Abstract
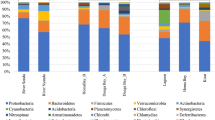
Bacterial community structure is one of the essential components of aquaculture dynamics and plays an important role in maintaining wetland health. The present work is an effort to study the structure of bacterial communities in the world’s largest sewage-fed fish farms, the East Kolkata Wetlands (EKWs), along with their predicted functional metabolic pathways and correlation with environmental variables. Sequencing data analysis revealed the abundance of genera such as Arcobacter (0–50%), Pseudomonas (0–15%), Sulfurospirillum (0–9%), Cloacibacterium (0–6%), hgcI clade (7–29%), C39 (0–9%), V6 (3–36%), Fluiivicola (1–6%) and Cyanobium (3–8%) in the EKWs. Further, water quality analysis of three treatment groups, i.e. Sewage, Sewage F-1 and Sewage F-2, revealed that dissolved oxygen (DO), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) differed significantly and violated the standard prescribed norms (Central Pollution Control Board, CPCB, New Delhi) for fishery propagation and irrigation in India. Further, the correlation matrix analysis between the abundance of bacterial genera and environmental variables indicated that DO, BOD and COD were mainly responsible for bacterial community structure and their proliferation in the EKWs. Our results indicated that the abundance of genera such as Arcobacter, Pseudomonas, Sulfurospirillum and Cloacibacterium has an inverse relationship with BOD and COD. Our observations based on the bacterial community structure and deteriorated water quality indicate the ineffective functioning and poor management of this man-made constructed wetland.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad U, Parveen S, Khan AA, Kabir HA, Mola HRA, Ganai AH (2011) Zooplankton population in relation to physic-chemical factors of sewage fed pond of Aligarh, (UP). India Biol Med 3:336–341
Alfano N, Tagliapietra V, Rosso F, Manica M, Arnoldi D, Pindo M, Rizzoli A (2019) Changes in microbiota across developmental stages of Aedes koreicus, an invasive mosquito vector in Europe: indications for microbiota-based control strategies. Front Microbiol 10:2832
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC.
Bardou P, Mariette J, Escudié F, Djemiel C, Klopp C (2014) jvenn: an interactive Venn diagram viewer. BMC Bioinf 15:293–300
Barka EA, Vatsa P, Sanchez L, Gaveau-Vaillant N, Jacquard C, Klenk HP, Clément C, Ouhdouch Y, van Wezel GP (2016) Taxonomy, physiology, and natural products of Actinobacteria. Microbiol. Mol Biol Rev 80:1–43
Bissett A, Bowman J, Burke C (2006) Bacterial diversity in organically-enriched fish farm sediments. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 55:48–56
Blancheton JP, Attramadal KJK, Michaud L, D'Orbcastel ER, Vadstein O (2013) Insight into bacterial population in aquaculture systems and its implication. Aquac Eng 53:30–39
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, Bokulich NA, Abnet CC, al-Ghalith GA, Alexander H, Alm EJ, Arumugam M, Asnicar F, Bai Y, Bisanz JE, Bittinger K, Brejnrod A, Brislawn CJ, Brown CT, Callahan BJ, Caraballo-Rodríguez AM, Chase J, Cope EK, da Silva R, Diener C, Dorrestein PC, Douglas GM, Durall DM, Duvallet C, Edwardson CF, Ernst M, Estaki M, Fouquier J, Gauglitz JM, Gibbons SM, Gibson DL, Gonzalez A, Gorlick K, Guo J, Hillmann B, Holmes S, Holste H, Huttenhower C, Huttley GA, Janssen S, Jarmusch AK, Jiang L, Kaehler BD, Kang KB, Keefe CR, Keim P, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koester I, Kosciolek T, Kreps J, Langille MGI, Lee J, Ley R, Liu YX, Loftfield E, Lozupone C, Maher M, Marotz C, Martin BD, McDonald D, McIver LJ, Melnik AV, Metcalf JL, Morgan SC, Morton JT, Naimey AT, Navas-Molina JA, Nothias LF, Orchanian SB, Pearson T, Peoples SL, Petras D, Preuss ML, Pruesse E, Rasmussen LB, Rivers A, Robeson MS II, Rosenthal P, Segata N, Shaffer M, Shiffer A, Sinha R, Song SJ, Spear JR, Swafford AD, Thompson LR, Torres PJ, Trinh P, Tripathi A, Turnbaugh PJ, Ul-Hasan S, van der Hooft JJJ, Vargas F, Vázquez-Baeza Y, Vogtmann E, von Hippel M, Walters W, Wan Y, Wang M, Warren J, Weber KC, Williamson CHD, Willis AD, Xu ZZ, Zaneveld JR, Zhang Y, Zhu Q, Knight R, Caporaso JG (2019) Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 37:852–857
Bowen JL, Ward BB, Morrison HG, Hobbie JE, Valiela I, Deegan LA, Sogin ML (2011) Microbial community composition in sediments resists perturbation by nutrient enrichment. The ISME J 5:1540–1548
Boyd CE, Tucker CS (1998) Pond aquaculture water quality management. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell
Brown RM, McClelland NI, Deininger RA, O’Connor, MF (1972) A water quality index-crashing the psychological barrier. Indicators of environmental quality, Springer 173–182
Cai L, Feng J, Zhang T (2014) Tracking human sewage microbiome in a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:3317–3326
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJ, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13:581–583
Carnevali O, Maradonna F, Gioacchini G (2017) Integrated control of fish metabolism, wellbeing and reproduction: the role of probiotic. Aquaculture 472:144–155
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), (2008), Guidelines for Water Quality Management, 1-41. (http://www.cpcb.nic.in)
Chandra K, Raghunathan C, Mao AA (2020) Biodiversity profile of East Kolkata Wetlands, 1-326 (ISBN:978-81-8171-547-0). Publisher Director Zool. Surv, India
Chiang E, Schmidt ML, Berry MA, Biddanda BA, Burtner A, Johengen TH, Palladino D, Denef VJ (2018) Verrucomicrobia are prevalent in north-temperate freshwater lakes and display class-level preferences between lake habitats. PLoS ONE 13:e0195112
Chong J, Liu P, Zhou G, Xia J (2020) Using MicrobiomeAnalyst for comprehensive statistical, functional, and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nat Protoc 15:799–821
De Schryver P, Vadstein O (2014) Ecological theory as a foundation to control pathogenic invasion in aquaculture. The ISME J 8:2360–2368
Deep PR, Bhattacharyya S, Nayak B (2013) Cyanobacteria in wetlands of the industrialized Sambalpur District of India. Aquat Biosyst 9:14
Dhal PK, Kopprio GA, Gärdes A (2020) Insights on aquatic microbiome of the Indian Sundarbans mangrove areas. PLoS ONE 15:e0221543
Dhariwal A, Chong J, Habib S, King I, Agellon LB, Xia J (2017) MicrobiomeAnalyst - a web-based tool for comprehensive statistical, visual and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nucleic Acids Res 45:180–188
Drobac D, Tokodi N, Lujić J, Marinović Z, Subakov-Simić G, Dulić T, Svirčev Z (2016) Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins in fishponds and their effects on fish tissue. Harmful Algae 55:66–76
Ehiagbonare JE, Ogunrinde YO (2010) Physicochemical analysis of fish pond water in Okada and its environs. Niger J Biotechnol 9:5922–5928
Eissler Y, Gálvez MJ, Dorador C, Hengst M, Molina V (2019) Active microbiome structure and its association with environmental factors and viruses at different aquatic sites of a high-altitude wetland. MicrobiologyOpen 8:e00667
Enderlein US, Enderlien RE, Williams WP (1997) Chapter 2: Water quality requirements. In: Bartram J, Balance R (eds) Water pollution control. World Health Organization, London
Environment Protection Agency (EPA) (2001) Parameters of water quality, interpretation and standards. published by the Environmental Protection Agency, Ireland
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations) (2018) The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture: meeting the sustainable development goals. FAO, Rome
Ganesan A, Chaussonnerie S, Tarrade A, Dauga C, Bouchez T, Pelletier E, Paslier DL, Sghir A (2008) Cloacibacillus evryensis gen. nov., sp nov., a novel asaccharolytic, mesophilic, amino-acid-degrading bacterium within the phylum ‘Synergistetes,’ isolated from an anaerobic sludge digester. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2003–2012
Gao P, Xu W, Sontag P, Li X, Xue G, Liu T, Sun W (2016) Correlating microbial community compositions with environmental factors in activated sludge from four full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants in Shanghai, China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:4663–4673
Gao T, Cui B, Kong X, Bai Z, Zhuang X, Qian Z (2019) Investigation of bacterial diversity and pathogen abundances in gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) ponds during a cyprinid herpesvirus 2 outbreak. MicrobiologyOpen 8:e907
Ghosh A, Maity B, Chakrabarti K, Chattopadhyay D (2007) Bacterial diversity of East Calcutta Wet Land area: possible identification of potential bacterial population for different biotechnological uses. Microb Ecol 54:452–459
HELCOM (ed) (1988) Guidelines for the Baltic monitoring programme for the third stage. Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission. Balt Sea Environ Proc 27D:161
Hornick KM, Buschmann AH (2018) Insights into the diversity and metabolic function of bacterial communities in sediments from Chilean salmon aquaculture sites. Ann. Microbiol 68:63–77
Horton DJ, Theis KR, Uzarski DG, Learman DR (2019) Microbial community structure and microbial networks correspond to nutrient gradients within coastal wetlands of the Laurentian Great Lakes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 95:fiz033
Huang X, Zhu J, Duan W, Gao J, Li W (2020) Biological nitrogen removal and metabolic characteristics in a full-scale two-staged anoxic-oxic (A/O) system to treat optoelectronic wastewater. Bioresour Technol 300:122595
Hubert CR, Oldenburg TB, Fustic M, Gray ND, Larter SR, Penn K, Rowan AK, Seshadri R, Sherry A, Swainsbury R, Voordouw G, Voordouw JK, Head IM (2012) Massive dominance of Epsilonproteobacteria in formation waters from a Canadian oil sands reservoir containing severely biodegraded oil. Environ Microbiol 14:387–404
Kaevska M, Videnska P, Sedlar K, Slana I (2016) Seasonal changes in microbial community composition in river water studied using 454-pyrosequencing. Springer Plus 5:409
Kanehisa M (2019) Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci 28:1947–1951
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:27–30
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Furumichi M, Morishima K, Tanabe M (2019) New approach for understanding genome variations in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D590–D595
Katoh K, Standley DM (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mole Biol Evol 30:772–780
Kirchman DL (2002) The ecology of cytophaga-flavobacteria in aquatic environments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 39:91–100
Klase G, Lee S, Liang S, Kim J, Gun Zo Y, Lee J (2019) The microbiome and antibiotic resistance in integrated fishfarm water: implications of environmental public health. Sci Total Environ 649:1491–1501
Klinger D, Naylor R (2012) Searching for solutions in aquaculture: charting a sustainable course. Annu Rev Env Resour 37:247–276
Langille MGI (2018) Exploring linkages between taxonomic and functional profiles of the human microbiome. mSystems 3:e00163–e00117
Larsson U, Hajdu S, Walve J, Elmgren R (2001) Baltic Sea nitrogen fixation estimated from the summer increase in upper mixed layer total nitrogen. Limnology and Oceanography 46:811–820
Lawson TB (1995) Fundamentals of aquacultural engineering. Chapman and Hall, New York
Lehner A, Tasara T, Stephan R (2005) Relevant aspects of Arcobacter spp. as potential foodborne pathogen. Int J Food Microbiol 102:127–135
Li X, Lu S, Liu S, Zheng Q, Shen P, Wang X (2020) Shifts of bacterial community and molecular ecological network at the presence of fluoroquinolones in a constructed wetland system. Sci Total Environ 708:135156
Lin X, Green S, Tfaily M, Prakash O, Konstantinidis K, Corbett J et al (2012) Microbial community structure and activity linked to contrasting biogeochemical gradients in bog and fen environments of the Glacial Lake Agassiz Peatland. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:7023–7031
Lu X, Tian C, Pei H, Hu W, Xie J (2013) Environmental factors influencingcyanobacteria community structure in Dongping Lake, China. J Environ Sci 25:2196–2206
Martınez-Porchas M, Vargas-Albores F (2017) Microbial metagenomics in aquaculture: a potential tool for a deeper insight into the activity. Rev Aquac 9:42–56
Mauléon VP, Labadi L, Bouges N, Ménard A, Mégraud F (2006) Arcobacter butzleri: underestimated enteropathogen. Emerging Infectious Diseases 2:307–309
Oh WT, Kim JH, Jun JW, Giri SS, Yun S, Kim HJ, Park SC (2019) Genetic characterization and pathological analysis of a novel bacterial pathogen, Pseudomonas tructae, in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Microorganisms 7:432
Peralta RM, Ahn C, Gillevet PM (2013) Characterization of soil bacterial community structure and physicochemical properties in created and natural wetlands. Sci Total Environ 443:725–732
Philosof A, Sabehi G, Béjà O (2009) Comparative analyses of actinobacterial genomic fragments from Lake Kinneret. Environ Microbiol 11:3189–3200
Pramanik A, Sengupta S, Bhattacharyya M (2019) Microbial diversity and community analysis of the Sundarbans Mangrove, a World Heritage site. In microbial diversity in the genomic era (65-76). Elsevier.
Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP (2010) FastTree 2–approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PloS one 5:e9490
Råbergh CMI, Bylund G, Eriksson JE (1991) Histopathological effect of microcystin LR a cyclic polypeptide from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa on common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquat Tox 20:131–146
Rapala J, Lahti K, Sivonen K, Niemelä SI (1994) Biodegradability and adsorption on lake sediments of cyanobacterial hepatotoxins and anatoxin-a. Letters in Applied Microbiol 19:423–428
Rashid M, Stingl U (2015) Contemporary molecular tools inmicrobial ecology and their application to advancing biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv 33:1755–1773
Rathlavath S, Mishra S, Kumar S, Nayak BB (2016) Incidence of Arcobacter spp. in fresh seafood from retail markets in Mumbai. India Ann Microbiol 66:165–170
Raychaudhuri S, Mishra M, Nandy P, Thakur AR (2008) Waste management: a case study of ongoing traditional practices at East Calcutta Wetland. Am J Agri Biol Sci 3:315–320
Roalkvam I, Drønen K, Dahle H, Wergeland HI (2019) Microbial communities in a flow-through fish farm for Lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus L.) during healthy rearing conditions. Front. Microbiol. 10:1594
Salipante SJ, Sengupta DJ, Rosenthal C, Costa G, Spangler J, Sims EH, Jacobs MA, Miller SI, Hoogestraat DR, Cookson BT, McCoy C, Matsen FA, Shendure J, Lee CC, Harkins TT, Hoffman NG (2013) Rapid 16S rRNA next-generation sequencing of polymicrobial clinical samples for diagnosis of complex bacterial infections. PLoS One 8:e65226
Sarkar S, Ghosh PB, Mukherjee K, Sil AK, Saha T (2009) Sewage treatment in a single pond system at East Kolkata Wetland, India. Water Sci Technol 60:9
Schreier HJ, Mirzoyan N, Saito K (2010) Microbial diversity of biological filters in recirculating aquaculture systems. Curr Opin Biotech 21:318–325
Sengupta K (2018) Shrinkage of East Kolkata Wetlands and its effect. International Journal of Academic Research and Development 3(1):57–67
Serkebaeva YM, Kim Y, Liesack W, Dedysh SN (2013) Pyrosequencing-based assessment of the bacteria diversity in surface and subsurface peat layers of a northern wetland, with focus on poorly studied phyla and candidate divisions. PloS One 8:e63994
Shchegolkova NM, Krasnov GS, Belova AA, Dmitriev AA, Kharitonov SL, Klimina KM, Melnikova NV, Kudryavtseva AV (2016) Microbial community structure of activated sludge in treatment plants with different wastewater compositions. Front Microbiol 7:90
Stone N, Shelton JL, Haggard BE, Thomforde HK (2013) Interpretation of water analysis reports for fish culture. SRAC Publication No. 4606:1–12
Strauss M (1997) Health (pathogen) considerations regarding the use of human waste in aquaculture. Environmental Research Forum 5(6):83–98
Sundberg LR, Ketola T, Laanto E, Kinnula H, Bamford JK, Penttinen R, Mappes J (2016) Intensive aquaculture selects for increased virulence and interference competition in bacteria. Proc R Soc B 283:20153069
Tudu AK, Rath S, Deuti K, Kosygin K (2020) Chapter 29: Fishes, 222-235, Biodiversity profile of East Kolkata Wetlands, 1-326 (ISBN:978-81-8171-547-0). Publisher Director Zool. Surv, India
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, (2012) Water quality standards handbook: second edition. EPA- 823-B-12-002. Available at (http://water.epa.gov/scitech/swguidance/standards/handbook/index.cfm)
Vikram S, Guerrero LD, Makhalanyane TP, Le PT, Seely M, Cowan DA (2016) Metagenomic analysis provides insights into functional capacity in a hyperarid desert soil niche community. Environ Microbiol 18:1875–1888
Wang Y, Zhang R, Zheng Q, Deng Y, Van Nostrand JD, Zhou J et al (2016) Bacterioplankton community resilience to ocean acidification: evidence from microbial network analysis. ICES J Mar Sci 73:865–875
Wang X, Zhu M, Li N, Du S, Yang J, Li Y (2018) Effects of CeO2 nanoparticles on bacterial community and molecular ecological network in activated sludgesystem. Environ Pollut 238:516–523
Weiss S, Xu ZZ, Peddada S, Amir A, Bittinger K, Gonzalez A, Lozupone C, Zaneveld JR, Vázquez-Baeza Y, Birmingham A, Hyde ER (2017) Normalization and microbial differential abundance strategies depend upon data characteristics. Microbiome 5:27
Woyke T, Chertkov O, Lapidus A, Nolan M, Lucas S, del Rio TG, Tice H, Cheng JF, Tapia R, Han C, Goodwin L, Pitluck S, Liolios K, Pagani I, Ivanova N, Huntemann M, Mavromatis K, Mikhailova N, Pati A, Chen A, Palaniappan K, Land M, Hauser L, Brambilla EM, Rohde M, Mwirichia R, Sikorski J, Tindall BJ, Göker M, Bristow J, Eisen JA, Markowitz V, Hugenholtz P, Klenk HP, Kyrpides NC (2011) Complete genome sequence of the gliding freshwater bacterium Fluviicola taffensis type strain (RW262). Stand Genomic Sci 5:21–29
Wu L, Yang Y, Chen S, Zhao M, Zhu Z, Yang S, Qu Y, Ma Q, He Z, Zhou J, He Q (2016) Long-term successional dynamics of microbial association networks in anaerobic digestion processes. Water Res 104:1–10
Yi J, Dong B, Jin J, Dai X (2014) Effect of increasing total solids contents on anaerobic digestion of food waste under mesophilic conditions: performance and microbial characteristics analysis. PLoS One 9:e102548
Yildiz H, Aydin S (2006) Pathological effects of Arcobacter cryaerophilus infection in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum). Acta Vet Hung 54:191–199
Zhang J, Zhu C, Guan R, Xiong Z, Zhang W, Shi J, Sheng Y, Zhu B, Tu J, Ge Q, Chen T, Lu Z (2017) Microbial profiles of a drinking water resource based on different 16S rRNAV regions during a heavy cyanobacterial bloom in Lake Taihu, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:12796–12808
Zhang Z, Li D, Xu W, Tang R, Li L (2019) Microbiome of co-cultured fish exhibits host selection and niche differentiation at the organ scale. Front Microbiol 10:2576
Zweig RD, Morton JD, Stewart MM (1999) Source water quality for aquaculture, a guide for assessment, environmental and socially sustainable development. The World Bank, Washington D.C., pp 1–59
Data and materials availability
The raw reads were submitted to the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) GenBank under the BioProject ID PRJNA633732.
Code availability
Not applicable
Funding
The authors are thankful to the Director, Zoological Survey of India, Kolkata for his constant support and providing lab facilities and permission to carry out the work. The work received financial support from ZSI-ARP-2019-22/IT/VK/KT core funding, Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change under the project ‘DNA metasystematics studies for the assessment of the macrobiome and microbiome in freshwater ecosystem with relation to noxious pollutants’. We thank Prof. Rainer Breitling (rainer.breitling@manchester.ac.uk), University of Manchester for his help in English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology: IT, KT and VK; Software: IT and KT; Water Quality analysis and Data interpretation: IT and RB; Data interpretation: VK, IT and KT; Supervision of the project and Funding acquisition: KC and VK; Writing, Reading and Approving the final manuscript: All authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Robert Duran
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1102 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tyagi, I., Tyagi, K., Bhutiani, R. et al. Bacterial diversity assessment of world’s largest sewage-fed fish farms with special reference to water quality: a Ramsar site. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 42372–42386 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13756-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13756-2