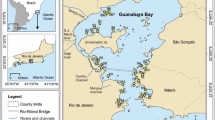
Abstract
During the last few decades, sedimentary carbons gain great concerns of research interest among the scientific committee worldwide due to their adverse impact on aquatic chemistry, ecology, and hence human health along with global climate change. In the present study, we investigated the spatial distribution of mass concentration of sedimentary carbon (viz. black carbon: BC, and its components, char and soot) along with their burial fluxes in the surface sediments of the South Yellow Sea (SYS). The concentration of sedimentary carbon is measured by using an emerging method of thermal/optical reflectance. The observed BC concentration is found in the range of 0.02–1.02 mg g−1 with a mean value of 0.49 ± 0.26 mg g−1. The mean burial fluxes of BC, char, and soot also have a similar spatial variation to their concentration with the mean value along with relative standard deviation (in bracket) 22.43 ± 12.49 (~ 56%), 5.90 ± 3.99 (~ 68%), and 16.53 ± 10.67 (65%), respectively. Relatively lower value of char/soot ratio, i.e., 0.48 ± 0.22, indicates the dominance of soot in surface sediments that could be mainly derived from the fossil fuel combustion which is further confirmed from emission inventory data suggesting maximum contribution, i.e., ~ 66–80%, of the total BC emission emitted from residential and industrial emission sources. The back trajectories analysis revealed a significant impact of long-range transportation on BC concentration in the surface sediments of SYS. Further study of BC concentrations in sea sediments and their interaction with other organic/inorganic compounds in continental shelves is highly needed for a better understanding of the global carbon cycle.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali U, Syed JH, Junwen L, Sánchez-García L, Malik RN, Chaudhry MJI, Arshad M, Li J, Zhang G, Jones KC (2014) Assessing the relationship and influence of black carbon on distribution status of organo-chlorines in the coastal sediments from Pakistan. Environ Pollut 190:82–90
Bahadur R, Praveen PS, Xu Y, Ramanathan V (2012) Solar absorption by elemental and brown carbon determined from spectral observations. PNAS 109(43):17366–17371
Bao K, Shen J, Wang G, Gao C (2015) Anthropogenic black carbon emission increase during the last 150 years at coastal Jiangsu, China. PLoS One 10:0129680
Bhardwaj P, Ki SJ, Kim YH, Woo JH, Song CK, Park SY, Song CH (2019) Recent changes of trans-boundary air pollution over the Yellow Sea: implications for future air quality in South Korea. Environ Pollut 247:401–409
Bond TC, Doherty SJ, Fahey DW, Forster PM, Berntsen T, DeAngelo BJ, Flanner MG, Ghan S, Karcher B, Koch D, Kinne S, Kondo Y, Quinn PK, Sarofim MF, Schultz MG, Schulz M, Venkataraman C, Zhang H, Zhang S, Bellouin N, Guttikunda SK, Hopke PK, Jacobson MZ, Kaiser JW, Klimont Z, Lohmann U, Schwarz JP, Shindell D, Storelvmo T, Warren SG, Zender CS (2013) Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: a scientific assessment. J Geophys Res Atmos 118:5380–5552
Boonyatumanond R, Wattayakorn G, Togo A, Takada H (2006) Distribution and origins of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in riverine, estuarine, and marine sediments in Thailand. Mar Pollut Bull 52:942–956
Buchard V, Randles C, Da Silva A, Darmenov A, Colarco P, Govindaraju R, Ferrare R, Hair J, Beyersdorf A, Ziemba L (2017) The MERRA-2 aerosol reanalysis, 1980 onward. Part II: evaluation and case studies. J Clim 30:6851–6872
Cao G, Zhang X, Zheng F (2006) Inventory of black carbon and organic carbon emissions from China. Atmos Environ 40(34):6516–6527
Chan CK and Yao X (2008) Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos Environ 42(1):1–42
Chen S, Russell LM, Cappa CD, Zhang X, Kleeman MJ, Kumar A, Liu D, Ramanathan V (2019) Comparing black and brown carbon absorption from AERONET and surface measurements at wintertime Fresno. Atmos Environ 199:164–176
Cong Z, Kang S, Gao S, Zhang Y, Li Q, Kawamura K (2013) Historical trends of atmospheric black carbon on Tibetan Plateau as reconstructed from a 150-year lake sediment record. Environ Sci Technol 47(6):2579–2586
Coppola AI, Ziolkowski LA, Masiello CA, Druffel ERM (2014) Aged black carbon in marine sediments and sinking particles. Geophys Res Lett 41:2427–2433
Draxler RR, Rolph GD (2003) HYSPLIT (HYbrid single-particle Lagrangian integrated trajectory). NOAA Air Resources Laboratory, College Park, MD
Fang, Y., Chen, Y., Hu, L., Tian, C., Luo, Y., Li, J., Zhang, G., Zheng, M., Lin, T. (2019) Large-river dominated black carbon flux and budget: a case study of the estuarine-inner shelf of East China Sea, China. Sci. Total Environ 651: 2489–2496
Fang Y, Chen Y, Tian C, Wang X, Lin T, Hu L et al (2018) Cycling and budgets of organic and black carbon in coastal Bohai Sea, China: impacts of natural and anthropogenic perturbations. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 32:971–986
Fang Y, Chen Y, Tian C, Lin T, Hu L, Li J, Zhang G (2016) Application of PMF receptor model merging with PAHs signatures for source apportionment of black carbon in the continental shelf surface sediments of the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China. J Geophys Res Oceans 121:1346–1359
Fang, Y., Y. Chen, C. Tian, T. Lin, L. Hu, G. Huang, J. Tang, J. Li, and G. Zhang (2015) Flux and budget of BC in the continental shelf seas adjacent to Chinese high BC emission source regions, Glob Biogeochem. Cycles 29: 957–972
Fontela M, Francés G, Quintana B, Álvarez-Fernández MJ, Nombela MA, Alejo I, Pedrosa MC, Péreza FF (2019) Dating the Anthropocene in deep-sea sediments: how much carbon is buried in the Irminger Basin? Glob Planet Chang 175:92–102
Gunsch MJ, Kirpes RM, Kolesar KR, Barrett TE, China S, Sheesley RJ, Laskin A, Wiedensohler A, Tuch T, Pratt KA (2017) Contributions of transported Prudhoe Bay oil field emissions to the aerosol population in Utqiaġvik. Alaska Atmos Chem Phys 17:10879–10892
Gustafsson Ö, Gschwend PM (1998) The flux of black carbon to surface sediments on the New England Continental Shelf. Geochim Cosmo him Acta 62(3):465–472
Han YM, Cao JJ, Yan BZ, Kenna TC, Jin ZD, Cheng Y, Chow JC, An ZS (2011) Comparison of elemental carbon in lake sediments measured by three different methods and 150-year pollution history in Eastern China. Environ Sci Technol 45(12):5287–5293
Han YM, Cao JJ, An ZS, Chow JC, Watson JG, Jin ZD, Fung K, Liu SX (2007) Evaluation of the thermal/optical reflectance method for quantification of elemental carbon in sediments. Chemosphere 69(4):526–533
Han YM, Cao JJ, Lee SC, Ho KF, An ZS (2010) Different characteristics of char and soot in the atmosphere and their ratio as an indicator for source identification in Xi’an, China. Atmos Chem Phys 10:595–607
Han YM, Wei C, Bandowe BAM, Wilcke W, Cao JJ, Xu BQ, Gao SP, Tie XX, Li GH, Jin ZD, An ZS (2015) Elemental carbon and polycyclic aromatic compounds in a 150-year sediment Core from Lake Qinghai, Tibetan Plateau, China: influence of regional and local sources and transport pathways. Environ Sci Technol 49:4176–4183
Hu L, Guo Z, Feng J, Yang Z, Fang M (2009) Distributions and sources of bulk organic matter and aliphatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of the Bohai Sea. China Mar Chem 113(3–4):197–211
Hu L, Shi X, Bai Y, Fang Y, Chen Y, Qiao S, Liu S, Yang G, Kornkanitnan N, Khokiattiwong S (2016) Distribution, input pathway and mass inventory of black carbon in sediments of the Gulf of Thailand, SE Asia. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 170:10–19
Huang L, Zhang J, Wu Y, Wang J (2016) Distribution and preservation of black carbon in the East China Sea sediments: perspectives on carbon cycling at continental margins. Deep-Sea Research II 124:43–52
Hung CC, Gong GC, Ko FC, Chen HY, Hsu ML, Wu JM, Peng SC, Nan FH, Yeager KM, Santschi PH (2010) Relationships between persistent organic pollutants and carbonaceous materials in aquatic sediments of Taiwan. Mar Pollut Bull 60(7):1010–1017
Hung CC, Gong GC, Ko FC, Lee HJ, Chen HY, Wu JM, Hsu ML, Peng SC, Nan FH, Santschi PH (2011) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of the East China Sea and their relationship with carbonaceous materials. Mar Pollut Bull 63(5–12):464–470
Jacbson MZ (2001) Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nature 409:695–697
Jiang XH, Chen YJ, Tang JH, Huang GP, Liu DY, Li J, Zhang G (2010) The distribution of black carbon in the surface sediments of coastal zone, Bohai Bay [in Chinese]. Ecol Environ Sci 19(7):1617–1621
Jing A, Zhu B, Wang H, Yu X, An J, Kang H (2019) Source apportionment of black carbon in different seasons in the northern suburb of Nanjing, China. Atmos Environ 201:190–200
Justice CO, Giglio L, Korontzi S, Owens J, Morisette J, Roy D, Descloitres J, Alleaume S, Petitcolin F, Kaufman YJ (2002) The MODIS fire products. Remote Sens Environ 83:244–262
Lelieveld J, Evans JS, Fnais M, Giannadaki D, Pozzer A (2015) The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 525:367–371
Li FY, Li XG, Song JM, Wang GZ, Cheng P, Gao S (2006) Sediment flux and source in northern Yellow Sea by 210Pb technique. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 24(3):255–263
Li Y, Meng J, Liu J, Xu Y, Guan D, Tao W, Huang Y, Tao S (2016) Inter-provincial reliance for improving air quality in China: a case study on black carbon aerosol. Environ. Sci Technol 50: 4118–4126
Lin H, Wang X, Gong P, Ren J, Wang C, Yuan X, Wang L, Yao T (2017) The influence of climate change on the accumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, black carbon and mercury in a shrinking remote lake of the southern Tibetan Plateau. Sci Total Environ 601:1814
Liu K, Wang F, Li J, Tiwari S, Chen B (2019) Assessment of trends and emission sources of heavy metals from the soil sediments near the Bohai Bay. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:29095–29109
Lohmann, R., K. Bollinger, M. Cantwell, J. Feichter, I. Fischer-Bruns, and M. Zabel (2009) Fluxes of soot black carbon to South Atlantic sediments, Glob Biogeochem. Cycles, 23: GB1015, doi:https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GB003253
Lu Y, Wang Q, Zhang X, Qian Yu, Qian X (2019) China’s black carbon emission from fossil fuel consumption in 2015, 2020, and 2030. Atmos Environ 212: 201–207
Masiello C, Druffel E (1998) Black carbon in deep-sea sediments. Science 280(5371):1911–1913
Masiello CA (2004) New directions in black carbon organic geochemistry. Mar Chem 92:201–213
Meng W, Zhong Q, Chen Y, Shen H, Yun X, Smith KR, Li B, Liu J, Wang X, Ma J, Cheng H, Zeng EY, Guan D, Russell AG, Tao S (2019) Energy and air pollution benefits of household fuel policies in northern China. PNAS 116(34):16773–16780
Mitra S, Zimmerman A, Hunsinger G, Woerner W (2013) Black carbon in coastal and large river systems. In: Bianchi T, Allison M, Cai WJ (eds) Biogeochemical dynamics at major river-coastal interfaces: linkages with global change. Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, pp 200–236
Neupane B, Kang S, Chen P, Zhang Y, Ram K, Rupakheti D, Tripathee L, Sharma CM, Cong Z, Li C, Hou J, Xu M, Thapa P (2019) Historical black carbon reconstruction from the lake sediments of the Himalayan-Tibetan Plateau. Environ Sci Technol 53(10):5641–5651
Pani SK, Yang CF, Wang SH, Ogren JA, Sheridan PJ, Sheu GR, Lin NH (2019) Relationship between long-range transported atmospheric black carbon and carbon monoxide at a high-altitude background station in East Asia. Atmos Environ 210:86–99
Preston CM, Schmidt MWI (2006) Black (pyrogenic) carbon in boreal forests: a synthesis of current knowledge and uncertainties. Biogeosciences 3:397–420
Qin Y, Zheng B, Lei K, Lin T, Hu L, Guo Z (2011) Distribution and mass inventory of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediments of the south Bohai Sea. China Mar Pollut Bull 62(2):371–376
Ramanathan V, Garmichael G (2008) Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat Geosci 1:221–227
Ruppel MM, Gustafsson O., Rose NL, Pesonen A, Yang H, Weckstr € om J, € Palonen V, Oinonen MJ, Korhola A (2015). Spatial and temporal patterns in black carbon deposition to dated Fennoscandian Arctic Lake sediments from 1830 to 2010. Environ Sci Technol 49: 13954–13963
Sahu L, Kondo Y, Miyazaki Y, Pongkiatkul P, Kim Oanh N (2011) Seasonal and diurnal variations of black carbon and organic carbon aerosols in Bangkok. J Geophys Res Atmos 116:D15302. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JD015563
Sánchez-García, L., I. Cato, and Ö. Gustafsson (2012) The sequestration sink of soot black carbon in the Northern European shelf sediments, Global Biogeochem. Cycles, 26: GB1001, doi:https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GB003956
Sánchez-García L, de Andrés JR, Gélinas Y, Schmidt MWI, Louchouarn P (2013) Different pools of black carbon in sediments from the Gulf of Cádiz (SW Spain): method comparison and spatial distribution. Mar Chem 151:13–22
Sarkar C, Roy A, Chatterjee A, Ghosh SK, Raha S (2019) Factors controlling the long-term (2009–2015) trend of PM2.5 and black carbon aerosols at eastern Himalaya, India. Sci. Total Environ 656:280–296
Shindell D, Kuylenstierna JC, Vignati E, van Dingenen R, Amann M, Klimont Z, Anenberg SC, Muller N, Janssens-Maenhout G, Raes F, Schwartz J, Faluvegi G, Pozzoli L, Kupiainen K, Höglund-Isaksson L, Emberson L, Streets D, Ramanathan V, Hicks K, Oanh NT, Milly G, Williams M, Demkine V, Fowler D (2012) Simultaneously mitigating near-term climate change and improving human health and food security. Science 335:183–189
Smith DM, Griffin JJ, Goldberg ED (1973) Elemental carbon in marine sediments: a baseline for burning. Nature 241(5387):268–270
Suman DO, Kuhlbusch TAJ, Lim B (1997) Marine sediments: a reservoir for black carbon and their use as spatial and temporal records of combustion. In: Clark JS (ed) Sediment records of biomass burning and global change (NATO ASI subseries I: global environment change). Springer, Berlin, pp 271–293
Sun X, Peng Pa, Song J, Zhang G, Hu J (2008) Sedimentary record of black carbon in the Pearl River estuary and adjacent northern South China Sea. Appl Geochem 23:3464–3472
Titos G, del Águila A, Cazorla A, Lyamani H, Casquero-Vera JA, Colombi C, Cuccia E, Gianelle V, Močnik G, Alastuey A, Olmo FJ, Alados-Arboledas L (2017) Spatial and temporal variability of carbonaceous aerosols: assessing the impact of biomass burning in the urban environment. Sci Total Environ 578:613–625
Tiwari S, Kumar A, Pratap V, Singh AK (2019) Assessment of two intense dust storm characteristics over Indo – Gangetic basin and their radiative impacts: a case study. Atmos Res 210:86–99
Tiwari S, Dumka UC, Kaskaoutis DG, Ram K, Panicker AS, Srivastava MK, Tiwari S, Attri SD, Soni VK, Pandey AK (2016a) Aerosol chemical characterization and role of carbonaceous aerosol on radiative effect over Varanasi in central Indo-Gangetic Plain. Atmos Environ 125:437–449
Tiwari S, Mishra A, Singh AK (2016b) Aerosol climatology over the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea inferred from space-borne radiometers and lidar observations. Aerosol Air Qual Res 16:2855–2868
Tiwari S, Srivastava AK, Singh AK, Singh S (2015) Identification of aerosol types over indo-Gangetic Basin: implications to optical properties and associated radiative forcing. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:12246–12260
Wang, F., Feng, T., Guo, Z., Li., Y., Lin T., and Rose, N.L. (2019) Sources and dry deposition of carbonaceous aerosols over the coastal East China Sea: implications for anthropogenic pollutant pathways and deposition. Environ Pollut 245: 771–779
Wang Q, Huang RJ, Cao J, Tie X, Shen Z, Zhao Z, Han Y, Li G, Li Z, Ni H, Zhou Y, Wang M, Chen Y, Su X (2016) Contribution of regional transport to the black carbon aerosol during winter haze period in Beijing. Atmos Environ 132:11–18
Wang R, Tao S, Wang W, Liu J, Shen H, Shen G, Wang B, Liu X, Li W, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Lu Y, Chen H, Chen Y, Wang C, Zhu D, Wang X, Li B, Liu W, Ma J (2012) Black carbon emissions in China from 1949 to 2050. Environ Sci Technol 46:7595–7603
Wiedemeier DB, Hilf MD, Smittenberg RH, Haberle SG, Schmidt MWI (2013) Improved assessment of pyrogenic carbon quantity and quality in environmental samples by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1304:246–250
Wu Y, Ya M, Chen H, Li Y, Guo W, Wang X (2019) Distribution and isotopic composition of sedimentary black carbon in a subtropical estuarine-coastal region of the western Taiwan Strait: implications for tracing anthropogenic inputs. Sci. Total Environ 684:509–518
Xing R, Hanaoka T, Kanamori Y, Masui T (2018) Achieving China’s intended nationally determined contribution and its co-benefits: effects of the residential sector. J Clean Prod 172:2964–2977
Xu W, Wang F, Li J, Tian L, Jiang X, Yang J, Chen B (2017) Historical variation in black carbon deposition and sources to Northern China sediments. Chemosphere 172:242–248
Yang J, Kang S, Chen D, Ji Z, Tripathee L, Chen X, Du W, Qiu G (2019) Quantifying the contributions of various emission sources to black carbon and assessment of control strategies in western China. Atmos Res 215:78–192
Yang J, Wang W, Chen G, Bao Q, Qi Q, Zhou S (2018) Intraseasonal variation of the black carbon aerosol concentration and its impact on atmospheric circulation over the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. J Geophys Res-Atmos 123:10,881–10,894
Yin L, Du P, Zhang M, Liu M, Xu T, Song Y (2019) Estimation of emissions from biomass burning in China (2003–2017) based on MODIS fire radiative energy data. Biogeosciences 16:1629–1640
Zhang R, Wang G, Song G, Zamora ML, Qi Y, Yun L, Wang W, Min H, Yuan W (2015) Formation of urban fine particulate matter. Chem Rev 115
Zhao Y, Nielsen CP, Lei Y, McElroy MB, Hao J (2011) Quantifying the uncertainties of a bottom-up emission inventory of anthropogenic atmospheric pollutants in China. Atmos Chem Phys 11:2295–2308
Zheng G, Duan F, Ma Y, Zhang Q, Huang T, Kimoto T, Cheng Y, Su H, He K (2016) Episode-based evolution pattern analysis of haze pollution: method development and results from Beijing, China. Environ Sci Technol 50:4632–4641
Zheng H, Kong S, Wu F, Cheng Y, Niu Z, Zheng S, Yang G, Yao L, Yan Q, Wu J, Zheng M, Chen N, Xu K, Yan Y, Liu D, Zhao D, Zhao T, Bai Y, Li L, Qi S (2019) Intra-regional transport of black carbon between the south edge of the North China Plain and central China during winter haze episodes. Atmos Chem Phys 19:4499–4516
Zhu Q, Liu Y, Jia R, Hua S, Shao T, Wang B (2018) A numerical simulation study on the impact of smoke aerosols from Russian forest fires on the air pollution over Asia. Atmos Environ 182:263–274
Zhu Y, Chang R (2000) Preliminary study of the dynamic origin of the distribution pattern of bottom sediments on the continental shelves of the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 51(5):663–680
Zhuang BL, Chen HM, Li S, Wang TJ, Liu J, Zhang LJ, Liu HN, Xie M, Chen PL, Li MM, Zhao M (2019) The direct effects of black carbon aerosols from different source sectors in East Asia in summer. Clim Dyn 53:5293–5310
Zong Z, Chen Y, Tian C, Fang Y, Wang X, Huang G, Zhang F, Li J, Zhang G (2015) Radiocarbon-based impact assessment of open biomass burning on regional carbonaceous aerosols in North China. Sci Total Environ 518–519:1–7
Acknowledgments
One of the authors, Dr. Shani Tiwari, is also thankful to Shandong University, China, for the financial support under the International Postdoctoral Exchange Program. We acknowledge the use of Peking University (PKU) Inventory data, MEERA–2 reanalysis data, and National Centre for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) for synoptic meteorological data and NOAA HYSPLIT model for back trajectory analysis. We are also thankful to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions to improve the manuscript.
Funding
This research has received funding from the Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province (2017GHY215005), Laboratory for Marine Geology, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Grant No. MGQNLM-KF201703), and Taishan Scholars (No. ts201712003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gerhard Lammel
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 823 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiwari, S., Kun, L. & Chen, B. Spatial variability of sedimentary carbon in South Yellow Sea, China: impact of anthropogenic emission and long-range transportation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 23812–23823 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08686-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08686-4