Abstract
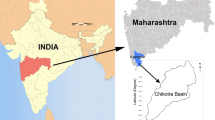
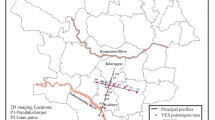
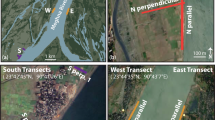
Hydrogeological active zones found in mine waste (tailings) dumping sites are a major source of concern that threatens the safety of the environment and groundwater, especially in karstic areas. Therefore, detecting and identifying these regions correctly will help in selecting the appropriate sites for tailings disposal and avoid consequential environmental problems. In this study, electrical resistivity imaging (ERI) surveys with high-resolution data were carried out to detect hydrogeological active zones in an area proposed as a settling pond for mining tailings accumulated from El Mochito mine property, located in the north-western section of Honduras. Two-dimensional (2-D) inversion results of thirty-four survey lines revealed several zones of low resistivity. These zones indicate water-/clay-bearing regions that are structurally weak. However, some survey lines, the limestone beneath the surface is entirely compacted; as such, it is considered to be an ideal site for tailings pond construction. In addition, on the eastern side of the valley, there is a large chunk limestone layer that is compacted and can be considered for tailings pond construction. The ERI method provided insight and developed an informative subsurface map to detect the hydrogeological active zones, thus proving it as a beneficial tool used for selecting disposal sites for mining tailings in karstic areas.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed AM, Sulaiman WN (2001) Evaluation of groundwater and soil pollution in a landfill area using electrical resistivity imaging survey. Environ Manag 28:655–663
Ault KM (2004) Sulfur and lead isotope study of the El Mochito Zn-Pb-Ag deposit. Econ Geol 99:1223–1231
Bakalowicz M (2005) Karst groundwater: a challenge for new resources. Hydrogeol J 13:148–160
Bengtsson L, Bendz D, Hogland W, Rosqvist H, Åkesson M (1994) Water balance for landfills of different age. J Hydrol 158:203–217
Binley, A., and A. Kemna, 2005. DC resistivity and induced polarization methods, in Hydrogeophysics, Springer, 129–156
Bundschuh J, Alvarado GE (2012) Central America, two volume set: geology, Resources and Hazards. CRC Press
Calo F, Parise M (2009) Waste management and problems of groundwater pollution in karst environments in the context of a post-conflict scenario: the case of Mostar (Bosnia Herzegovina). Habitat Int 33:63–72
Caputo R, Piscitelli S, Oliveto A, Rizzo E, Lapenna V (2003) The use of electrical resistivity tomographies in active tectonics: examples from the Tyrnavos Basin, Greece. J Geodyn 36:19–35
Cardarelli E, Cercato M, Cerreto A, Di Filippo G (2010) Electrical resistivity and seismic refraction tomography to detect buried cavities. Geophys Prospect 58:685–695
Cardona A, Gutierrez-Ojeda C, Martinez-Morales M, Ortiz-Flores G, González-Hita L (2018) Hydrogeochemical characterization and evolution of a regional karst aquifer in the Cuatrociénegas area, Mexico. Environ Earth Sci 77:785
Chalikakis K, Plagnes V, Guerin R, Valois R, Bosch FP (2011) Contribution of geophysical methods to karst-system exploration: an overview. Hydrogeol J 19:1169
Chambers JE, Kuras O, Meldrum PI, Ogilvy RD, Hollands J (2006) Electrical resistivity tomography applied to geologic, hydrogeologic, and engineering investigations at a former waste-disposal site. Geophysics 71:B231–B239
Cunningham, C. G., 1984. Earth and water resources and hazards in Central America: US Department of the Interior, Geological Survey
Cushing, M., A. Revil, C. Gélis, D. Jougnot, F. Lemeille, J. Cabrera, A. De Hoyos, and M. Rocher, 2008. Resistivity survey aiming at identifying hydrogeologically active zones in limestone and clay formations: application to the Tournemire Experimental Station (Aveyron, France). 3rd AMIGO workshop, 15–18
Dobrin, M. B., and C. H. Savit, 1960. Introduction to geophysical prospecting: McGraw-hill New York
Drahor MG, Göktürkler G, Berge MA, Kurtulmucs TÖ (2006) Application of electrical resistivity tomography technique for investigation of landslides: a case from Turkey. Environ Geol 50:147–155
Eissa R, Cassidy N, Pringle J, Stimpson I (2019) Electrical resistivity tomography array comparisons to detect cleared-wall foundations in brownfield sites. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol qjegh2018-192
Éric, V., M. P. Cullen, and D. G. Feasby, 2018. NI 43–101 technical report amended preliminary economic assessment for the optimization and expansion of the El Mochito mine
Finch RC (1981) Mesozoic stratigraphy of Central Honduras. AAPG Bull 65:1320–1333
Ford D, Williams PD (2013) Karst hydrogeology and geomorphology. Wiley
Foster, S., R. Hirata, D. Gomes, M. D’Elia, and M. Paris, 2002. Groundwater quality protection: a guide for water service companies, Municipal Authorities and Environment Agencies: The World Bank
Frid V, Liskevich G, Doudkinski D, Korostishevsky N (2008) Evaluation of landfill disposal boundary by means of electrical resistivity imaging. Environ Geol 53:1503–1508
Gao H-Y, Xu Z-M, Wang K, Ren Z, Yang K, Tang Y-J, Tian L, Chen J-P (2019) Evaluation of the impact of karst depression-type impoundments on the underlying karst water systems in the Gejiu mining district, southern Yunnan, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ:1–16
Garcia GPB, Grohmann CH (2019) DEM-based geomorphological mapping and landforms characterization of a tropical karst environment in southeastern Brazil. J S Am Earth Sci 93:14–22
Gélis C, Revil A, Cushing ME, Jougnot D, Lemeille F, Cabrera J, De Hoyos A, Rocher M (2010) Potential of electrical resistivity tomography to detect fault zones in limestone and argillaceous formations in the experimental platform of Tournemire, France. Pure Appl Geophys 167:1405–1418
Georgaki I, Soupios P, Sakkas N, Ververidis F, Trantas E, Vallianatos F, Manios T (2008) Evaluating the use of electrical resistivity imaging technique for improving CH4 and CO2 emission rate estimations in landfills. Sci Total Environ 389:522–531
Gogu RC, Dassargues A (2000) Current trends and future challenges in groundwater vulnerability assessment using overlay and index methods. Environ Geol 39:549–559
Gose WA, Finch RC (1992) Stratigraphic implications of palaeomagnetic data from Honduras. Geophys J Int 108:855–864
Greve AK, Acworth RI, Kelly BFJ (2011) 3D cross-hole resistivity tomography to monitor water percolation during irrigation on cracking soil. Soil Res 49:661–669
Gutiérrez F, Parise M, De Waele J, Jourde H (2014) A review on natural and human-induced geohazards and impacts in karst. Earth Sci Rev 138:61–88
Han G, Liu C-Q (2004) Water geochemistry controlled by carbonate dissolution: a study of the river waters draining karst-dominated terrain, Guizhou Province, China. Chem Geol 204:1–21
Hauck, C., C. Kneisel, And others, 2008. Applied Geophysics in Periglacial Environments: Cambridge University Press
Heng, M., L. Geotomo, and M. H. Loke, 2016. Least-squares Deconvolution of apparent resistivity Pseudosections
Keller, G. V., and F. C. Frischknecht, 1966. Electrical methods in geophysical prospecting
Kemna A, Binley A, Ramirez A, Daily W (2000) Complex resistivity tomography for environmental applications. Chem Eng J 77:11–18
Kim J-H, Supper R, Tsourlos P, Yi M-J (2013) Four-dimensional inversion of resistivity monitoring data through L p norm minimizations. Geophys J Int 195:1640–1656
Kumar A, Yang T, Sharma MP (2019) Greenhouse gas measurement from Chinese freshwater bodies: a review. J Clean Prod 233:368–378
Leney GW (1966) Field studies in iron ore geophysics. Mining Geophys 1:391
Li Y, Oldenburg DW (2000) 3-D inversion of induced polarization data. Geophysics 65:1931–1945
Li Z, Xu X, Xu C, Liu M, Wang K (2018) Dam construction impacts on multiscale characterization of sediment discharge in two typical karst watersheds of Southwest China. J Hydrol 558:42–54
Loke MH, Chambers JE, Rucker DF, Kuras O, Wilkinson PB (2013) Recent developments in the direct-current geoelectrical imaging method. J Appl Geophys 95:135–156
Maillot EE, Sumner JS (1966) Electrical properties of porphyry deposits at Ajo, Morenci, and Bisbee, Arizona. Mining Geophys 1:273–287
Martinez J, Benavente J, Garcia-Aróstegui JL, Hidalgo MC, Rey J (2009) Contribution of electrical resistivity tomography to the study of detrital aquifers affected by seawater intrusion--extrusion effects: the river Vélez delta (Vélez-Málaga, southern Spain). Eng Geol 108:161–168
Matias MS, da Silva MM, Ferreira P, Ramalho E (1994) A geophysical and hydrogeological study of aquifers contamination by a landfill. J Appl Geophys 32:155–162
Milanovic P (2002) The environmental impacts of human activities and engineering constructions in karst regions. Episodes 25:13–21
Milanović P, Maksimovich N, Meshcheriakova O (2019) Characterization of surface and underground karst features, in dams and reservoirs in evaporites. Springer:35–51
Morales T, Uriarte JA, Angulo B, Olazar M, Arandes JM, Antigüedad I (2018) Characterization of flow and transport dynamics in karst aquifers by analyzing tracer test results in conduits and recharge areas (the Egino massif, Basque Country, Spain): environmental and management implications. Environ Earth Sci 77:291
Neyamadpour A, Wan Abdullah WAT, Taib S, Neyamadpour B (2010) Comparison of Wenner and dipole--dipole arrays in the study of an underground three-dimensional cavity. J Geophys Eng 7:30–40
Oldenborger GA, Routh PS, Knoll MD (2005) Sensitivity of electrical resistivity tomography data to electrode position errors. Geophys J Int 163:1–9
Oldenburg DW, Li Y (1994) Inversion of induced polarization data, vol 59, pp 1327–1341
Oldenburg DW, McGillivray PR, Ellis RG (1993) Generalized subspace methods for large-scale inverse problems. Geophys J Int 114:12–20
Ortoleva, P., 2002. Methods and systems for simulation-enhanced fracture detections in sedimentary basins
Qian, W., 2007. Borehole resistivity tomography for mineral exploration. 69th EAGE conference and exhibition incorporating 2007
Qian, W., B. Milkereit, G. McDowell, K. Stevens, and S. Halladay, 2007. Borehole resistivity logging and tomography for mineral exploration. Proceedings of exploration 07: fifth decennial international conference on mineral exploration, 1115–1118
Rusjan S, Sapač K, Petrič M, Lojen S, Bezak N (2019) Identifying the hydrological behavior of a complex karst system using stable isotopes. J Hydrol 577:123956
Samson IM, Williams-Jones AE, Ault KM, Gagnon JE, Fryer BJ (2008) Source of fluids forming distal Zn-Pb-Ag skarns: evidence from laser ablation--inductively coupled plasma--mass spectrometry analysis of fluid inclusions from El Mochito, Honduras. Geology 36:947–950
Schwartz FW, McClymont GL (1977) Applications of surface resistivity methods. Groundwater 15:197–202
Slater LD, Lesmes D (2002) IP interpretation in environmental investigations. Geophysics 67:77–88
Slob E, Sato M, Olhoeft G (2010) Surface and borehole ground-penetrating-radar developments. Geophysics 75:75A103–75A120
Soupios P, Papadopoulos I, Kouli M, Georgaki I, Vallianatos F, Kokkinou E (2007) Investigation of waste disposal areas using electrical methods: a case study from Chania, Crete, Greece. Environ Geol 51:1249–1261
Storz H, Storz W, Jacobs F (2000) Electrical resistivity tomography to investigate geological structures of the earth’s upper crust. Geophys Prospect 48:455–471
Sudha K, Israil M, Mittal S, Rai J (2009) Soil characterization using electrical resistivity tomography and geotechnical investigations. J Appl Geophys 67:74–79
Telford WM, Telford WM, Geldart LP, Sheriff RE, Sheriff RE (1990) Applied geophysics. Cambridge university press
Urish DW (1983) The practical application of surface electrical resistivity to detection of ground-water pollution. Groundwater 21:144–152
White WB (2007) A brief history of karst hydrogeology: contributions of the NSS. J Cave Karst Stud 69:13–26
Zhou W, Beck BF, Stephenson JB (2000) Reliability of dipole-dipole electrical resistivity tomography for defining depth to bedrock in covered karst terranes. Environ Geol 39:760–766
Zhou QY, Shimada J, Sato A (2001) Three-dimensional spatial and temporal monitoring of soil water content using electrical resistivity tomography. Water Resour Res 37:273–285
Zhou W, Beck BF, Adams AL (2002) Effective electrode array in mapping karst hazards in electrical resistivity tomography. Environ Geol 42:922–928
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Honduras Mining Company for permission to publish.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, M.A., Sun, S., Qian, W. et al. Electrical resistivity imaging for detection of hydrogeological active zones in karst areas to identify the site of mining waste disposal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 22486–22498 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08738-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08738-9