Abstract
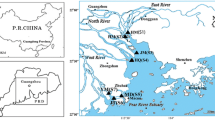
Phthalates (PAEs) in drinking water sources such as the Yangtze River in developing countries had aroused widespread concern. Here, the water, suspended particulate matter (SPM), and sediment samples were collected from 15 sites in wet and dry seasons in Zhenjiang, for the determination of six PAEs (DMP, DEP, DIBP, DBP, DEHP, and DOP) using the solid-phase extraction (SPE) or ultrasonic extraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The total concentrations of six PAEs (Σ6PAEs) spanned a range of 2.65–39.31 μg L−1 in water, 1.97–34.10 μg g−1 in SPM, and 0.93–34.70 μg g−1 in sediment. The partition coefficients (Kd1) of PAEs in water and SPM phase ranged from 0.004 to 3.36 L g−1 in the wet season and from 0.12 to 2.84 L g−1 in the dry season. Kd2 of PAEs in water and sediment phase was 0.001–9.75 L g−1 in the wet season and 0.006–8.05 L g−1 in the dry season. The dominant PAEs were DIBP, DBP, and DEHP in water and SPM, DIBP, DEHP, and DOP in sediment. The concentration of DBP in water exceeded the China Surface Water Standard. The discharge of domestic sewage and industrial wastewater might be the main potential sources of PAEs. The risk quotient (RQ) method used for the risk assessment revealed that DBP (0.01 < RQ < 1) posed a medium risk, while DIBP and DEHP (RQ > 1) posed a high environmental risk in water, DIBP (RQ > 1) also showed a high risk in sediment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blair JD, Ikonomou MG, Kelly BC, Surridge B, Gobas FAPC (2009) Ultra-trace determination of phthalate estermetabolites in seawater, sediments, and biota from an urbanized marine inlet by LC/ESI-MS/MS. Environ Sci Technol 43:6262–6268. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9013135
Cheng J, Ko F (2018) Occurrence of PBDEs in surface sediments of metropolitan rivers: sources, distribution pattern, and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 637-638:1578–1585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.075
Daiem MMA, Rivera-Utrilla J, Ocampo-Perez R, Mendez-Diaz JD, Sanchez-Polo M (2012) Environmental impact of phthalic acid esters and their removal from water and sediments by different technologies - a review. J Environ Manag 109:164–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.05.014
EC (2003) European Commission Technical Guidance Document in Support of Commission Directive 93/67/EEC on Risk Assessment for New Notified Substances and Commission Regulation (EC) No. 1488/94 on Risk Assessment for Existing Substance, Part II. Brussels, Belgium. In: Commission, E. (Ed.) pp. 100-103
Feng C, Xing X, Shen Z, Zhou Z (2007) Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Wuhan section of the Yangtze River, China. Environ Monit Assess 133:447–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9599-5
Foster PMD, Cattley RC, Mylchreest E (2000) Effects of di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) on male reproductive development in the rat: implications for human risk assessment. Food Chem Toxicol 38:S97–S99. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0278-6915(99)00128-3
He H, Hu GJ, Sun C, Chen SL, Yang MN, Li J, Zhao Y, Wang H (2011) Trace analysis of persistent toxic substances in the main stream of Jiangsu section of the Yangtze River, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18(4):638–648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-010-0414-z
He Q, Kang L, Sun XF, Jia RX, Zhang Y, Ma JS, Li H, Ai HN (2018) Spatiotemporal distribution and potential risk assessment of microcystins in the Yulin River, a tributary of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J Hazard Mater 347:184–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.01.001
Kang Y, Man YB, Cheung KK, Wong MH (2012) Risk assessment of human exposure to bioaccessible phthalate esters via indoor dust around the Pearl River Delta. Environ Sci Technol 46:8422–8430. https://doi.org/10.1021/es300379v
Keizer-Schrama SD, Main KM, Swan S, Foster P, Jensen AA (2006) Possible impact of phthalates on infant reproductive health - discussion. Int J Androl 29(1):180-180. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2605.2005.00642.x
Kong YL, Shen JM, Chen ZL, Kang J, Li TP, Wu XF, Kong XZ, Fan LT (2017) Profiles and risk assessment of phthalate acid esters (PAEs) in drinking water sources and treatment plants, East China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(30):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9783-x
Li X, Yin P, Zhao L (2016) Phthalate esters in water and surface sediments of the Pearl River Estuary: distribution, ecological, and human health risks. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(19):19341–19349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7143-x
Li R, Liang J, Duan H, Gong Z (2017a) Spatial distribution and seasonal variation of phthalate esters in the Jiulong River estuary, Southeast China. Mar Pollut Bull 122(1-2):38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.05.062
Li RL, Liang J, Gong ZB, Zhang NN, Duan HL (2017b) Occurrence, spatial distribution, historical trend and ecological risk of phthalate esters in the Jiulong River, Southeast China. Sci Total Environ 580:388–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.190
Liu H, Liang HC, Liang Y, Zhang D, Wang C, Cai HS, Shvartsev SL (2010) Distribution of phthalate esters in alluvial sediment: a case study at JiangHan Plain, Central China. Chemosphere 78:382–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.11.009
Net S, Delmont A, Sempéré R, Paluselli A, Ouddane B (2015) Reliable quantification of phthalates in environmental matrices (air, water, sludge, sediment and soil): a review. Sci Total Environ 515-516:162–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.013
Niu LL, Xu Y, Xu C, Yun LX, Liu WP (2014) Status of phthalate esters contamination in agricultural soils across China and associated health risks. Environ Pollut 195:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.08.014
Paluselli A, Aminot Y, Galgani F, Net S, Sempere R (2018a) Occurrence of phthalate acid esters (PAEs) in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea and the Rhone River. Prog Oceanogr 163:221–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2017.06.002
Paluselli A, Fauvelle V, Schmidt N, Galgani F, Net S, Sempéré R (2018b) Distribution of phthalates in Marseille Bay (NW Mediterranean Sea). Sci Total Environ 621:578–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.306
Peng XW, Feng LJ, Li XG (2013) Pathway of diethyl phthalate photolysis in sea-water determined by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and compound-specific isotope analysis. Chemosphere 90(2):220–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.06.045
Romero-Franco M, Hern´andez-Ram´ırez RU, Calafat AM, Cebri´an ME, Needham LL, Teitelbaum S, Wolf MS, Lopez-Carrillo L (2011) Personal care product use and urinary levels of phthalate metabolites in Mexican women. Environ Int 37(5):867–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.12.071
Roslev P, Vorkamp K, Aarup J, Frederiksen K, Nielsen PH (2007) Degradation of phthalate esters in an activated sludge wastewater treatment plant. Water Res 41(5):969–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.11.049
Selvaraj KK, Sundaramoorthy G, Ravichandran PK, Girijan GK, Sampath S, Ramaswamy BR (2015) Phthalate esters in water and sediments of the Kaveri River, India: environmental levels and ecotoxicological evaluations. Environ Geochem Health 37(1):83–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9632-5
Shao XL, Zou YM, Wang FX, Zhang Z, Wang SM, Han SL, Wang SS, Chen Y, Wu XY, Chen ZL (2013) Determination of phthalate acid esters in water and sediment samples by GC-MS. Adv Mater Res 610-613:157–162. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.610-613.157
Shi W, Hu XX, Zhang FX, Hu GJ, Hao YQ, Zhang XW, Liu HL, Wei S, Wang XR, Giesy JP (2012) Occurrence of thyroid hormone activities in drinking water from eastern China: contributions of phthalate esters. Environ Sci Technol 46:1811–1818. https://doi.org/10.1021/es202625r
Si QQ, Li FM, Gao CC, Wang C, Wang ZY, Zhao J (2016) Detection of phthalate esters in seawater by stir bar sorptive extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Mar Pollut Bull 108:163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.04.034
Simoneit BRT, Medeiros PM, Didyk BM (2005) Combustion products of plastics as indicators for refuse burning in the atmosphere. Environ Sci Technol 39(18):6961–6970. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050767x
Singh S, Li SSL (2012) Epigenetic effects of environmental chemicals bisphenol A and phthalates. Int J Mol Sci 13(8):10143–10153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130810143
Sirivithayapakorn S, Limtrakul S (2008) Distribution coefficient and adsorption–desorption rates of di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) onto and from the surface of suspended particles in fresh water. Water Air Soil Pollut 190:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9578-7
Suzuki T, Yaguchi K, Suzuki S (2001) Monitoring of phthalic acid monoesters in river water by solid-phase extraction and GC-MS determination. Environ Sci Technol 35:3757–3763. https://doi.org/10.1021/es001860i
United States Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA) (2011) Priority Pollutants (Accessed 05.10.11). http://water.epa.gov/scitech/methods/cwa/pollutants.cfm.
Van Wezel AP, Vlaardingen Pvan PR, Crommentuijn GH, Sijm DTHM (2000) Environmental risk limits for two phthalates, with special emphasis on endocrine disruptive properties. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 46:305–321. https://doi.org/10.1006/eesa.2000.1930
Vethaak AD, Lahr J, Schrap SM, Belfroid AC, Rijs GBJ, Gerritsen A, Boer J, Bulder AS, Grinwis GCM, Kuiper RV (2005) An integrated assessment of estrogenic contamination and biological effects in the aquatic environment of the Netherlands. Chemosphere 59(4):511–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.12.053
Wang F, Xia X, Sha Y (2008) Distribution of phthalic acid esters in Wuhan section of the Yangtze River, China. J Hazard Mater 154(1):317–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.028
Wang C, Liu J, Zhou J (2017a) N deposition affects allelopathic potential of amaranthus retroflexus with different distribution regions. An Acad Bras Cienc 89(2):919–926. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201720160513
Wang LJ, Liu MM, Tao WD, Zhang WJ, Wang L, Shi XM, Lu XW, Li XP (2017b) Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of phthalate esters in urban soil in the typical semi-arid city of Xi'an, Northwest China. Chemosphere 191:467–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.066
Yang DD, Feng LJ, Li MF, Duan XY, Zhang DH, Li XG (2016) Occurrence and distribution characteristics of phthalic acid esters (PAEs) in surface sediments of the East China Sea. J Ocean Univ China 46(3):074–081. https://doi.org/10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20140404
Zeng F, Cui KY, Xie ZY, Liu M, Li YJ, Lin YJ, Zeng ZX, Li FB (2008) Occurrence of phthalate esters in water and sediment of urban lakes in a subtropical city, Guangzhou, South China. Environ Int 34(3):372–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2007.09.002
Zeng F, Wen J, Cui K, Wu L, Li Y, Lin Y (2009) Seasonal distribution of phthalate esters in surface water of the urban lakes in the subtropical city, Guangzhou, China. J Hazard Mater 169:719–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.006
Zhang LF, Dong L, Ren LJ, Shi SX, Zhou L, Zhang T, Huang YR (2012) Concentration and source identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalic acid esters in the surface water of the Yangtze River Delta, China. J Environ Sci (China) 24(2):335–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(11)60782-1
Zhang ZM, Zhang HH, Zhang J, Wang QW, Yang GP (2017) Occurrence, distribution, and ecological risks of phthalate esters in the seawater and sediment of Changjiang River Estuary and its adjacent area. Sci Total Environ 619-620:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.070
Zheng X, Zhang BT, Teng Y (2014) Distribution of phthalate acid esters in lakes of Beijing and its relationship with anthropogenic activities. Sci Total Environ 476-477:107–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.111
Zhou Z, Liang Y, Shi YL, Xu L, Cai YQ (2013) Occurrence and transport of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs), including short-chain PFAAs in Tangxun Lake, China. Environ Sci Technol 47:9249–9257. https://doi.org/10.1021/es402120y
Acknowledgments
Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions and Collaborative Innovation Center of Technology and Material of Water Treatment are acknowledged.
Funding
This work was financially supported by State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology Open Fund KF 2017-19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ester Heath
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Hui Chen and Wei Mao are co-first authors
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 264 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Mao, W., Shen, Y. et al. Distribution, source, and environmental risk assessment of phthalate esters (PAEs) in water, suspended particulate matter, and sediment of a typical Yangtze River Delta City, China . Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 24609–24619 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05259-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05259-y