Abstract
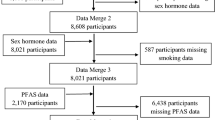
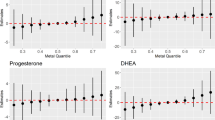
As observed among residents in electronic waste (e-waste) recycling areas, dioxins can disrupt the homeostasis of endocrine hormones and the balance of thyroid hormones. Few studies, however, have examined whether e-waste recycling activities influence steroid hormone equilibrium in the general adult male population. This study evaluated the association between steroid hormones and the physical burdens of dioxins in the general adult male population residing in an e-waste region. In September 2017, 74 adult males residing in an e-waste dismantling region were enrolled in the current study. Approximately 10 mL of blood was collected from each adult male, and the serum samples were separated through centrifugation. Then, the levels of dioxin and steroid hormones in the serum of the participants were measured. We treated dioxin levels as categorical variables in the general linear model according to quartiles (25, 50, and 75 percentile). Comparing the findings with a reference group (< 25th percentile), we noted significantly higher dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) level in men with low serum polychlorinated dibenzofuran-toxic equivalent (PCDFs-TEQ) level between 3.80 and 6.31 pg/g lipid (1933 vs. 1447 pg/ml) and low polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans-TEQ (PCDD/PCDFs-TEQ) between 8.57 and 15.11 pg/g lipid (1996 vs. 1360 pg/ml). Moreover, a significantly higher androstenedione (A-dione) level was found in men whose serum PCDFs-TEQ ≥ 11.34 pg/g lipd (2404 vs. 1848). What’s more, there were significantly higher 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β-HSD) concentrations in low- and high-2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) groups (1.30–1.67 and ≥ 2.64 pg-TEQ/g lipid, respectively with 719 and 807 vs. 496, respectively). Our findings suggest that specific dioxin exposure may disturb normal DHEA, A-dione levels, and enzyme activity in the general adult male population in an e-waste region of China.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anh LT, Kido T, Honma S, Manh HD, Koike I, Oyama Y, Phuc HD, Okamoto R, Nakagawa H, Nakayama SF, Nhu DD, Minh NH, Toan NV, Son LK (2017) A relationship in adrenal androgen levels between mothers and their children from a dioxin-exposed region in Vietnam. Sci Total Environ 607-608:1312–1318
Baldé CP, Forti V, Gray V, Kuehr R, Stegmann P (2017) The Global E-waste Monitor 2017: Quantities, Elows, and Resources. https://collections.unu.edu/eserv/UNU:6341/Global-E-waste_Monitor_2017__electronic_single_pages_.pdf. Accessed 3 May 2020
Bhatt MR, Khatri Y, Rodgers RJ, Martin LL (2017) Role of cytochrome b5 in the modulation of the enzymatic activities of cytochrome P450 17α-hydroxylase/17, 20-lyase (P450 17A1). J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 170:2–18
Chan JKY, Wong MH (2013) A review of environmental fate, body burdens, and human health risk assessment of PCDD/Fs at two typical electronic waste recycling sites in China. Sci Total Environ 463-464:1111–1123
Chan JKY, Xing GU, Xu Y, Liang Y, Chen LX, Wu SC, Wong CK, Leung CK, Wong MH (2007) Body loadings and health risk assessment of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans at an intensive electronic waste recycling site in China. Environ Sci Technol 41:7688–7674
Chen A, Dietrich KN, Xia H, Ho SM (2011) Developmental neurotoxicants in e-waste: an emerging health concern. Environ Health Perspect 119:431–438
Duan HB, Hu JK, Tan QY, Liu L, Wang Y, Li J (2015) Systematic characterization of generation and management of e-waste in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1929–1943
Gu WH, Bai JF, Yao HY, Zhao J, Zhuang X, Huang Q, Zhang C, Wang J (2017) Heavy metals in soil at a waste electronic and electronic equipment processing area in China. Waste Manag Res 35:1183–1191
Gu W, Bai J, Yuan W, Ma E, Zhang C, Wang J (2019) Pollution analysis of soil polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from informal electronic waste dismantling areas in Xinqiao, China. Waste Manag Res 37:394–401
Gupta A, Ketchum N, Roehrborn CG, Schecter A, Aragaki CC, Michalek JE (2006) Serum dioxin, testosterone, and subsequent risk of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a prospective cohort study of air force veterans. Environ Health Perspect 114:1649–1654
Ju Y, Xu GJ, Chen L, Jiang Q, Li LP, Yang KD, Jiang Q, Li LP, Yang KD, Chen XM (2008) Analyses of levels of thyroid hormones and its receptor expression in puerperants and newborns from an e-waste dismantling site. Front Med 2:276–282
Karman BN, Basavarajappa MS, Hannon P, Flaws JA (2012) Dioxin exposure reduces the steroidogenic capacity of mouse antral follicles mainly at the level of HSD17B1 without altering atresia. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 264(1):1–12
Kido T, Dao TV, Ho MD, Dang ND, Pharm NT, Okamato R, Pham TT, Maruzeni S, Nishijo M, Nakawa H et al (2014) High cortisol and cortisone levels are associated with breast milk dioxin concentrations in Vietnamese women. Eur J Endocrinol 170(1):131–139
Kido T, Honma S, Nhu DD, Manh HD, Van Tung D, Sun XL, Anh LT, Okamoto R, Maruzeni S, Nakagawa H, Hung NN, Son L (2016) Inverse association of highly chlorinated dioxin congeners in maternal breast milk with dehydroepiandrosterone levels in three-year-old Vietnamese children. Sci Total Environ 550:248–255
Kutner MH, Nachtsheim CJ, Neter J, Li W (2005) Applied linear statistic models, 5th edn. McGraw-Hill Irwin, New York, p 346
Li J, Jiang Y, Xu ZM (2017) Eddy current separation technology for recycling printed circuit boards from crushed cell phones. J Clean Prod 141:1316–1323
Luong HV, Tai PT, Nishijo M, Trung DM, Thao PN, Van Son P, Van Long N, Linh NT, Nishijo H (2018) Association of dioxin exposure and reproductive hormone levels in men living near the Bien Hoa airbase, Vietnam. Sci Total Environ 628-629:484–489
Man YB, Chow KL, Xing GH, Chan JKY, Wu SC, Wong MH (2017) A pilot study on health risk assessment based on body loadings of PCBs of lactating mothers at Taizhou, China, the world's major site for recycling transformers. Environ Pollut 227:364–371
Manh HD, Kido T, Okamoto R, Sun XL, Anh LT, Supratman S, Maruzeni S, Nishijo M, Nakagawa H, Honma S et al (2014) Serum dioxin levels in Vietnamese men more than 40 years after herbicide spraying. Environ Sci Technol 48(6):3496–3503
Miller WL, Auchus RJ (2011) The molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology of human steroidogenesis and its disorders. Endocr Rev 32(1):81–151
Miyashita C, Araki A, Mitsui T, Itoh S, Goudarzi H, Kajiwara J, Hori T, Cho K, Moriya K, Shinohara N et al (2018) Sex-related differences in the associations between maternal dioxin-like compounds and reproductive and steroid hormones in cord blood: the Hokkaido study. Environ Int 117:175–185
Ni HG, Zeng EY (2009) Law enforcement and global collaboration are the keys to containing e-waste tsunami in China. Environ Sci Technol 43:3991–3994
Oanh NTP, Kido T, Honma S, Oyama Y, Anh LT, Phuc HD, Viet NH, Manh HD, Okamoto R, Nakagawa H, Nakayama SF, Nhu DD, van Tung D, van Chi V, Minh NH, van Toan N (2018) Androgen disruption by dioxin exposure in 5-year-old Vietnamese children: decrease in serum testosterone level. Sci Total Environ 640-641:466–474
Pitt JA, Buckalew AR, House DE, Abbott BD (2000) Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) and corticosterone secretion by perifused pituitary and adrenal glands from rodents exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Toxicology 151:25–35
Shen H, Ding G, Han G, Wang X, Xu X, Han J, Lou X, Xu C, Cai D, Song Y, Lu W (2010) Distribution of PCDD/Fs, PCBs, PBDEs and organochlorine residues in children’s blood from Zhejiang, China. Chemosphere 80:170–175
Shen H, Guan R, Ding G, Chen Q, Lou X, Chen Z, Zhang L, Xing M, Han J, Wu Y (2017) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/furans (PCDD/Fs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in Zhejiang foods (2006–2015): market basket and polluted areas. Sci Total Environ 574:120–127
Shridhar S, Farley A, Reid RL, Foster WG, Van Vugt DA (2001) The effect of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on corticotrophin-releasing hormone, arginine vasopressin, and pro-opiomelanocortin mRNA levels in the hypothalamus of the cynomolgus monkey. Toxicol Sci 63:181–188
Song XL, Wang JW, Yang JX, Lu B (2017) An updated review and conceptual model for optimizing WEEE management in China from a life cycle perspective. Front Environl Sci Eng 11:3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-017-0985-8
Sun XL, Kido T, Okamoto R, Manh HD, Maruzeni S, Nishijo M, Nakagawa H, Honma S, Nakano T, Takasuga T, Nhu DD, Hung NN, Son LK (2014) Relationship between dioxin and steroid hormones in sera of Vietnamese men. Biomarkers 19(3):236–240
Sun XL, Kido T, Honma S, Koh E, Okamoto R, Manh HD, Maruzeni S, Nishijo M, Nakagawa H, Nakano T, Takasuga T, Nhu DD, Hung NN, Son LK (2017) The relationship between dioxins exposure and risk of prostate cancer with steroid hormone and age in Vietnamese men. Sci Total Environ 595:842–848
Sun XL, Okamoto R, Kido T, Honma S, Manh HO, Viet NH, Anh LT, Phuc HD, Oanh NTP, Maruzeni S et al (2020) Association of dioxin in maternal breast milk and salivary steroid hormone levels in preschool children: a five-year follow-up study of a Vietnam cohort. Chemosphere. 241:124899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.Chemosphere.2019.124899
Turyk M, Anderson H, Persky VW (2007) Relationships of thyroid hormone deficiency with polychlorinated biphenyls, dioxins, furans, and DDE in adults. Environ Health Perspect 115:1197–11203
Van den Berg M, Birnbaum LS, Denison M, De Vito M, Farland W, Feeley M, Fiedler H, Hakansson H, Hanberg A, Haws L, Rose M, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tohyama C, Tritscher A, Tuomisto J, Tysklind M, Walker N, Peterson RE (2006) The 2005 World Health Organization Reevaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol Sci 93:223–241
van den Dungen MW, Rijk JCW, Kampman E, Steegenga WT, Murk AJ (2015) Steroid hormone related effects of marine persistent organic pollutants in human H295R adrenocortical carcinoma cells. Toxicol in Vitro 29:769–778
Wang Z, Hang JG, Feng H, Shi LL, Dong JJ, Shen B, Luo T, Cai RM, Shen LJ, Kido T, Sun XL (2019) Effects of perinatal dioxin exposure on development of children: a three-year follow-up study of China cohort. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(20):20780–20786
Xiao X, Hu JF, Peng P, Chen DY, Bi XH (2016) Characterization of polybrominated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PBDDs/Fs) in environmental matrices from an intensive electronic waste recycling site, South China. Environ Pollut 212:464–471
Xu PW, Lou XM, Ding GA, Shen H, Wu L, Chen Z, Han J, Han G, Wang X (2014) Association of PCB, PBDE and PCDD/F body burdens with hormone levels for children in an e-waste dismantling area of Zhejiang Province, China. Sci Total Environ 499:55–61
Xu P, Lou X, Ding G, Shen H, Wu L, Chen Z, Han J, Wang X (2015) Effects of PCBs and PBDEs on thyroid hormone, lymphocyte proliferation hematology and kidney injury markers in residents of an e-waste dismantling area in Zhejiang, China. Sci Total Environ 536:215–222
Yamashita K, Miyashiro Y, Maekubo H, Okuyama M, Honma S, Takahashi M, Numazawa M (2009) Development of highly sensitive quantification method for testosterone and sdihydrotestosterone in human serum and prostate tissue by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Steroids 74:920–926
Yuan J, Chen L, Chen D, Guo H, Bi X, Ju Y, Jiang P, Shi J, Yu Z, Yang J, Li L, Jiang Q, Sheng G, Fu J, Wu T, Chen X (2008) Elevated serum polybrominated diphenyl ethers and thyroid-stimulating hormone associated with lymphocytic micronuclei in Chinese workers from an E-waste dismantling site. Environ Sci Technol 42:2195–2200
Zhang JQ, Jiang YH, Zhou J, Wu B, Liang Y, Peng Z, Fang D, Liu B, Huang H, He C, Wang C, Lu F (2010) Elevated body burdens of PBDEs, dioxin, and PCBs on thyroid hormone homeostasis at an electronic waste recycling site in China. Environ Sci Technol 44:3956–3962
Zhang M, Shi J, Meng Y, Guo W, Li H, Liu X, Zhang Y, Ge H, Yao M, Hu Q (2019) Occupational exposure characteristics and health risk of PBDEs at different domestic e-waste recycling workshops in China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:532–539
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge local hospital staff, the participants, and their families.
Funding
The work was supported by the Zhejiang Province Public Welfare Technology Application Research Project (CN) (grant number LGF18H260008) and the Jiaxing Science and Technology Bureau (CN) (grant number 2020AY30005; 2017AY33075).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
We obtained written informed consent from the participants. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Jiaxing University School of Medicine.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 634 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, L.L., Wang, M.Q., Nakayama, S.F. et al. The association between dioxins and steroid hormones in general adult males: a cross-sectional study in an e-waste region of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 26511–26519 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09086-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09086-4