Abstract
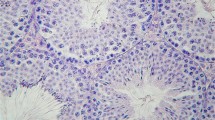
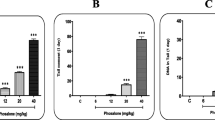
Exposure to lead (Pb) is a major risk factor in reproductive toxicity, somatic, and germ cell genotoxicity. Exposure via deteriorating Pb paints and contaminated air, soil, and water had been the primary routes. However, with increasing reports of Pb accumulation in mushrooms and other food items may increase the etiology of Pb poisoning. The study herein investigated somatic genotoxicity and reproductive abnormalities in mice fed extracts of Pb-contaminated Pleurotus ostreatus. Male mice were fed aqueous extracts of P. ostreatus cultivated in 0, 10, 20, 100, 200, 500, and 1000 mg/L of Pb-contaminated rice straw for 35 days. Testes were analyzed for Pb accumulation, histopathology and relative weight gain, caudal epididymis for abnormal sperm morphology, and bone marrow for micronucleus test. Concentration-related significant increase in Pb accumulation was observed in P. ostreatus and testes of exposed mice. Decrease testicular weight, congestion of blood vessels, necrosis, and disorganization of the seminiferous tubules were observed in treated mice. In addition, fold increase of 2.78, 3.39, 6.67, 7.21, 9.63, and 9.70 in abnormal sperm morphology in accordance with the Pb concentrations respectively, confirmed reproductive toxicity. Significant increase in micronucleated polychromatic (PCE) and normochromatic (NCE) erythrocytes and concentration-related decrease PCE-NCE ratio in the bone marrow of treated mice suggest genome instability. Pb-contaminated P. ostreatus increased somatic and germ cell genotoxicity in mice. This may predispose the mice to genetic related syndromes and reproductive syndromes. It further suggests caution in the consumption of metal laden wild mushrooms and crop plants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya UR, Rathore RM, Mishra M (2003) Role of vitamin C on lead acetate induced spermatogenesis in Swiss mice. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:9–14
Adenipekun CO, Ogunjobi AA, Ogunseye OA (2011) Management of polluted soils by a white-rot fungus: Pleurotus pulmonarius. Assumption Univ J Technol 15(1):57–61
Alemu F (2014) Cultivation of Pleurotus ostreatus on Grevillea robusta leaves at Dilla University. Ethiopia J Yeast Fungal Res 5:74–83
Ali A, Guo D, Mahar A, Wang P, Shen F, Li R, Zhang Z (2017) Mycoremediation of potentially toxic trace elements-a biological tool for soil cleanup: a review. Podosphere 27(2):205–222
Alimba CG, Aladeyelu AM, Nwabisi IA, Bakare AA (2018) Micronucleus cytome assay in the differential assessment of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of cadmium and lead in Amietophrynus regularis. EXCLI 17:89–101
Alimba CG, Bakare AA (2016) In vivo micronucleus test in the assessment of cytogenotoxicity of landfill leachates in three animal models from various ecological habitats. Ecotoxicol 25:310–319
Allam AA, Hegazy AK, Ajarem JS (2015) Assessment of heavy metals accumulation in the ecosystem and hazardous effects on the testes and embryo of wild Libyan Jird, Meriones libycus collected from petroleum oil polluted Arid region. Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3–5 September 2015. CEST2015:00235–00235
Al Othman ZA (2010) Lead contamination in selected foods from Riyadh city market and estimation of the daily intake. Mole 15:7482–7497
Anyakorah CI, Nwude D, Jinadu T (2015) Lead accumulation in oyster mushroom, Pleurotus tuber-regium (Sing) from a continuously lead contaminated soil. Mycosphere 6:145–149
Arvay J, Tomas J, Hauptvogl M, Massanyi P, Harangozo L, Toth T, Stanovic R, Bryndzova S, Bumbalova M (2015) Human exposure to heavy metals and possible public health risks via consumption of wild edible mushrooms from Slovak Paradise National Park, Slovakia. J Environ Sci Healt Part B 50:833–843
Asgher M, Bhatti HN, Ashraf M, Legge RL (2008) Recent developments in biodegradation of industrial pollutants by white rot fungi and their enzyme system. Biodegrad 19:771–783
Bartke A, Weir JA, Mathison P, Roberson C, Dalterio S (1974) Testicular function in mouse strains with different age of sexual maturation. J Hered 65:204–208
Bruggeman JE, Route WT, Redig PT, Key RL (2018) Patterns and trends in lead (Pb) concentrations in bald eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus) nestlings from the western Great Lakes region. Ecotoxicol 27(5):605–618
Cervellin G, Comelli I, Rastelli G, Sanchis-Gomar F, Negri F, De Luca C, Lippi G (2018) Epidemiology and clinics of mushroom poisoning in northern Italy: a 21-year retrospective analysis. Hum Exp Toxicol 37:697–703
Cocchi L, Vescovi L, Petrini LE, Petrini O (2006) Heavy metals in edible mushrooms in Italy. Food Chem 98(2):277–264
Damber JE, Bergh A, Daehlin L (1985) Testicular blood flow, vascular permeability, and testosterone production after stimulation of unilaterally cryptorchid adult rats with human chorionic gonadotropin. Endocrinol 117:1906–1913
FAO/WHO Standards (1976) List of maximum levels recommended for contaminants by the Joint FAO/WHO Codex Alimentarius Commission, Second Series. CACIFAL Rome 3:1–8
Gad SC (2007) Animal models in toxicology (2nd edn.). CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group 6000 Broken Sound Parkway NW, Suite 300, Boca Raton, pp: 151–217
Grzmil P, Gołas A, Muller C, Styrna J (2007) The influence of the deletion on the long arm of the Y chromosome on sperm motility in mice. Theriogenology 67:760–766
Hernberg S (2000) Lead poisoning in a historical perspective. Ame J Ind Med 38:244–254
Hirai S, Hatayama N, Naito M, Nagahori K, Kawata S, Hayashi S, Qu N, Terayama H, Shoji S, Itoh M (2017) Pathological effect of arterial ischaemia and venous congestion on rat testes. Sci Report 7:5422–5431
Isildak O, Turkekul I, Elmastas M, Tuzen M (2004) Analysis of heavy metals in some wild-grown edible mushrooms from the middle black sea region, Turkey. Food Chem 86(4):547–552
Kumar TR, Doreswamy K, Shrilatha B, Muralidhara (2002) Oxidative stress associated DNA damage in testis of mice: induction of abnormal sperms and effects on fertility. Mutat Res 513:103–111
Krishna G, Hayashi M (2000) In vivo rodent micronucleus assay: protocol, conduct and data interpretation. Mutat Res 455:155–166
Lanning L, Creasy D, Chapin R, Mann P, Barlow N, Regan K, Goodman A (2002) Recommended approaches for the evaluation of testicular and epididymal toxicity. Toxicol Pathol 30(4):507–520
Li Y, Qin J, Wei X, Li C, Wang J, Jiang M, Liang X, Xia T, Zhang Z (2016) The risk factors of child lead poisoning in China: a meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13:296–309
Llorente-Mirandes T, Llorens-Muñoz M, Funes-Collado V, Sahuquillo A, López-Sánchez JF (2016) Assessment of arsenic bioaccessibility in raw and cooked edible mushrooms by a PBET method. Food Chem 194:849–856
MacGregor JT, Heddle JA, Hite M, Margolin BH, Ramel C, Salamone MF, Tice RR, Wild D (1987) Guidelines for the conduct of micronucleus assays in mammalian bone marrow erythrocytes. Mutat Res 189:103–112
Martiniakova M, Omelka R, Jancova A, Formicki G, Stawarz R, Bauerova M (2012) Accumulation of risk elements in kidney, liver, testis, uterus and bone of free-living wild rodents from a polluted area in Slovakia. J Environ Sci Healt Part A Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Engr 47:1202–1206
Meyer PA, Brown MJ, Falk H (2008) Global approach to reducing lead exposure and poisoning. Mutat Res 659(1–2):166–175
Michelota D, Siobud E, Dore J, Viel C, Poirier F (1998) Update on metal content profiles in mushrooms - toxicological implications and tentative approach to the mechanism of bioaccumulation. Toxicon 36:1997–2012
Moszynski P (2010) Lead poisoning in Nigeria causes “unprecedented” emergency. BMJ 341:c4031
Ndimele CC, Ndimele PE, Chukwuka KS (2017) Accumulation of heavy metals by wild mushrooms in Ibadan, Nigeria. J Healt Pollut 16:26–30
Obidike IR, Ezema WS, Aka LO, Omoja VU, Odo RI, Onuoha EO, Obodoechi LO (2013) Effects of aqueous garlic (Allium sativum) extract on testicular morphology and function in lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2)-treated albino rats. Comp Clin Pathol 22:685–690
Onifade RS, Alimba CG, Adenipekun CO, Bakare AA (2016) White rot fungus (Pleurotus pulmonarius) cultivated on lead contaminated rice straw induced haematotoxicity and lead accumulation in liver and kidney of Wistar rats. J Drug Metabol Toxicol 7:210. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7609.1000210
Papanikolaou NC, Hatzidaki EG, Belivanis S, Tzanakakis GN, Tsatsakis AM (2005) Lead toxicity update. A brief review. Med Sci Monit 11:RA329–RA336
Rajeshkumar S, Li X (2018) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fish species from the Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake, China. Toxicol Rep 5:288–295
Rankin CW, Nriagu JO, Aggarwal JK, Arowolo TA, Adebayo K, Flegal AR (2005) Lead contamination in cocoa and cocoa products: isotopic evidence of global contamination. Environ Health Perspect 113:1344–1348
Sabiu S, Ajani EO, Abubakar AA, Sulyman AO, Nurain OI, Irondi AE, Quadri DF, Abubakar YA (2015) Toxicological evaluations of Stigma maydis (corn silk) aqueous extract on hematological and lipid parameters in Wistar rats. Toxicol Rep 2:638–644
Sarikurkcu C, Copur M, Yildiz D, Akata I (2011) Metal concentration of wild edible mushrooms in Soguksu National Park in Turkey. Food Chem 128(3):731–734
Shimizu N, Itoh N, Utiyama H, Wahl GM (1998) Selective entrapment of extra-chromosomally amplified DNA by nuclear budding and micronucleation during S phase. J Cell Biol 140:1307–1320
Styrna J, Kilarski W, Krzanowska H (2003) Influence of the CBA genetic background on sperm morphology and fertilization efficiency in mice with a partial Y chromosome deletion. Reproduction 126:579–588
Tapisso JT, Marques CC, da Luz MM, da Graca RM (2009) Induction of micronuclei and sister chromatid exchange in bone-marrow cells and abnormalities in sperm of Algerian mice (Mus spretus) exposed to cadmium, lead and zinc. Mutat Res 678:59–64
Thongbai B, Rapior S, Hyde KD, Wittstein K, Stadler M (2015) Hericium erinaceus, an amazing medicinal mushroom. Mycol Prog 14:91–113
Tirima S, Bartrem C, von Lindern I, von Braun M, Lind D, Anka SM, Abdullahi A (2016) Environmental remediation to address childhood lead poisoning epidemic due to artisanal gold mining in Zamfara, Nigeria. Environ Health Perspect 124:1471–1478
Tirima S, Bartrem C, von Lindern I, von Braun M, Lind D, Anka SM, Abdullahi A (2018) Food contamination as a pathway for lead exposure in children during the 2010–2013 lead poisoning epidemic in Zamfara, Nigeria. J Environ Sci 67:260–272
Toure A, Szot M, Mahadevaiah SK, Rattigan A, Ojarikre OA, Burgoyne PS (2004) A new deletion of the mouse Y chromosome long arm associated with the loss of Ssty expression, abnormal sperm development and sterility. Genetics 166:901–912
Weber P, Behr ER, Knorr CD, Vendruscolo DS, Flores EMM, Dressler VL, Baldisserotto B (2013) Metals in the water, sediment, and tissues of two fish species from different trophic levels in a subtropical Brazilian river. Microchem J 106:61–66
Wurgler FE, Kramers PGN (1992) Environmental effects of genotoxins (eco-genotoxicology). Mutagenesis 7(5):321–327
Wyrobek AJ, Bruce WR (1975) Chemical induction of sperm abnormalities in mice (25 chemicals/mutagens/teratogens/carcinogens). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 72:4425–4429
Wyrobek AJ, Gordon LA, Burkhart JG, Francis MW, Kapp RW Jr, Letz G, Malling HV, Topham JC, Whorton MD (1983) An evaluation of the mouse sperm morphology test and other sperm tests in nonhuman mammals: a report of the U.S. environmental protection agency Gene-Tox program. Mutat Res 115(1):1–72
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guide for care and use of laboratory animals in accordance with the US National Institute of Health (NIH Publication No. 85-23, revised in 1996) (Gad 2007) was strictly adhered.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olatunji-Ojo, A.M., Alimba, C.G., Adenipekun, C.O. et al. Experimental simulation of somatic and germ cell genotoxicity in male Mus musculus fed extracts of lead contaminated Pleurotus ostreatus (white rot fungi). Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 19754–19763 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08494-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08494-w