Abstract
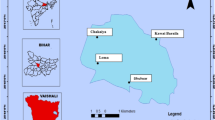
Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of selected heavy metals such as barium (Ba), chromium (Cr), nickel (Ni), lead (Pb), vanadium (V), arsenic (As), zinc (Zn), and copper (Cu) in sediments of the Brahmaputra River watershed in Bangladesh was investigated. The mean abundances (ppm) of heavy metals in sediment samples were in decreasing order Ba (375.60) > V (67.60) > Cr (54.10) > Zn (48.20) > Ni (22.28) > Pb (20.25) > Cu (7.59) > As (4.21). Concentrations of Pb and As in the sediments are enriched relative to the average upper continental crust composition, while Ba, V, Cr, Zn, Ni, and Cu decrease considerably. A higher concentration of Pb and Ni indicates that Brahmaputra River watershed samples receive a significant contribution from anthropogenic sources of heavy metals. Chromium displays marked positive correlation with V (r = 0.91, p = < 0.01), inferring a similar source materials input into the watershed. The geo-accumulation index (Igeo) values suggest that the sediments were uncontaminated to moderately contaminated by Ni, Zn, Pb, V, and Cr, whereas moderate to heavily contaminated by As and Cu. The contamination factor (CF) confirmed that sediments in the watershed were moderate to highly contaminated by As, Cu, and Cr. The pollution load index (PLI) values for most of the samples were over one (> 1), indicating an advanced decline in the watershed sediment quality. The overall results of a multivariate statistical analysis suggest that Ba, V, Cr, and Zn contents were all-natural sources, and Pb, Ni, As, and Cu were derived from both natural and anthropogenic sources.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Ahmad MK, Islam S, Rahman S, Haque MR, Islam MM (2010) Heavy metals in water, sediment and some fishes of Buriganga River, Bangladesh. Int J Environ Res 4:321–332
Algül F, Beyhan M (2020) Concentrations and sources of heavy metals in shallow sediments in Lake Bafa, Turkey. Sci Rep 10:11782. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-68833-2
Ali MM, Ali ML, Islam MS, Rahman MZ (2016) Preliminary assessment of heavy metals in water and sediment of Karnaphuli River, Bangladesh. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 5:27–35
Ali MM, Islam MS, Islam ARMT, Bhuyan MS, Ahmed ASS, Rahman MZ, Rahman MM (2022) Toxic metal pollution and ecological risk assessment in water and sediment at ship breaking sites in the Bay of Bengal Coast, Bangladesh. Mar Pollut Bull 175:113274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.113274
Balabanova B, Stafilov T, Šajn R (2021) Use of multivariate statistical techniques to determine the source apportionment of heavy metals in soils and sediments In: Kumer, V., et al. (Eds.), Heavy Metals in the Environment: Impact, Assessment, and Remediation, Elsevier, Netherland, 230 pp.
Bhuiyan MAH, Parvez L, Islam MA, Dampare SB, Suzuki S (2010) Heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh. J Hazard Mater 173:384–392
Bhuiyan MAH, Suruvi NI, Dampare SB, Islam MA, Quraishi SB, Ganyaglo S, Suzuki S (2011) Investigation of the possible sources of heavy metal contamination in lagoon and canal water in the tannery industrial area in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ Monit Assess 175:633–649
Bhuyan MS, Bakar MA, Rashed-Un-Nabi M, Senapathi V, Chung SY, Islam MS (2019) Monitoring and assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediment of the Old Brahmaputra River. Bangladesh Appl Water Sci 9:125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1004-y
Duncan AE, de Vries N, Nyarko KB (2018) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in the sediments of the River Pra and its tributaries. Water Air Soil Pollut 229:272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3899-6
Gad SS (2014) Encyclopedia of Toxicology (Third Edition), Academic Press, Elsevier
Guan J, Wang J, Pan H, Yang C, Qu J, Lu N, Yuan X (2018) Heavy metals in Yinma River sediment in a major Phaeozems zone, Northeast China: distribution, chemical fraction, contamination assessment and source apportionment. Sci Rep 8:12231. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30197-z
Guo R, He X (2013) Spatial variations and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments on the upper reaches of Hun River, Northeast China. Environ Earth Sci 70:1083–1090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2196-8
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hazarika AK, Kalita U (2020) Incidence of heavy metals and river restoration assessment of a major South Asian transboundary river. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:31595–31614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09328-5
Hossain HMZ (2020) Major, trace, and REE geochemistry of the Meghna River sediments, Bangladesh: constraints on weathering and provenance. Geol J 55(5):3321–3343. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3595
Hossain HMZ, Roser BP, Kimura J-I (2010) Petrography and whole-rock geochemistry of the Tertiary Sylhet succession, northeastern Bengal Basin, Bangladesh: provenance and source area weathering. Sediment Geol 228:171–183
Hossain MA, Ali NM, Islam MS, Hossain HMZ (2015) Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soils of Gebeng industrial city, Malaysia. Environ Earth Sci 73:115–126
Hossain HMZ, Kawahata H, Roser BP, Sampei Y, Manaka T, Otani S (2017) Geochemical characteristics of modern river sediments in Myanmar and Thailand: implications for provenance and weathering. Chem Erde 77:443–458
Hossain HMZ, Hossain QH, Islam MS (2019) Spatial distribution of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Ganges River basin, Bangladesh. Arab J Geosci 12(22):676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4841-y
Hren MT, Chamberlain CP, Hilley GE, Blisniuk PM, Bookhagen B (2007) Major ion chemistry of the Yarlung Tsangpo-Brahmaputra river: chemical weathering, erosion, and CO2 consumption in the southern Tibetan plateau and eastern syntaxis of the Himalaya. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71:2907–2935
Hsu L-C, Huang C-Y, Chuang Y-H, Chen H-W, Chan Y-T, Teah HY, Chen T-Y, Chang C-F, Liu Y-T, Tzou Y-M (2016) Accumulation of heavy metals and trace elements in fluvial sediments received effluents from traditional and semiconductor industries. Sci Rep 6:34250. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34250
Huang X, Sillanpää M, Gjessing ET, Vogt RD (2009) Water quality in the Tibetan Plateau: Major ions and trace elements in the headwaters of four major Asian rivers. Sci Total Environ 407:6242–6254
Huang P, Li T-g, Li A-c, Yu X-k, Hu N-J (2014) Distribution, enrichment and sources of heavy metals in surface sediments of the North Yellow Sea. Cont Shelf Res 73:1–13
Islam MR, Begum SF, Yamaguchi Y, Ogawa K (1999) The Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers in Bangladesh: basin denudation and sedimentation. Hydrol Process 13:2907–2923
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Habibullah-Al-Mamun M, Hoque MF (2015) Preliminary assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from a river in Bangladesh. Environ Earth Sci 73:1837–1848
Jiang R, Lin C, Zhou K, Liu Y, Chen J, Wang S, Pan Z, Sun X, Wang W, Lin H (2022) Pollution, ecological risk, and source identification of potentially toxic elements in sediments of a landscape urban lagoon, China. Mar Pollut Bull 174:113192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.113192
Kabir MH, Rashid MH, Wang Q, Wang W, Lu S, Yonemochi S (2021) Determination of heavy metal contamination and pollution indices of roadside dust in Dhaka city, Bangladesh. Processes 9:1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9101732
Khan MZH, Hasan MR, Khan M, Aktar S, Fatema K (2017) Distribution of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Bay of Bengal coast. J Toxicol 2017:9235764. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9235764
Kimura J-I, Yamada Y (1996) Evaluation of major and trace element XRF analyses using a flux to sample ratio of two to one glass beads. J Mineral Petrol Econ Geol 91:62–72
Kouassi NLB, Yao KM, Sangare N, Trokourey A, Metongo BS (2019) The mobility of the trace metals copper, zinc, lead, cobalt, and nickel in tropical estuarine sediments, Ebrie Lagoon, Côte d’Ivoire. J Soils Sediments 19:929–944
Kuehl SA, Allison MA, Goodbred SL, Kudrass H (2005) The Ganges-Brahmaputra delta. In: Gosian, L., Bhattacharya, J., (Eds.), River Deltas-Concepts, Models, and Examples. Society for Sedimentary Geology (SEPM), Special Publication 83:413–434.
Manaka T, Ushie H, Araoka D, Otani S, Inamura A, Suzuki A, Hossain HMZ, Kawahata H (2015) Spatial and seasonal variation in surface water pCO2 in the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna Rivers on the Indian subcontinent. Aquat Geochem 21:437–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-015-9262-2
Manaka T, Araoka D, Yoshimura T, Hossain HMZ, Nishio Y, Suzuki A, Kawahata H (2017) Downstream and seasonal changes of lithium isotope ratios in the Ganges-Brahmaputra river system. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 18:3003–3015. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GC006738
McLennan SM, Hemming S, McDaniel DK, Hanson GN (1993) Geochemical approaches to sedimentation, provenance, and tectonics. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap 284:21–40
Milliman JD, Meade RH (1983) World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans. J Geol 91:1–21
Müller G (1969) Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 2:108–118
Rudnick RL, Gao S (2014) Composition of the continental crust. pp. 1–51. In: The Crust (ed. R.L. Rudnick), Vol. 4, Treatise on Geochemistry (eds. H.D. Holland and K.K. Turekian), 2nd Edition, Elsevier-Pergamon, Oxford.
Sarin MM, Krishnaswami S, Dilli K, Somayajulu BLK, Moore WS (1989) Major ion chemistry of the Ganga-Brahmaputra river system: weathering processes and fluxes to the Bay of Bengal. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:4809–4814
Saroop S, Tamchos S (2021) Monitoring and impact assessment approaches for heavy metals. In: Kumer, V., et al. (Eds.), Heavy Metals in the Environment: Impact, Assessment, and Remediation, Elsevier, Netherland, 230 pp.
Selvaraj K, Mohan VR, Szefer P (2004) Evaluation of metal contamination in coastal sediments of the Bay of Bengal, India: geochemical and statistical approaches. Mar Pollut Bull 49:174–185
Shirani M, Afzali KN, Jahan S, Strezov V, Soleimani-Sardo M (2020) Pollution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Jazmurian playa in southeast Iran. Sci Rep 10:4775. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61838-x
Shorna S, Quraishi SB, Hosen MM, Hossain MK, Saha B, Hossain A, Habibullah-Al-Mamun M (2021) Ecological risk assessment of trace metals in sediment from the Old Brahmaputra River in Bangladesh. Chem Ecol 37:809–826. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2021.1989422
Singh M, Müller G, Singh IB (2003) Geogenic distribution and baseline concentration of heavy metals in sediments of the Ganges River, India. J Geochem Explor 80:1–17
Singh SK, Sarin MM, France-Lanord C (2005) Chemical erosion in the eastern Himalaya: Major ion composition of the Brahmaputra and δ13C of dissolved inorganic carbon. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:3573–3588
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen 33:566–575
Tsering T, Wahed MSMA, Iftekhar S, Sillanpää M (2019) Major ion chemistry of the Teesta River in Sikkim Himalaya, India: chemical weathering and assessment of water quality. J Hydrol: Reg Stud 24:100612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2019.100612
Turekian KK, Wedepohl KH (1961) Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geol Soc Am Bull 72:175–192
Uddin MJ, Jeong Y-K (2021) Urban river pollution in Bangladesh during last 40 years: potential public health and ecological risk, present policy, and future prospects toward smart water management. Heliyon 7:e06107
Wedepohl KH (1995) The composition of the continental crust. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:1217–1232
Yoshimura T, Wakaki S, Kawahata H, Hossain HMZ, Manaka T, Suzuki A, Ishikawa T, Ohkouchi N (2021) Stable strontium isotopic compositions of river water, groundwater and sediments from the Ganges–Brahmaputra–Meghna River system in Bangladesh. Front Earth Sci 9:592062. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.592062
Yuan X, Zhang L, Li J, Wang C, Ji J (2014) Sediment properties and heavy metal pollution assessment in the river, estuary and lake environments of a fluvial plain, China. CATENA 119:52–60
Zhou J, Ma D, Pan J, Nie W, Wu K (2008) Application of multivariate statistical approach to identify heavy metal sources in sediment and waters: a case study in Yangzhong, China. Environ Geol 54:373–380
Acknowledgements
The author thanks, Prof. Md. Sultan-ul-Islam for logistical support during fieldwork. Thanks also to Barry P. Roser and Y. Sawada for the analytical support, and Md. Amjed Hossain for the multivariate statistical analysis. The suggestions of Xianliang Yi, the Editor, and comments from two anonymous reviewers were useful in improving this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Monbukagakusho (MEXT) and Heiwa Nakajima Foundation (HNF) scholarships to HMZ Hossain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The author conducted fieldwork, data analysis, manuscript text, and figures and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent for participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hossain, H.M.Z. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in sediments from the Brahmaputra River watershed in Bangladesh. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 81557–81570 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21522-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21522-1