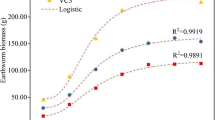
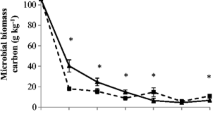
Abstract
Nanoparticles (NPs) are prevalent in dewatered sludge, and their presence increases the environmental risks associated with the subsequent sludge treatment process. However, until now, their potential effects on sludge vermicomposting have not been clarified. This study investigated the effects of NPs on sludge humification and microbial profiles during vermicomposting by comparing fresh dewatered sludge substrates with substrates mixed with 0 mg/kg NPs (control), 100 mg/kg TiO2, 500 mg/kg TiO2, 100 mg/kg ZnO, and 500 mg/kg ZnO. The results showed that addition of TiO2 and ZnO NPs to sludge did not significantly affect the growth rate of earthworms and the superoxide dismutase activity in their guts during vermicomposting. Moreover, higher concentrations of the selected NPs promoted the humification index of sludge by 20.7–49.6%, through the formation of polysaccharides, aromatic substances, and organic acids in final vermicomposts. Compared with the control without NP addition, bacterial community diversity was enhanced in treatments with TiO2 and ZnO NPs, and dominant genera differed according to the type and concentration of NPs. This study suggests that the presence of TiO2 and ZnO NP residuals modify the microbial community of sludge, thus promoting sludge humification during vermicomposting.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhat SA, Singh S, Singh J, Kumar S, Vig AP (2018) Bioremediation and detoxification of industrial wastes by earthworms: vermicompost as powerful crop nutrient in sustainable agriculture. Bioresour Technol 252:172–179
Chen W, Westerhoff P, Leenheer JA, Booksh K (2003) Fluorescence Excitation-Emission Matrix Regional Integration to Quantify Spectra for Dissolved Organic Matter. Environ Sci Technol 37:5701–5710
Choi S, Johnston M, Wang GS, Huang CP (2018) A seasonal observation on the distribution of engineered nanoparticles in municipal wastewater treatment systems exemplified by TiO2 and ZnO. Sci Total Environ 625:1321–1329
Fang W, Wei Y, Liu J (2016) Comparative characterization of sewage sludge compost and soil: heavy metal leaching characteristics. J Hazard Mater 310:1–10
Fernández-Gómez MJ, Nogales R, Plante A, Plaza C, Fernández JM (2015) Application of a set of complementary techniques to understand how varying the proportion of two wastes affects humic acids produced by vermicomposting. Waste Manag 35:81–88
Fu X, Cui G, Huang K, Chen X, Li F, Zhang X, Li F (2016) Earthworms facilitate the stabilization of pelletized dewatered sludge through shaping microbial biomass and activity and community. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(5):4522–4530
Ge Y, Schimel JP, Holden PA (2011) Evidence for negative effects of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles on soil bacterial communities. Environ Sci Technol 45(4):1659–1664
Ge Y, Schimel JP, Holden PA, (2012) Identification of Soil Bacteria Susceptible to TiO and ZnO Nanoparticles. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 78 (18):6749–6758
Horn MA, Drake HL, Schramm A (2006) Nitrous oxide reductase genes (nosz) of denitrifying microbial populations in soil and the earthworm gut are phylogenetically similar. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1019–1026
Hu CW, Li M, Cui YB, Li DS, Chen J, Yang LY (2010) Toxicological effects of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles in soil on earthworm Eisenia fetida. Soil Biol Biochem 42:586–591
Hu S, Zhang W, Li J, Lin K, Ji R (2016) Antioxidant and gene expression responses of Eisenia fetida following repeated exposure to BDE209 and Pb in a soil-earthworm system. Sci Total Environ 556:163–168
Huang K, Li F, Wei Y, Chen X, Fu X (2013) Changes of bacterial and fungal community compositions during vermicomposting of vegetable wastes by Eisenia foetida. Bioresour Technol 150:235–241
Huang K, Xia H, Li F, Wei Y, Cui G, Fu X, Chen X, (2016) Optimal growth condition of earthworms and their vermicompost features during recycling of five different fresh fruit and vegetable wastes. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 23(13):13569–13575
Huang K, Xia H, Wu Y, Chen J, Cui G, Li F, Chen Y, Wu N (2018) Effects of earthworms on the fate of tetracycline and fluoroquinolone resistance genes of sewage sludge during vermicomposting. Bioresour Technol 259:32–39
Hussain N, Abbasi T, Abbasi SA (2016) Vermicomposting transforms allelopathic parthenium into a benign organic fertilizer. J Environ Manag 180:180–189
Karmegam N, Vijayan P, Prakash M, Paul JAJ (2019) Vermicomposting of paper industry sludge with cow dung and green manure plants using Eisenia fetida: A viable option for cleaner and enriched vermicompost production. J Clean Prod 228:718–728
Li K, Qian J, Wang J, Wang C, Fan X, Lu B, Tian X, Jin W, He H, Guo W, (2019) Toxicity of Three Crystalline TiO Nanoparticles in Activated Sludge: Bacterial Cell Death Modes Differentially Weaken Sludge Dewaterability. Environmental Science & Technology 53 (8):4542–4555
Li X, Xing M, Yang J, Huang Z (2011) Compositional and functional features of humic acid-like fractions from vermicomposting of sewage sludge and cow dung. J Hazard Mater 185:740–748
Li D, Li B, Wang Q, Hou N, Li C, Cheng X (2016) Toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticle to denitrifying strain CFY1 and the impact on microbial community structures in activated sludge. Chemosphere. 144:1334–1341
Liu R, Lal R (2015) Potentials of engineered nanoparticles as fertilizers for increasing agronomic productions. Sci Total Environ 514:131–139
Ma B, Li S, Wang S, Gao M, Guo L, She, Zhao Y, Jin C, Yu N, Zhao C (2018) Effect of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on composition and spectroscopic characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances from activated sludge. Process Biochem 75:212–220
Mu H, Chen Y, Xiao N (2011) Effects of metal oxide nanoparticles (TiO2, Al2O3, SiO2 and ZnO) on waste activated sludge anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 102:10305–10311
Nowack B, Bucheli TD (2007) Occurrence, behavior and effects of nanoparticles in the environment. Environ Pollut 150(1):5–22
Oleszczuk P, Czech B, Kończak M, Bogusz A, Siatecka A, Godlewska P, Wiesner M (2019) Impact of ZnO and ZnS nanoparticles in sewage sludge-amended soil on bacteria, plant and invertebrates. Chemosphere 237:124359
Otero-González L, Field JA, Sierra-Alvarez R (2014) Inhibition of anaerobic wastewater treatment after long-term exposure to low levels of CuO nanoparticles. Water Res 58:160–168
Pérez-Hernández H, Fernández-Luqueño F, Huerta-Lwanga E, Mendoza-Vega J, Álvarez-Solís José D (2020) Effect of engineered nanoparticles on soil biota: Do they improve the soil quality and crop production or jeopardize them? Land Degrad Dev 31:2213–2230
Raheem A, Sikarwar VS, He J, Dastyar W, Dionysiou DD, Wang W, Zhao M (2018) Opportunities and challenges in sustainable treatment and resource reuse of sewage sludge: A review. Chem Eng J 337:616–641
Sánchez-López KB, De los Santos-Ramos FJ, Gómez-Acata ES, Luna-Guido M, Navarro-Noya YE, Fernández-Luqueño F, Dendooven L, (2019) TiO nanoparticles affect the bacterial community structure and (Savigny, 1826) in an arable soil. PeerJ 7:e6939
Santhosh C, Velmurugan V, Jacob G, Jeong SK, Grace AN, Bhatnagar A (2016) Role of NPs in water treatment applications: A review. Chem Eng J 306:1116–1137
Simonin M, Richaume A, Guyonnet JP, Dubost A, Martins JM, Pommier T (2016) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles strongly impact soil microbial function by affecting archaeal nitrifiers. Sci Rep 6:33643
Stamou I, Antizar-Ladislao B (2016) The impact of silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the in-vessel composting of municipal solid waste. Waste Manag 56:71–78
Suleiman H, Rorat A, Grobelak A, Grosser A, Milczarek M, Płytycz B, Kacprzak M, Vandenbulcke F (2017) Determination of the performance of vermicomposting process applied to sewage sludge by monitoring of the compost quality and immune responses in three earthworm species: Eisenia fetida, Eisenia andrei and Dendrobaena veneta. Bioresour Technol 241:103–112
Sun X, Sheng Z, Liu Y (2013) Effects of silver nanoparticles on microbial community structure in activated sludge. Sci Total Environ 443:828–835
Swati A, Hait S, (2017) Fate and bioavailability of heavy metals during vermicomposting of various organic wastes—A review. Process Safety and Environmental Protection 109:30–45
Valerio-Rodríguez M, Trejo-Téllez L, Aguilar-González M, Medina-Pérez G, Zúñiga-Enríquez J, Ortegón-Pérez A, Fernández-Luqueño F (2020) Effects of ZnO, TiO2 or Fe2O3 Nanoparticles on the body mass, reproduction, and survival of Eisenia fetida. Pol J Environ Stud 29(3):2383–2394
Valsami-Jones E, Lynch I (2015) How safe are NPs? Science 350(6259):388–389
Wang D, Chen Y (2016) Critical review of the influences of nanoparticles on biological wastewater treatment and sludge digestion. Crit Rev Biotechnol 36:816–828
Wang S, Gao M, She Z, Zheng D, Jin C, Guo L, Zhao Y, Li Z, Wang X (2016) Long-term effects of ZnO nanoparticles on nitrogen and phosphorus removal, microbial activity and microbial community of a sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour Technol 216:428–436
Xia H, Chen J, Chen X, Huang K, Wu Y (2019) Effects of tetracycline residuals on humification, microbial profile and antibiotic resistance genes during vermicomposting of dewatered sludge. Environ Pollut 252:1068–1077
Xia S, Zhao H, Wu Y, Han S, Mi W, Kang Y, Hu J, Feng K (2020) Effect of feeding conditions on the degradation of tetracycline in sewage sludge by earthworm. Biochem Eng J 160:107608
Xie Y, He Y, Irwin PL, Jin T, Shi X (2011) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Campylobacter jejuni. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(7):2325–2331
Xing M, Li X, Yang J, Huang Z, Lu Y (2012) Changes in the chemical characteristics of water-extracted organic matter from vermicomposting of sewage sludge and cow dung. J Hazard Mater 205-206:24–31
Yadav A, Garg VK (2019) Biotransformation of bakery industry sludge into valuable product using vermicomposting. Bioresour Technol 274:512–517
Yang L, Bai Y, Wang X, Wang L, Wang H (2011) Study on the colorimetric method of extracted soil humic substances. Humic Acid 1:15–19
Yang Y, Quensen J, Mathieu J, Wang Q, Wang J, Li M, Tiedje JM, Alvarez PJJ (2014) Pyrosequencing reveals higher impact of silver nanoparticles than Ag+ on the microbial community structure of activated sludge. Water Res 48:317–325
Zeng G, Zhang L, Dong H, Chen Y, Zhang J, Zhu Y, Yuan Y, Xie Y, Fang W (2018) Pathway and mechanism of nitrogen transformation during composting: Functional enzymes and genes under different concentrations of PVP-AgNPs. Bioresour Technol 253:112–120
Zhang L, Zeng G, Dong H, Chen Y, Zhang J, Yan M, Zhu Y, Yuan Y, Xie Y, Huang Z (2017) The impact of silver nanoparticles on the co-composting of sewage sludge and agricultural waste: Evolutions of organic matter and nitrogen. Bioresour Technol 230:132–139
Zhang L, Dong H, Zhu Y, Zhang J, Zeng G, Yuan Y, Cheng Y, Li L, Fang W (2019) Evolutions of different microbial populations and the relationships with matrix properties during agricultural waste composting with amendment of iron (hydr) oxide nanoparticles. Bioresour Technol 289:121697
Acknowledgments
We also thanks for the help of Prof. Yongzhi Chen for better revise this paper.
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Funding
This study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51868036, 51668033), Foundation of A Hundred Youth Talents Training Program of Lanzhou Jiaotong University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xia Hui performed the investigation, analyzed the data, and prepared the manuscript, who was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. Huang Kui designed and funded the experiment and revised the draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Chris Lowe
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hui, X., Kui, H. Effects of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles on vermicomposting of dewatered sludge: studies based on the humification and microbial profiles of vermicompost. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 38718–38729 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13226-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13226-9