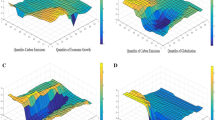
Abstract
On one divide, energy types have been linked with the varying degree of environmental damage. Another perspective argued on the severity of the damaged base on per capita and/or population consumption pattern. As such, this study investigates the nexus of per capita natural gas consumption-carbon dioxide emissions and per capita income-carbon dioxide emissions in the case of the People of the Republic of China. This study objectively expanded to illustrate whether the N-shaped environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis holds in the case of China or not. The employed autoregressive distributed lag bound testing approach incorporated additional explanatory variables (urbanization) within the N-shaped EKC hypothesis over the period 1971–2018. Importantly, the results show an evidence of inverted N-shaped EKC relationship. In addition, the study posits a positive relationship between natural gas consumption and carbon dioxide emissions and between urbanization and carbon dioxide emissions. Thus, the study proposes renewable energy development and decongestion of the urban centers as a means of controlling global warming.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Notes
The data reported is for until 2015, which is the latest year with complete data in all groups.
At the current consumption levels, excluding unproven reserves. Source: Statistical Review of World Energy and Energy International Agency (EIA).
References
Adedoyin FF, Alola AA, Bekun FV (2020a) An assessment of environmental sustainability corridor: the role of economic expansion and research and development in EU countries. Sci Total Environ:136726
Adedoyin FF, Alola AA, Bekun FV (2020b) The nexus of environmental sustainability and agro-economic performance of Sub-Saharan African countries. Heliyon 6(9):e04878
Allard A, Takman J, Uddin GS, Ahmed A (2018) The N-shaped environmental Kuznets curve: an empirical evaluation using a panel quantile regression approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(6):5848–5861
Al-Mulali U, Tang CF, Ozturk I (2015) Does financial development reduce environmental degradation? Evidence from a panel study of 129 countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:14891–14900
Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I (2015) The effect of energy consumption, urbanization, trade openness, industrial output, and the political stability on the environmental degradation in the MENA (Middle East and North African) region. Energy 84:382–389
Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I, Solarin SA (2016) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in seven regions: The role of renewable energy. Ecol Indic 67:267–282
Alola AA, Akadiri SS., Usman O (2020) Domestic material consumption and greenhouse gas emissions in the EU‐28 countries: Implications for environmental sustainability targets. Sustainable Development.
Alola AA, Yildirim H (2019) The renewable energy consumption by sectors and household income growth in the United States. Int J Green Energy 16(15):1414–1421
Alola AA, Alola UV, Saint Akadiri S (2019a) Renewable energy consumption in Coastline Mediterranean Countries: impact of environmental degradation and housing policy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(25):25789–25801
Alola AA, Yalçiner K, Alola UV, Saint Akadiri S (2019b) The role of renewable energy, immigration and real income in environmental sustainability target. Evidence from Europe largest states. Sci Total Environ 674:307–315
Amadeh H, Ghazi M, Abbasifar Z (2009) Causality relation between energy consumption and economic growth and employment in Iranian economy. Tahghighat-eeghtesadi Journal 44(86):1–38
An-bing W (2013) Study on the dynamic equilibrium and causality between natural gas consumption and economic growth. Guide Bus 23:108–111
Apergis N, Payne J (2010) NG consumption and economic growth: a panel investigation of 67 countries. Appl Energy 87(8):2759–2763
Apergis N, Loomis D, Payne JE (2010) Are shocks to natural gas consumption temporary a permanent? Evidence from a panel U.S.States. Energy Policy 38(8):4734–4736
Aqeel A, Butt MS (2001) The relationship between energy consumption and economic growth in Pakistan. Asia Pac Dev J 8:101–110
Asghar Z (2008) Energy-GDP relationship: a causal analysis for the five countries of South Asia. Appl Econ Int Dev 8(1)
Balitskiy S, Bilan Y, Strielkowski W, Štreimikienė D (2016) Energy efficiency and NG consumption in the context of economic development in the European Union. Renew Sust Energ Rev 55:156–168
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Shahbaz M, Roubaud D, Farhani S (2018) How economic growth, renewable electricity and natural resources contribute to CO2 emissions? Energy Policy 113:356–367
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Bekun FV, Etokakpan MU, Driha OM (2019a) A road to enhancements in natural gas use in Iran: a multivariate modeling approach. Res Policy 64:101485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.101485
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Shahbaz M, Jabbour CJC, Driha OM (2019b) The role of energy innovation and corruption in carbon emissions: evidence based on the EKC hypothesis. In: Energy and environmental strategies in the era of globalization. Springer, Cham, pp 271–304
Barış-Tüzemen Ö, Tüzemen S, Çelik AK (2020) Does an N-shaped association exist between pollution and ICT in Turkey? ARDL and quantile regression approaches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:20786–20799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08513-w
Bartleet M, Gounder R (2010) Energy consumption and economic growth in New Zealand: results of trivariate and multivariate models. Energy Policy 38(4):3508–3517
Basher SA, Fachin S (2013) The long-run relationship between savings and investment in oil-exporting developing countries: a case study of the Gulf Arab states. OPEC Energy Rev 37(4):429–446
Bekun FV, Alola AA, Sarkodie SA (2019) Toward a sustainable environment: nexus between CO2 emissions, resource rent, renewable and nonrenewable energy in 16-EU countries. Sci Total Environ 657:1023–1029
Bekun FV, Yalçiner K, Etokakpan MU, Alola AA (2020) Renewed evidence of environmental sustainability from globalization and energy consumption over economic growth in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:29644–29658
Bildirici M, Bakirtas T (2014) The relationship among oil, NG and coal consumption and economic growth in BRICTS (Brazil, Russian, India, China, Turkey, and South Africa) countries. Energy 65:134–144
Das A, McFarlane A, Chowdhury M (2013) The dynamics of NG consumption and GDP in Bangladesh. Renew Sust Energ Rev 22:269–274
Dickey PA, Fuller WA (1979) Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time- series with a unit root. J Am Stat Assoc 74:427–431
Dinda S (2004) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: a survey. Ecol Econ 49:431–455
Dogan E (2015) Revisiting the relationship between NG consumption and economic growth in Turkey. Energy Sources B Energy Econ. Plan Policy 10(4):361–370
Eluwole KK, Saint Akadiri S, Alola AA, Etokakpan MU (2020) Does the interaction between growth determinants a drive for global environmental sustainability? Evidence from world top 10 pollutant emissions countries. Sci Total Environ 705:135972
Etokakpan MU, Solarin SA, Yorucu V, Bekun FV, Sarkodie SA (2020) Modeling natural gas consumption, capital formation, globalization, CO2 emissions and economic growth nexus in Malaysia: Fresh evidence from combined cointegration and causality analysis. Energy Strat Rev 31:100526
Farhani S, Shahbaz M, Arouri M, Teulon F (2014) The role of NG consumption and trade in Tunisia’s output. Energy Policy 66:677–684
Fatai K, Oxley L, Scrimgeour F (2004) Modeling the causal relationship between energy consumption and GDP in New Zealand, Australia, India, Indonesia, the Philippines and Thailand. Math Comput Simul 64(3):431–445
Furuoka F (2016) Natural gas consumption and economic development in China and Japan: an empirical examination of the Asian context. Renew Sust Energ Rev 56:100–115
Giles D (2013) ARDL models. https://davegiles.blogspot.com/2013/06/ ardl-models-part-ii-bounds-tests.html. Accessed 20 April 2020
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1991) Environmental impacts of a North American free-trade agreement. NBER working paper series, Working Paper No. 3914. https://www.nber.org/papers/w3914.pdf. Accessed 16 Sept 2019.
Hafeznia H, Pourfayaz F, Maleki A (2017) An assessment of Iran’s NG potential for transition toward low-carbon economy. Renew Sust Energ Rev 79:71–81
Hu JL, Lin CH (2008) Disaggregated energy consumption and GDP in Taiwan: a threshold co-integration analysis. Energy Econ 30(5):2342–2358
Hu H, Xie N, Fang D, Zhang X (2018) The role of renewable energy consumption and commercial services trade in carbon dioxide reduction: evidence from 25 developing countries. Appl Energy 211:1229–1244
Ibrahim MD, Alola AA (2020) Integrated analysis of energy-economic development-environmental sustainability nexus: case study of MENA countries. Sci Total Environ 737:139768
Ighodaro C (2010) Cointegration and causality relationship between energy consumption and economic growth: further empirical evidence for Nigeria. J Bus Econ Manag 1:97–111
Ike GN, Usman O, Alola AA, Sarkodie SA (2020) Environmental quality effects of income, energy prices and trade: the role of renewable energy consumption in G-7 countries. Sci Total Environ 721:137813
International Gas Union (2010) https://www.igu.org/resources/annual-report-2010/. Accessed 25 Aug 2020
Isik C (2010) NG consumption and economic growth in Turkey: a bound test approach. Energy Syst 1(4):441–456
Jun F (2015) Research on the relationship between China’s coal and natural consumption and economic growth. Chin Collect Econ 25:14–15
Kang YQ, Zhao T, Yang YY (2016) Environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions in China: a spatial panel data approach. Ecol Indic 63:231–239
Kasman A, Duman YS (2015) CO2 emissions, economic growth, energy consumption, trade and urbanization in new EU member and candidate countries: a panel data analysis. Econ Model 44:97–103
Katircioğlu ST (2014) Testing the tourism-induced EKC hypothesis: the case of Singapore. Econ Model 41:383–391
Komen MH, Gerking S, Folmer H (1997) Income and environmental R&D: empirical evidence from OECD countries. Environ Dev Econ 2:505–515
Kose N, Bekun FV, Alola AA (2020) Criticality of sustainable research and development-led growth in EU: the role of renewable and non-renewable energy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(11):12683–12691
Kraft J, Kraft A (1978) On the relationship between energy and GNP. J Energy Dev:401–403
Kum H, Ocal O, Aslan A (2012) The relationship among natural gas energy consumption, capital and economic growth: bootstrap-corrected causality tests from G- 7 countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 16:2361–2365
Kuznets S (1955) Economic growth and income inequality. Am Econ Rev 45:1–28
Kwiatkowski D, Phillips PCB, Schmidt P, Shin Y (1992) Testing the null hypothesis of stationarity against the alternative of a unit root. J Econ 54:159–178
Lasisi TT, Alola AA, Eluwole KK, Ozturen A, Alola UV (2020) The environmental sustainability effects of income, labour force, and tourism development in OECD countries. Environ Sci.Pollut 27(17):21231–21242
Lee JW, Brahmasrene T (2014) ICT, CO2 emissions and economic growth: evidence from a panel of ASEAN. Glob Econ Rev 43:93–109
Lee C, Chang C (2005) Structural breaks, energy consumption, and economic growth revisited: evidence from Taiwan. Energy Econ 27(6):857–872
Li J (2012) Relationship between the consumption of natural gas and economic growth in the united states: its enlightenment to China. Special Zone Econ 7:127–130
Lim HJ, Yoo SH (2012) Natural gas consumption and economic growth in Korea: A causality analysis. Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning, and Policy 7(2):169–176
Liu Y, Zhou Y, Wu W (2015) Assessing the impact of population, income, and technology on energy consumption and industrial pollutant emissions in China. Appl Energy 155:904–917
Liu Q, Wang S, Zhang W, Li J (2018) Income distribution and environmental quality in China: a spatial econometric perspective. J Clean Prod 205:14–26
Liu Q, Wang S, Zhang W, Li J, Kong Y (2019) Examining the effects of income inequality on CO2 emissions: evidence from non-spatial and spatial perspectives. Appl Energy 236:163–171
Lorente DB, Álvarez-Herranz A (2016) Economic growth and energy regulation in the environmental Kuznets curve. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(16):16478–16494
Lotfalipour MR, Ali Falahi M, Ashena M (2010) Economic growth, CO2 emissions, and fossil fuel consumption in Iran. Energy 35:5115–5120
Muhammad S, Lean H H, Abdul F. (2012). Natural gas consumption and economic growth in Pakistan.MRPA Paper .p. 40959. Available at: /http://mpra. ub.uni-muenchen.de/40959/S.multi-page.pdf. Accessed 16 Sept 2019.
Narayan PK, Smyth R, Prasad A (2007) Electricity consumption in G7 countries: a panel cointegration analysis of residential demand elasticities. Energy Policy 35(9):4485–4494
Ozturk I, Acaravci A (2010) CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in Turkey. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14:3220–3225
Ozturk I, Al-Mulali U (2015) NG consumption and economic growth nexus: panel data analysis for GCC countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 51:998–1003
Panayotou T (1993) Empirical tests and policy analysis of environmental degradation at different stages of economic development. ILO working papers, WP238. International Labour Organization. International Labour Organization Publications, Geneva.
Payne JE (2011) US disaggregate fossil fuel consumption and real GDP: an empirical note. Energy Sources, Part B+: Economics. Plan Policy 6(1):63–68
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith R (2001) Bound testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16:289–326
Pirlogea C, Cicea C (2012) The econometric perspective of the energy consumption and economic growth relation in the European Union. Renew Sust Energ Rev 16:5718–5726
Rafindadi A, Ozturk I (2015) NG consumption and economic growth nexus: is the 10th Malaysian plan attainable within the limits of its resource. Renew Sust Energ Rev 49:1221–1232
Ramey VA (2011) Identifying government spending shocks: it’s all in the timing. Q J Econ 126(1):1–50
Reynolds D, Kolodziej M (2008) Former Soviet Union oil production and GDP decline: Granger causality and the multi-cycle Hubbert curve. Energy Econ 30(2):271–289
Saboori B, Sulaiman J (2013) Environmental degradation, economic growth, and energy consumption: evidence of the environmental Kuznets curve in Malaysia. Energy Policy 60:892–905
Saint Akadiri S, Alola AA, Akadiri AC, Alola UV (2019a) Renewable energy consumption in EU-28 countries: policy toward pollution mitigation and economic sustainability. Energy Policy 132:803–810
Saint Akadiri S, Lasisi TT, Uzuner G, Akadiri AC (2019b) Examining the impact of globalization in the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: the case of tourist destination states. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(12):12605–12615
Saint Akadiri S, Alola AA, Alola UV, Nwambe CS (2020) The role of ecological footprint and the changes in degree days on environmental sustainability in the USA. Environ Sci.Pollut 27(20):24929–24938
Sari R, Ewing B, Soytas U (2008) The relationship between disaggregate energy consumption and industrial production in the United States: an ARDL approach. Energy Econ 30(5):2302–2313
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V (2018) The empirical study of the environmental Kuznets curve and environmental sustainability curve hypothesis for Australia, China, Ghana and USA. J Clean Prod 201:98–110
Shafik N, Bandyopadhyay S (1992) Economic growth and environmental quality: time series and cross-country evidence. In: Policy research working paper series, WPS 0904. The World Bank http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/833431468739515725/pdf/
Shahbaz M, Hye QMA, Tiwari AK, Leitão NC (2013a) Economic growth, energy consumption, financial development, international trade and CO2 emissions in Indonesia. Renew Sust Energ Rev 25:109–121
Shahbaz M, Khan S, Tahir MI (2013b) The dynamic links between energy consumption, economic growth, financial development and trade in China: fresh evidence from multivariate framework analysis. Energy Econ 40:8–21
Shahiduzzaman M, Alam K (2014) A reassessment of energy and GDP relationship: the case of Australia. Environ Dev Sustain 16:323–344
Shahbaz M, Sbia R, Hamdi H, Ozturk I (2014) Economic growth, electricity consumption, urbanization and environmental degradation relationship in United Arab Emirates. Ecol Indic 45:622–631
Sharif A, Raza SA, Ozturk I, Afshan S (2019) The dynamic relationship of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption with carbon emission: a global study with the application of heterogeneous panel estimations. Renew Energy 133:685–691
Siddiqui R (2004) Energy and economic growth in Pakistan. Pak Dev Rev 43:175–200
Solarin SA, Lean HH (2016) Natural gas consumption, income, urbanization, and CO2 emissions in China and India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(18):18753–18765
Solarin SA, Ozturk I (2016) The relationship between NG consumption and economic growth in OPEC members. Renew Sust Energ Rev 58:1348–1356
Solarin SA, Shahbaz M (2015) NG consumption and economic growth: the role of foreign direct investment, capital formation and trade openness in Malaysia. Renew Sust Energ Rev 42:835–845
Solarin SA, Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I (2017) Validating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in India and China: the role of hydroelectricity consumption. Renew Sust Energ Rev 80:1578–1587
Sun H, Edziah BK, Sun C, Kporsu A K (2019) Institutional quality, green innovation and energy efficiency. Energy policyv 135:111002
Soytas U, Sari R (2003) Energy consumption and GDP: causality relationship in G-7 countries and emerging markets. Energy Econ 25(1):33–37
Stern D (2003) Environmental Kuznets curve. Encycl Energy 2:517–525
Stern DI (2004) The rise and fall of the environmental Kuznets curve. World Dev 32(8):1419–1439
The Oxford Institute for Energy Studies (2020) https://www.oxfordenergy.org/publications/. Accessed 20 Oct 2020
United States Energy International Agency (2018). China surpassed the United States as the world’s largest crude oil importer in 2017. https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=37821.
Villada J, Olaya Y (2013) A simulation approach for analysis of short-term security of natural gas supply in Colombia. Energy Policy 53:11–26
Wang Y, Han R, Kubota J (2016) Is there an environmental Kuznets curve for SO2 emissions? A semi-parametric panel data analysis for China. Renew Sust Energ Rev 54:1182–1188
Worldometer (2020) https://www.worldometers.info/gas/. Accessed 25 Aug 2020
Wu B, Li T, Baležentis T, Štreimikienė D (2019) Impacts of income growth on air pollution-related health risk: exploiting objective and subjective measures. Resour Conserv Recycl 146:98–105
Yang HY (2000) Coal consumption and economic growth in Taiwan. Energy Sources 22(2):109–115
Yu E, Choi J (1985) The causal relationship between energy and GNP: an international comparison. J Energy Dev 10(2):249–272
Zamani M (2007) Energy consumption and economic activities in Iran. Energy Econ 29(6):1135–1140
Zhang Z, Meng X (2019) Internet penetration and the environmental Kuznets curve: a cross-National Analysis. Sustainability 11:1358
Zhang C, Zhao W (2014) Panel estimation for income inequality and CO2 emissions: a regional analysis in China. Appl Energy 136:382–392
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Andrew Adewale ALOLA: formal analysis, investigation, methodology, and corresponding; Mfonobong Udom ETOKAKPAN: writing-original draft and data curation; Seyi Saint AKADIRI: writing and conceptualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Per capita income and environmental quality in China exhibit a “rise and fall” relationship.
• An inverted N-shaped environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis holds for China.
• Natural gas utilization hampers environmental quality in China.
• Increasing rate of urbanization is detrimental to the environment.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Etokakpan, M.U., Akadiri, S.S. & Alola, A.A. Natural gas consumption-economic output and environmental sustainability target in China: an N-shaped hypothesis inference. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 37741–37753 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13329-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13329-3