Abstract
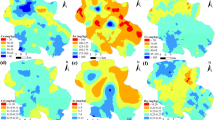
We investigated the horizontal and vertical distribution of heavy metals (Hg, Pb, Zn, Cu, Cd, As, Ni, and Cr) in soils in the water source protection zone for Shanghai to study the origins of these metals, their connections with urbanization, and their potential risk posed on the ecosystem. Determination of metal concentrations in 50 topsoil samples and nine soil profiles indicated that Hg, Pb, Zn, and Cu were present in significantly higher concentrations in topsoil than in deep soil layers. The spatial distributions of Hg, Pb, Zn, and Cu and contamination hotspots for these metals in the study area were similar to those near heavy industries and urban built-up areas. Emissions from automobiles resulted in increased soil concentrations of Cu, Pb, and Zn along roadsides, while high concentrations of Hg in the soil resulted from recent atmospheric deposition. Calculation of the potential ecological risk indicated that the integrative risk of these heavy metals in most areas was low, but a few sites surrounding high density of factories showed moderate risks.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajmone-Marsan F, Biasioli M (2010) Trace elements in soils of urban areas. Water Air Soil Pollut 213:121–143
Argyraki A, Kelepertzis E (2014) Urban soil geochemistry in Athens, Greece: the importance of local geology in controlling the distribution of potentially harmful trace elements. Sci Total Environ 482–483:366–377
Biasioli M, Barberis R, Ajmone-Marsan F (2006) The influence of a large city on some soil properties and metals content. Sci Total Environ 356:154–164
Cazier F, Dewaele D, Delbende A, Nouali H, Garçon G, Verdin A, Courcot D, Bouhsina S, Shirali P (2011) Sampling analysis and characterization of particles in the atmosphere of rural, urban and industrial areas. Procedia Environ Sci 4:218–227
Chen T, Zheng Y, Lei M, Huang Z, Wu H, Chen H, Fan K, Yu K, Wu X, Tian Q (2005) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 60:542–551
Chen W, Wu L, Chang AC, Hou Z (2009) Assessing the effect of long-term crop cultivation on distribution of Cd in the root zone. Ecol Model 220:1836–1843
Chen X, Xia X, Zhao Y, Zhang P (2010) Heavy metal concentrations in roadside soils and correlation with urban traffic in Beijing, China. J Hazard Mater 181:640–646
Chen YY, Wang J, Gao W, Sun XJ, Xu SY (2012) Comprehensive analysis of heavy metals in soils from Baoshan District, Shanghai: a heavily industrialized area in China. Environ Earth Sci 67:2331–2343
Cheng H, Li M, Zhao C, Li K, Peng M, Qin A, Cheng X (2014) Overview of trace metals in the urban soil of 31 metropolises in China. J Geochem Explor 139:31–52
CNEMC, 1990. The backgrounds of soil environment in China. China Environment Science Press (in Chinese), Beijing
Dayani M, Mohammadi J (2010) Geostatistical assessment of Pb, Zn and Cd contamination in near-surface soils of the urban-mining transitional region of Isfahan, Iran. Pedosphere 20:568–577
Guney M, Onay TT, Copty NK (2010) Impact of overland traffic on heavy metal levels in highway dust and soils of Istanbul, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 164:101–110
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hu KL, Zhang FR, Li H, Huang F, Li BG (2006) Spatial patterns of soil heavy metals in urban–rural transition zone of Beijing. Pedosphere
Hu Y, Liu X, Bai J, Shih K, Zeng EY, Cheng H (2013) Assessing heavy metal pollution in the surface soils of a region that had undergone three decades of intense industrialization and urbanization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:6150–6159
Johansson C, Norman M, Burman L (2009) Road traffic emission factors for heavy metals. Atmos Environ 43:4681–4688
Luo W, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Fu W, Wang B, Jiao W, Wang G, Tong X, Giesy JP (2010) Watershed-scale assessment of arsenic and metal contamination in the surface soils surrounding Miyun Reservoir, Beijing, China. J Environ Manag 91:2599–2607
Okuda T, Katsuno M, Naoi D, Nakao S, Tanaka S, He K, Ma Y, Lei Y, Jia Y (2008) Trends in hazardous trace metal concentrations in aerosols collected in Beijing, China from 2001 to 2006. Chemosphere 72:917–924
Peng C, Ouyang Z, Wang M, Chen W, Li X, Crittenden JC (2013) Assessing the combined risks of PAHs and metals in urban soils by urbanization indicators. Environ Pollut 178:426–432
Qu MK, Li WD, Zhang CR (2014) Spatial distribution and uncertainty assessment of potential ecological risks of heavy metals in soil using sequential Gaussian simulation. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 20:764–778
Reimann C, Caritat P (2000) Intrinsic flaws of element enrichment factors (EFs) in environmental geochemistry. Environ Sci Technol 34:5084–5091
Reimann C, Garrett RG (2005) Geochemical background—concept and reality. Sci Total Environ 350:12–27
Shi G, Chen Z, Xu S, Zhang J, Wang L, Bi C, Teng J (2008) Potentially toxic metal contamination of urban soils and roadside dust in Shanghai, China. Environ Pollut 156:251–260
Wei B, Yang L (2010) A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem J 94:99–107
Wong CSC, Li X, Thornton I (2006) Urban environmental geochemistry of trace metals. Environ Pollut 142:1–16
Wu S, Xia X, Lin C, Chen X, Zhou C (2010) Levels of arsenic and heavy metals in the rural soils of Beijing and their changes over the last two decades (1985–2008). J Hazard Mater 179:860–868
Xia X, Chen X, Liu R, Liu H (2011) Heavy metals in urban soils with various types of land use in Beijing, China. J Hazard Mater 186:2043–2050
Yuan GL, Sun TH, Han P, Li J, Lang XX (2014) Source identification and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in topsoil using environmental geochemical mapping: typical urban renewal area in Beijing, China. J Geochem Explor 136:40–47
Zhang G, Yang F, Zhao Y, Zhao W, Yang J, Gong Z (2005) Historical change of heavy metals in urban soils of Nanjing, China during the past 20 centuries. Environ Int 31:913–919
Zhao YF, Shi XZ, Huang B, Yu DS, Wang HJ, Sun WX, ÖBoern I, BlombÄCk K (2007) Spatial distribution of heavy metals in agricultural soils of an industry-based peri-urban area in Wuxi, China. Pedosphere 17:44–51
Zhou L, Yang B, Xue N, Li F, Seip HM, Cong X, Yan Y, Liu B, Han B, Li H (2014) Ecological risks and potential sources of heavy metals in agricultural soils from Huanghuai Plain, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:1360–1369
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41401588, 41501580).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Summary
We investigated the spatial and vertical distribution of heavy metals in soil in the Shanghai water supply area to determine the sources of contamination and the impacts of urbanization.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 516 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, Y., Wang, M., Peng, C. et al. Impacts of urbanization on the distribution of heavy metals in soils along the Huangpu River, the drinking water source for Shanghai. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 5222–5231 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5745-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5745-3