Abstract
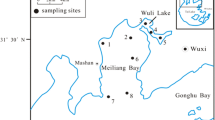
Zooplankton biomass and water environment factors in Xiaoxingkai Lake were investigated, and the correlation between biomass and water environment factors was performed using the Pearson correlation analysis and redundancy analysis (RDA). The results showed that the highest zooplankton biomass was recorded in summer and the lowest in spring. Water depth, transparency (SD), electric conductivity, and total nitrogen were the highest in spring, while temperature and total phosphorus were the highest in summer. The values of pH and turbidity were the highest in autumn, while chloride ion and chlorophyll a were the highest in winter. During the spring period, Protozoa were positively correlated with conductivity, transparency (SD), and total nitrogen. While Rotifera demonstrated a strong correlation with turbidity, pH, temperature, and total phosphorus in summer and autumn seasons, and Cladocera were correlated with water depth. There were negative correlations of chlorophyll a and chlorine on Copepoda during the winter. RDA results displayed that zooplankton had strong relationships with the physicochemical characteristics in Xiaoxingkai Lake.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen GR, Zhong P, Zhang XF, Xie YF, LI CH (2008) Zooplankton and its relationship with water quality in Huizhou West Lake. J Lake Sci 20(3):351–356 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Dana T (2001) Zooplankton diversity and physico-chemical condition of two wetlands of Jalpaiguri District. India. 2(3):576–583
Gao FJ, Lei GP, Song G, Zhou J, Du GM (2011) Study on agricultural non-point source pollution critical source area identification and control measures in Xingkai watershed. J Northeast Agric Univ 42(5):121–126 +151. (in Chinese with English abstract
Gao Y, Lai ZN, Li J, Wang C, Zeng YY, Liu QF, Yang WL (2013) Spatial pattern of zooplankton diversity in Lianjiang River, Guangdong Province, China. Biodivers Sci 21(6):699–708 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ji XY, Liu TL, Liu J, Li JM, Pan BQ (2013) Investigation and study on water quality and pollution condition in Lake Xingkai of China. Envir Moni in China 29(6):79–84 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jiang ZF, Dong CZ, Zhan PR, Zhao JW, Zhao CG, Tang FJ, Han Y (2003) The population structure of zooplankton in Daxingkai Lake. J Dalian Fish Univ 18(4):292–295 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jin XC, Tu QY (1990) Specifications for lakes eutrophication survey: 2nd edn. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. (in Chinese)
Jin P, Dai KY, Yang C, Guo M, Xu TT, Lin QW, Ma JM (2012) Community structure characteristics of zooplankton in Muye Lake and correlations between zooplankton and environmental factors. J Hydroecol 31(4):869–901 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li R, Zhang QZ, Jiang YB, Zhang L, Shao XM (2011) Species diversity of plant communities of Xingkai Lake wetlands under different levels of disturbance. Wetl Sci 9(2):179–184 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lin Q, You WH, Xu FJ, Yu QJ, Yu HG (2014) Zooplankton community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in Dishui Lake. Acta Ecol Sin 34(23):6918–6929 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu XP, Wang LQ, Zhang N, Tao XM, Ma WH (2013a) Community structure of metazoan zooplankton and its relationships with environmental factors in Qingcaosha Reservoir of Shanghai, East China. Chin J Ecol 32(5):1238–1248 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu XC, Li XP, Wang YF, Wei ZM, Cheng X, Chen XH, Wang FF, Chen WQ (2013b) Simulation of the response of eutrophic state to nutrient input in Lake Xingkai based on ecological dynamic model. J Lake Sci 25(6):862–871 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Park KS, Shin HW (2007) Studies on phyto-and-zooplankton composition and its relation to fish productivity in a west coast fish pond ecosystem. J Environ Biol 28(1):415–422
Qiu XC, Zhao HX, Sun XX (2012) Relationships between zooplankton and water environmental factors in Shahu Lake, Ningxia of Northwest China: a multivariate analysis. Chin J Ecol 31(4):896–901 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu L, Feng WS, Zhang TL, Xu H, Yu YH (2011) The annual fluctuation of zooplankton community and its relation with environmental factors in Lake Xiliang, Hubei Province. J Lake Sci 23(4):619–625 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang FY, Lv XG, Lou YJ, Lou XN (2012) Fish resources on Xingkai Lake National Nature Reserve, Heilongjiang Province, China. Chin J Zool 47(6):44–53 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yu SL, Li XJ, Li XY, Wen BL (2013) Evaluation of water quality of Xiaoxingkai Lake. Wetl Sci 11(4):466–469 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yu SS, Jiang M, Yuan YX (2015) Spatial heterogeneity of water quality in Xiaoxingkai Lake. Wetl Sci 13(2):166–170 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yuan YX, Yu HX, Jiang M (2013) Phytoplankton community structure and diversity in Xiaoxingkai Lake. Wetl Sci 11(2):151–157 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang JM, He ZH (1991) Neilu Yuye Ziran Ziyuan Diaocha Shou Ce. China Agriculture Press, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang ZS, Huang XF (1991) Freshwater plankton research methods. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgements
We thank the leaders and workers of the Xingkai Lake National Nature Reserve Management office for their assistance and support with field sampling work.
Funding
The study was supported by programs of the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFC0500406).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ju, Y., Sun, X., Shabani, E.I. et al. Relationships between zooplankton biomass and environmental factors of Xiaoxingkai Lake in northeastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 30279–30285 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06171-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06171-1