Abstract
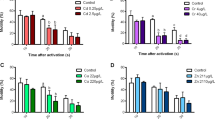
Fluoxetine (FLX) is one of the main antidepressants used worldwide. After human use, FLX enters the aquatic ecosystems, where it has commonly detected in the high ng/L concentration range. Several investigations have shown that exposure to different concentrations of FLX caused different adverse effects towards a number of aquatic species. However, the information on the onset and the relationship between molecular and behavioral FLX-induced effects remains scant. The aim of this study was to assess the effects induced by two FLX concentrations, namely 50 ng/L and 500 ng/L, on swimming activity of zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae at 96-h post-fertilization (hpf) and to investigate if such behavioral effects were related to modulation of the expression of oxidative stress-related (sod1, sod2, cat, gpxa, and gst), stress- and anxiety-related (oxtl, prl2, npy, and ucn3l) genes, and genes encoding for the transporters of the main neurotransmitters (slc6a3, slc6a4a, slc6a4b, slc6a11). Fluoxetine exposure altered the swimming behavior of larvae, as shown by the reduction of the distance traveled by treated larvae in response to an external stimulus. Such behavioral change was related, at molecular level, to an enhanced expression of sod1, cat, and gpxa, suggesting an overproduction of pro-oxidant molecules. In addition, FLX modulated the expression of oxtl, slc6a4a, slc6a4b, and slc6a11, suggesting its capability to affect anxiety- and neurotransmitter-related genes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu MS, Koakoski G, Ferreira D, Oliveira TA, Rosa JGS, Gusso D, Giacomini ACV, Piato AL, Barcellos LJG (2014) Diazepam and fluoxetine decrease the stress response in zebrafish. PLoS One 9. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0103232
Abreu MS, Giacomini ACV, Koakoski G, Oliveira TA, Gusso D, Baldisserotto B, Barcellos LJG (2015) Effects of waterborne fluoxetine on stress response and osmoregulation in zebrafish. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40:704–707
Abreu MS, Giacomini ACV, Gusso D, Rosa JGS, Koakoski G, Kalichak F, Idalêncio R, Oliveira TA, Barcellos HHA, Bonan CD, Barcellos LJG (2016) Acute exposure to waterborne psychoactive drugs attract zebrafish. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 179:37–43
AHFS (2013) AHFS Di Monographs. Drugscom http://www.drugs.com/monograph
Airhart MJ, Lee DH, Wilson TD, Miller BE, Miller MN, Skalko RG (2007) Movement disorders and neurochemical changes in zebrafish larvae after bath exposure to fluoxetine (PROZAC). Neurotoxicol Teratol 29:652–664
Al Aukidy M, Verlicchi P, Jelic A, Petrovic M, Barcelo D (2012) Monitoring the release of pharmaceutical compounds: occurrence and environmental risk assessment of two WWTP effluents and their receiving bodies in the Po Valley, Italy. Sci Total Environ 438:15–25
Barton BA (2002) Stress in fishes: a diversity of responses with particular reference to changes in circulating corticosteroids. Integr Comp Biol 42:517–525
Benton CS, Miller BH, Skwerer S, Suzuki O, Schultz LE, Cameron MD, Marron JS, Pletcher MT, Wiltshire T (2012) Evaluating genetic markers and neurobiochemical analytes for fluoxetine response using a panel of mouse inbred strains. Psychopharmacology 221:297–315
Bocquier A, Bezzou K, Nauleau S, Verger P (2008) Dispensing of anxiolytics and hypnotics in southeastern France: demographic factors and determinants of geographic variations. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 22:323–333
Braida D, Donzelli A, Martucci R, Capurro V, Busnelli M, Chini B, Sala M (2012) Neurohypophyseal hormones manipulation modulate social and anxiety related behavior in zebrafish. Psychopharmacology 220:319–330
Brooks BW (2014) Fish on Prozac (and Zoloft): ten years later. Aquat Toxicol 151:61–67
Calisto V, Domingues MRM, Esteves VI (2011) Photodegradation of psychiatric pharmaceuticals in aquatic environments — kinetics and photodegradation products. Water Res 45:6097–6106
Clements S, Schreck CB (2007) Chronic administration of fluoxetine alters locomotor behavior, but does not potentiate the locomotor stimulating effects of CRH in juvenile Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 147:43–49
Cryan JF, Sweeney FF (2011) The age of anxiety: role of animal models of anxiolytic action in drug discovery. Br J Pharmacol 164:1129–1161
Demeestere K, Petrović M, Gros M, Dewulf J, Van Langenhove H, Barceló D (2010) Trace analysis of antidepressants in environmental waters by molecularly imprinted polymer-based solid-phase extraction followed by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 396:825–837
Dulawa SC, Holick KA, Gundersen B, Hen R (2004) Effects of chronic fluoxetine in animal models of anxiety and depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1321–1330
Durant C, Christmas D, Nutt D (2010) The pharmacology of anxiety. In: Stein M, Steckler T (eds) Behavioral neurobiology of anxiety and its treatment, Curr Top Behav Neurosci, vol 2. Springer, Berlin, pp 303–330
Egan RJ, Bergner CL, Hart PC, Cachat JM, Canavello PR, Elegante MF, Elkhayat SI, Bartels BK, Tien AK, Tien DH, Mohnot S, Beeson E, Glasgow E, Amri H, Zukowska Z, Kalueff AV (2009) Understanding behavioral and physiological phenotypes of stress and anxiety in zebrafish. Behav Brain Res 205:38–44
Fong PP, Ford AT (2014) The biological effects of antidepressants on the molluscs and crustaceans: a review. Aquat Toxicol 151:4–13
Godwin J, Thompson R (2012) Nonapeptides and social behavior in fishes. Horm Behav 61:230–238
Gould GG, Brooks BW, Frazer A (2007) [3H] citalopram binding to serotonin transporter sites in minnow brains. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 101:203–210
Griebel G, Belzung C, Perrault G, Sanger DJ (2000) Differences in anxiety-related behaviours and in sensitivity to diazepam in inbred and outbred strains of mice. Psychopharmacology 148:164–170
Grohol J (2012) Top 25 Psychiatric Medication Prescriptions for 2011. Psych Central http://psychcentral.com/lib/top-25-psychiatric-medication-prescriptions-for2011
Huang GJ, Ben-David E, Tort Piella A, Edwards A, Flint J, Shifman S (2012) Neurogenomic evidence for a shared mechanism of the antidepressant effects of exercise and chronic fluoxetine in mice. PLoS One 7:e35901. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035901
Jacobson LH, Cryan JF (2010) Genetic approaches to modeling anxiety in animals. In: Stein M, Steckler T (eds) Behavioral neurobiology of anxiety and its treatment, Curr Top Behav Neurosci, vol 2. Springer, Berlin, pp 161–201
Kashiyama K, Ito C, Numata H, Goto SG (2010) Spectral sensitivity of light induced hatching and expression of genes mediating photoreception in eggs of the Asian tadpole shrimp Triops granarius. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 156:416–421
Kolpin DW, Furlong ET, Meyer MT, Thurman EM, Zaugg SD, Barber LD, Buxton HT (2002) Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in US streams, 1999-2000: a national reconnaissance. Environ Sci Technol 36:1202–1211
la Poza E, Guadalajara N, Jódar L, Merello P (2013) Modeling Spanish anxiolytic consumption: economic, demographic and behavioral influences. Math Comput Model 57:1619–1624
Landgraf R (2005) Neuropeptides in anxiety modulation. In: Holsboer F, Ströhle A (eds) Anxiety and Anxiolytic Drugs, Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, vol 169. Springer, Berlin, pp 335–369
Lee JH, Ko E, Kim YE, Min JY, Liu J, Kim Y, Shin M, Hong M, Bae H (2010) Gene expression profile analysis of genes in rat hippocampus from antidepressant treated rats using DNA microarray. BMC Neurosci 11:152
Li XM, Chlan-Fourney J, Juorio AV, Bennett VL, Shrikhande S, Bowen RC (2000) Antidepressants upregulate messenger RNA levels of the neuroprotective enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD1). J Psychiatry Neurosci 25:43–47
Lillesaar C (2011) The serotonergic system in fish. J Chem Neuroanat 4:294–308
Longone P, Di Michele F, D’Agati E, Romeo E, Pasini A, Rupprecht R (2011) Neurosteroids as neuromodulators in the treatment of anxiety disorders. Front Endocrinol 2:55
Magni S, Parolini M, Della Torre C, de Oliveira LF, Catani M, Guzzinati R, Cavazzini A, Binelli A (2017) Multi-biomarker investigation to assess toxicity induced by two antidepressants on Dreissena polymorpha. Sci Total Environ 578:452–459
Margiotta-Casaluci M, Owen SF, Cumming RI, de Polo A, Winter MJ, Panter GH, Rand-Weaver M, Sumpter JP (2014) Quantitative cross-species extrapolation between humans and fish: the case of the anti-depressant fluoxetine. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110467
Mennigen JA, Martyniuk CJ, Crump K, Xiong H, Zhao E, Popesku J, Anisman H, Cossins AR, Xia X, Trudeau VL (2008) Effects of fluoxetine on the reproductive axis of female goldfish (Carassius auratus). Physiol Genomics 35:273–282
Metcalfe CD, Chu S, Judt C, Li H, Oakes KD, Servos MR, Andrews DM (2010) Antidepressants and their metabolites in municipal wastewater, and downstream exposure in an urban watershed. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:79–89
Meyer-Lindenberg A, Domes G, Kirsch P, Heinrichs M (2011) Oxytocin and vasopressin in the human brain: social neuropeptides for translational medicine. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:524–538
Njagi J, Ball M, Best M, Wallace KN, Andreescu S (2010) Electrochemical quantification of serotonin in the live embryonic zebrafish intestine. Anal Chem 82:1822–1830
Onaka T, Takayanagi Y, Yoshida M (2012) Roles of oxytocin neurones in the control of stress, energy metabolism, and social behaviour. J Neuroendocrinol 24:587–598
Palmer PM, Wilson LR, O’Keefe P, Sheridan R, King T, Chen CY (2008) Sources of pharmaceutical pollution in the New York City watershed. Sci Total Environ 394:90–102
Park JW, Heah TP, Gouffon JS, Henry TB, Sayler GS (2012) Global gene expression in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) exposed to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (fluoxetine and sertraline) reveals unique expression profiles and potential biomarkers of exposure. Environ Pollut 167:163–170
Parker MO, Annan LV, Kanellopoulos AH, Brock AJ, Combe FJ, Baiamonte M, Teh MT, Brennan CH (2014) The utility of zebrafish to study the mechanisms by which ethanol affects social behavior and anxiety during early brain development. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 55:94–100
Parolini M, Ghilardi A, Della Torre C, Magni S, Prosperi L, Calvagno M, Del Giacco L, Binelli A (2017) Environmental concentrations of cocaine and its main metabolites modulated antioxidant response and caused cyto-genotoxic effects in zebrafish embryo cells. Environ Pollut 226:504–514
Pinna G, Costa E, Guidotti A (2004) Fluoxetine and norfluoxetine stereospecifically facilitate pentobarbital sedation by increasing neurosteroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:6222–6225
Pinna G, Costa E, Guidotti A (2006) Fluoxetine and norfluoxetine stereospecifically and selectively increase brain neurosteroid content at doses that are inactive on 5-HT reuptake. Psychopharmacology 186:362–372
Prieto MJ, Gutierrez HC, Arévalo RA, Chiaramoni NS, del Valle AS (2012) Effect of risperidone and fluoxetine on the movement and neurochemical changes of zebrafish. Open J Med Chem 2:129
Santos LHMLM, Araujo AN, Fachini A, Pena A, Delerue-Matos C, Montenegro MCBSM (2010) Ecotoxicological aspects related to the presence of pharma-ceuticals in the aquatic environment. J Hazard Mater 175:45–95
Sghendo L, Mifsud J (2012) Understanding the molecular pharmacology of the serotonergic system: using fluoxetine as a model. J Pharm Pharmacol 64:317–325
Silva BF, Jelic A, López-Serna R, Mozeto AA, Petrovic M, Barceló D (2011) Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals in surface water, suspended solids and sediments of the Ebro river basin, Spain. Chemosphere 85:1331–1339
Silva LJG, Lino CM, Meisel LM, Pena A (2012) Selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs) in the aquatic environment: an ecopharmacovigilance approach. Sci Total Environ 437:185–195
Stahl SM (1998) Mechnism of action of serotonin selective reuptake inhibitors: serotonin receptors and pathways mediate therapeutic effects and side effects. J Affect Disord 51:215–235
Styrishave B, Halling-Sørensen B, Ingerslev F (2011) Environmental risk assessment of three selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the aquatic environment: a case study including a cocktail scenario. Environ Toxicol Chem 30:254–261
Sztal TE, Ruparelia AA, Williams C, Bryson-Richardson RJ (2016) Using touch-evoked response and locomotion assays to assess muscle performance and function in zebrafish. J Vis Exp:116
Taylor S, Wakem M, Dijkman G, Alsarraj M, Nguyen M (2010) A practical approach to RT-qPCR—publishing data that conform to the MIQE guidelines. Methods 50:S1–S5
Thorsell A (2008) Central neuropeptide Y in anxiety- and stress-related behavior and in ethanol intake. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1148:136–140
Trent NL, Menard JL (2011) Infusions of neuropeptide Y into the lateral septum reduce anxiety-related behaviors in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 99:580–590
Udvardi M, Czechowski T, Scheible WR (2008) Eleven golden rules of quantitative RT-PCR. Plant Cell 20:1736–1737
Westenberg HG (2009) Recent advances in understanding and treating social anxiety disorder. CNS Spectr 14:24–33
Winder VL, Pennington PL, Hurd MW, Wirth EF (2012) Fluoxetine effects onsheepshead minnow (Cyprinodon variegatus) locomotor activity. J Environ Sci Health B 47:51–58
Wong RY, Oxendine SE, Godwin J (2013) Behavioral and neurogenomic transcriptome changes in wild-derived zebrafish with fluoxetine treatment. Genomics 14:348
Yoshida N, Maejima Y, Sedbazar U, Ando A, Kurita H, Damdindorj B, Takano E, Gantulga D, Iwasaki Y, Kurashina T, Onaka T, Dezaki K, Nakata M, Mori M, Yada T (2010) Stressor-responsive central nesfatin-1 activates corticotropin-releasing hormone, noradrenaline and serotonin neurons and evokes hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis." Aging 2: 775-784.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parolini, M., Ghilardi, A., De Felice, B. et al. Environmental concentration of fluoxetine disturbs larvae behavior and increases the defense response at molecular level in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 34943–34952 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06619-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06619-4