Abstract
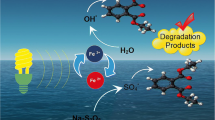
Nonylphenol ethoxylates are widely used industrial surfactants. Once released into environment compartments, these chemicals undergo degradation and generate more toxic short chain artificial compound nonylphenol (NP). The latter is a known endocrine disrupting compound and persistent micropollutant. In the present study, the performance of NP degradation in UV-induced PS, PS/Fe2+, PS/H2O2, and PS/H2O2/Fe2+ systems was examined. The effect of concentration of oxidant and activators on the efficiency of target compound decomposition was studied. The trials were conducted in ultrapure water and groundwater to assess the influence of matrix composition. The obtained results indicated that NP degradation by all the systems studied followed a pseudo-first-order kinetics. The application of UV-activated PS at lower concentrations of the oxidant improved NP oxidation in both water matrices. The addition of iron activator at a cost-effective concentration showed slight improvement in the studied PS-based systems. The application of UV-induced dual oxidant PS/H2O2 system demonstrated promising results in NP oxidation. In turn, the addition of Fe2+ to the UV/PS/H2O2 system accelerated the target compound oxidation at an optimized dose of iron activator. The radicals scavenging studies indicated that HO• was the predominant radical in all UV-induced PS-based systems. The results of this research could provide significant information for the removal of NP from different water matrices by means of UV-induced persulfate-based oxidation processes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anipsitakis GP, Dionysiou DD (2004) Radical generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants. Environ Sci Technol 38:3705–3712. https://doi.org/10.1021/es035121o
Babuponnusami A, Muthukumar K (2014) A review on Fenton and improvements to the Fenton process for wastewater treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 2:557–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.10.011
Barrera-Díaz CE, Frontana-Uribe BA, Rodríguez-Peña M, Gomez-Palma JC, Bilyeu B (2018) Integrated advanced oxidation process, ozonation-electrodegradation treatments, for nonylphenol removal in batch and continuous reactor. Catal Today 305:108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2017.09.003
Bertanza G, Pedrazzani R, Dal Grande M, Papa M, Zambarda V, Montani C, Steimberg N, Mazzoleni G, Di Lorenzo D (2011) Effect of biological and chemical oxidation on the removal of estrogenic compounds (NP and BPA) from wastewater: an integrated assessment procedure. Water Res 45:2473–2484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.01.026
Chu W, Wang YR, Leung HF (2011) Synergy of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in UV/S2O82−/H2O2 oxidation of iodinated X-ray contrast medium iopromide. Chem Eng J 178:154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.10.033
Dulov A, Dulova N, Trapido M (2013) Photochemical degradation of nonylphenol in aqueous solution: the impact of pH and hydroxyl radical promoters. J Environ Sci 25:1326–1330. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60205-8
Dulova N, Trapido M (2011) Application of Fenton’s reaction for food-processing wastewater treatment. J Adv Oxid Technol 14:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1515/jaots-2011-0101
Eisenberg G (1943) Colorimetric determination of hydrogen peroxide. Ind Eng Chem Anal Ed 15:327–328. https://doi.org/10.1021/i560117a011
ElShafei GMS, Yehia FZ, Eshaq G, ElMetwally AE (2017) Enhanced degradation of nonylphenol at neutral pH by ultrasonic assisted- heterogeneous Fenton using nano zero valent metals. Sep Purif Technol 178:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.01.028
Fang G-D, Dionysiou DD, Wang Y, Al-Abed SR, Zhou D-M (2012) Sulfate radical-based degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls: effects of chloride ion and reaction kinetics. J Hazard Mater 227-228:394–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.05.074
Frontistis Z (2019) Degradation of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug piroxicam from environmental matrices with UV-activated persulfate. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 378:17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.04.016
Giger W, Brunner PH, Schaffner C (1984) 4-Nonylphenol in sewage sludge: accumulation of toxic metabolites from nonionic surfactants. Science 225:623–625. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.6740328
Guenther K, Heinke V, Thiele B, Kleist E, Prast H, Raecker T (2002) Endocrine disrupting nonylphenols are ubiquitous in food. Environ Sci Technol 36:1676–1680. https://doi.org/10.1021/es010199v
Hesselsøe M, Jensen D, Skals K, Olesen T, Moldrup P, Roslev P, Mortensen GK, Henriksen K (2001) Degradation of 4-nonylphenol in homogeneous and nonhomogeneous mixtures of soil and sewage sludge. Environ Sci Technol 35:3695–3700. https://doi.org/10.1021/es010024l
Hori H, Yamamoto A, Hayakawa E, Taniyasu S, Yamashita N, Kutsuna S, Kiatagawa H, Arakawa R (2005) Efficient decomposition of environmentally persistent perfluorocarboxylic acids by use of persulfate as a photochemical oxidant. Environ Sci Technol 39:2383–2388. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0484754
Hu J, Wang C, Ye Z, Dong H, Li M, Chen J, Qiang Z (2019) Degradation of iodinated disinfection byproducts by VUV/UV process based on a mini-fluidic VUV/UV photoreaction system. Water Res 158:417–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.03.056
Hua Z, Kong X, Hou S, Zou S, Xu X, Huang H, Fang J (2019) DBP alteration from NOM and model compounds after UV/persulfate treatment with post chlorination. Water Res 158:237–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.04.030
Ince NH, Gültekin I, Tezcanli-Güyer G (2009) Sonochemical destruction of nonylphenol: effects of pH and hydroxyl radical scavengers. J Hazard Mater 172:739–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.058
Karci A, Arslan-Alaton I, Bekbolet M (2013) Oxidation of nonylphenol ethoxylates in aqueous solution by UV-C photolysis, H2O2/UV-C, Fenton and photo-Fenton processes: are these processes toxicologically safe? Water Sci Technol 68:1801–1809. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2013.422
Kim J, Korshin G, Velichenko A (2005) Comparative study of electrochemical degradation and ozonation of nonylphenol. Water Res 39:2527–2534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.04.070
Kulik N, Panova Y, Trapido M (2007) The Fenton chemistry and its combination with coagulation for treatment of dye solutions. Sep Sci Technol 42:1521–1534. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390701290185
Kümmerer K (2009) The presence of pharmaceuticals in the environment due to human use–present knowledge and future challenges. J Environ Manag 90:2354–2366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.01.023
Lee P-C, Lee W (1996) In vivo estrogenic action of nonylphenol in immature female rats. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 57:341–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001289900196
Liang C, Bruell CJ, Marley MC, Sperry KL (2004) Persulfate oxidation for in situ remediation of TCE. I. Activated by ferrous ion with and without a persulfate–thiosulfate redox couple. Chemosphere 55:1213–1223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.01.029
Liang C, Huang C-F, Mohanty N, Kurakalva RM (2008) A rapid spectrophotometric determination of persulfate anion in ISCO. Chemosphere 73:1540–1543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.08.043
Lin CK, Bashir MJK, Abu Amr SS, Sim LC (2016) Post-treatment of palm oil mill effluent (POME) using combined persulphate with hydrogen peroxide (S2O82−/H2O2) oxidation. Water Sci Technol 74:2675–2682. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.458
Litter IM, Quici N (2010) Photochemical advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment. Recent Patents Eng 4:217–241. https://doi.org/10.2174/187221210794578574
Liu X, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Luo L, Yang Y, Huang H, Peng H, Tang L, Mu Y (2018) Insight into electro-Fenton and photo-Fenton for the degradation of antibiotics: mechanism study and research gaps. Chem Eng J 347:379–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.04.142
Loyo-Rosales JE, Rice CP, Torrents A (2010) Fate and distribution of the octyl- and nonylphenol ethoxylates and some carboxylated transformation products in the Back River, Maryland. J Environ Monit 12:614–621. https://doi.org/10.1039/B913229E
Lutze HV, Kerlin N, Schmidt TC (2015) Sulfate radical-based water treatment in presence of chloride: formation of chlorate, inter-conversion of sulfate radicals into hydroxyl radicals and influence of bicarbonate. Water Res 72:349–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.006
Matzek LW, Carter KE (2016) Activated persulfate for organic chemical degradation: a review. Chemosphere 151:178–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.055
McKay G, Couch KD, Mezyk SP, Rosario-Ortiz FL (2016) Investigation of the coupled effects of molecular weight and charge-transfer interactions on the optical and photochemical properties of dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 50:8093–8102. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02109
Messele SA, Stüber F, Bengoa C, Fortuny A, Fabregat A, Font J (2012) Phenol degradation by heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction using Fe supported over activated carbon. Procedia Eng 42:1373–1377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2012.07.529
Mosteo R, Miguel N, Ormad Maria P, Ovelleiro JL (2010) Effect of advanced oxidation processes on nonylphenol removal with respect to chlorination in drinking water treatment. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 10:51–57. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2010.726
Naya S, Nikawa T, Kimura K, Tada H (2013) Rapid and complete removal of nonylphenol by gold nanoparticle/rutile titanium(IV) oxide plasmon photocatalyst. ACS Catal 3:903–907. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs400169u
Pignatello JJ, Oliveros E, MacKay A (2006) Advanced oxidation processes for organic contaminant destruction based on the Fenton reaction and related chemistry. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 36:1–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380500326564
Takdastan A, Kakavandi B, Azizi M, Golshan M (2018) Efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate by using ferroferric oxide supported on carbon/UV/US system: a new approach into catalytic degradation of bisphenol A. Chem Eng J 331:729–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.021
Vicente F, Santos A, Romero A, Rodriguez S (2011) Kinetic study of diuron oxidation and mineralization by persulphate: effects of temperature, oxidant concentration and iron dosage method. Chem Eng J 170:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.03.042
Waclawek S, Lutze HV, Grübel K, Padil VVT, Černík M, Dionysiou DD (2017) Chemistry of persulfates in water and wastewater treatment: a review. Chem Eng J 330:44–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.132
Waldemer RH, Tratnyek PG, Johnson RL, Nurmi JT (2007) Oxidation of chlorinated ethenes by heat-activated persulfate: kinetics and products. Environ Sci Technol 41:1010–1015. https://doi.org/10.1021/es062237m
Wu X, Gu X, Lu S, Xu M, Zang X, Miao Z, Qiu Z, Sui Q (2014) Degradation of trichloroethylene in aqueous solution by persulfate activated with citric acid chelated ferrous ion. Chem Eng J 255:585–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.06.085
Yim B, Yoo Y, Maeda Y (2003) Sonolysis of alkylphenols in aqueous solution with Fe(II) and Fe(III). Chemosphere 50:1015–1023. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00665-3
Ying G-G, Williams B, Kookana R (2002) Environmental fate of alkylphenols and alkylphenol ethoxylates—a review. Environ Int 28:215–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00017-X
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank M.Sc. Maria Martšenko and M.Sc. Svetlana Puustusmaa for their assistance in the experiments.
Funding
The financial support was provided by the Institutional Development Program of TUT for 2016-2022, project 2014-2020.4.01.16-0032, from EU Regional Development Fund and the Estonian Research Council grant PRG776.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1018 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, B., Kattel, E. & Dulova, N. Insights into nonylphenol degradation by UV-activated persulfate and persulfate/hydrogen peroxide systems in aqueous matrices: a comparative study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 22499–22510 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08886-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08886-y