. Waste Manag 168:256–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2023.05.056
Tang J, Zhuang JB, Aljerf L, Xia H, Wang TZ, Gao BY (2023b) Numerical simulation modelling on whole municipal solid waste incineration process by coupling multiple software for the analysis of grate speed and air volume ratio. Process Saf Environ Prot 176:506–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2023.05.101
Tong D, Zhang Q, Liu F, Geng GN, Zheng YX, Xue T, Hong CP, Wu RL, Qin Y, Zhao HY, Yang L, He KB (2018) Current emissions and future mitigation pathways of coal-fired power plants in China from 2010 to 2030. Environ Sci Technol 52:12905–12914. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b02919
Wang A (2016) Research on the capture behavior and mechanism of fine particles by a single droplet. Qinghua University, Beijing
Wang G, Ma ZZ, Deng JG, Li Z, Duan L, Zhang Q, Hao JM, Jiang JK (2019) Characteristics of particulate matter from four coal-fired power plants with low-low temperature electrostatic precipitator in China. Sci Total Environ 662:455–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.080
Wang RF, Ma DW, Jiang SY, Zhu RB, He J, Zhang BY (2020) Fine particulate emission characteristics of an ultra-low emission coal-fired power plant. Environ Sci 41:98–105. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.201904162
Wang CY, Zhou WF, Shen JZ, Zhang J, Zhang XF, Liu HJ (2023a) Characterization of metal element components in condensable particulate matter from stationary sources. Environ Pollut Prev 45(2):171–176+205
Wang Y, Hu H, Wang X, Liu H, Dong L, Luo G, Zhao Y, Yao H (2023b) A critical review on lead migration, transformation and emission control in Chinese coal-fired power plants. J Environ Sci 124:397–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2021.09.039
Xia H, Tang J, Aljerf L (2022) Dioxin emission prediction based on improved deep forest regression for municipal solid waste incineration process. Chemosphere 294:133716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133716
Xu YY, Xue JM, Wang HL, Li B, Guan YM, Liu J (2014) Research on synergistic control of mercury in conventional pollutant purification facilities for coal-fired flue gas. Chin J Electr Eng 34(23):3924–3931
Xu Y, Liu X, Zhang Y, Sun W, Zhou Z, Xu M, Pan S, Gao X (2016) Field measurements on the emission and removal of PM2.5 from coal-fired power stations: 3. direct comparison on the PM removal efficiency of electrostatic precipitators and fabric filters. Energy Fuel 30(7):5930–5936. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b00425
Xue Y, Yao Q, Chen JB, Zhang JC (2002) Experimental study on gas particle two-phase flow with temperature difference. Journal of Tsinghua University (Natural Science Edition) (12):1659-1662. https://doi.org/10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2002.12.026
Yang L (2016) Field testing and emission estimation of mercury emissions from coal-fired power plants. North China Electric Power University
Yao L, Jiao L, Liao XF, Zhu YJ, Zhang LN (2015) Establishment of heavy metal emission inventories from coal-fired exhaust gas in Hangzhou. China Environ Monit 31(5):115–119
Yi Q (2016) Study on the emission characteristics of heavy metal pollutants in flue gas for coal-fired units. Taiyuan University of Technology. https://doi.org/10.27352/d.cnki.gylgu.2016.000032
Yue T, Wang K, Wang C, Tong Y, Liang Q (2020) Emission characteristics of hazardous atmospheric pollutants from ultra-low emission coal-fired industrial boilers in China. Aerosol Air Qual Res 20(4):877–888. https://doi.org/10.4209/AAQR.2019.10.0531
Zhang XY, Li YZ, Zhang ZP, Nie MF, Wang L, Zhang HW (2021) Adsorption of condensable particulate matter from coal-fired flue gas by activated carbon. Sci Total Environ 778:146245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146245
Zhao G, Zhao Z, Guo X, Du Q, Gao J, Dong H, Cao Y, Han Q, Su L (2016) Emission and morphological characteristics and elemental compositions of fine particulate matter from an industrial pulverized coal boiler equipped with a fabric filter in China. Energy Fuel 30(5):4307–4317. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b00060
Zhuang J, Tang J, Aljerf L (2022) Comprehensive review on mechanism analysis and numerical simulation of municipal solid waste incineration process based on mechanical grate. Fuel 320:123826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.123826
Zou RJ, Luo GQ, Fang C, Zhang H, Yao H (2020) Modeling study of selenium migration behavior in wet flue gas desulfurization spray towers. Environ Sci Technol 54(24):16128–37. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c04700
Zuo PL, Wang CL, Tong L, Gao JJ, Zhang XX (2020) Characterization of heavy metal emissions in flue gas from small coal-fired units. Environ Sci Res 33(11):2599–2604
Funding
This work was supported by the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 3202029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Bowen Zhao, Wenting Liu, Xin Wang and Jianyi Lu. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Bowen Zhao and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme Luiz Dotto
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• We tested the removal effect of cold electrode electrostatic precipitator (CE-ESP) on particulate and gaseous heavy metals
• We compared and analyzed the removal of heavy metals in CPM by air pollution control devices (APCDs) and CE-ESP
• We set up different operation modes of CE-ESP and explored its optimal operation conditions
• We analyzed the action mechanism of CE-ESP on fine particulate matter and gaseous heavy metals
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, B., Liu, W., Wang, X. et al. Emission characteristics and removal of heavy metals in flue gas: a case study in waste incineration and coal-fired power plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 8883–8897 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31678-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31678-z