Abstract
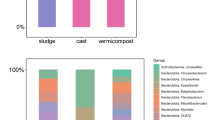
In the present study, maize stover was vermicomposted with the epigeic earthworm Eisenia fetida. The results showed that, during vermicomposting process, the earthworms promoted decomposition of maize stover. Analysis of microbial communities of the vermicompost by high-throughput pyrosequencing showed more complex bacterial community structure in the substrate treated by the earthworms than that in the control group. The dominant microbial genera in the treatment with the earthworms were Pseudoxanthomonas, Pseudomonas, Arthrobacter, Streptomyces, Cryptococcus, Guehomyces, and Mucor. Compared to the control group, the relative abundance of lignocellulose degradation microorganisms increased. The results indicated that the earthworms modified the structure of microbial communities during vermicomposting process, activated the growth of lignocellulose degradation microorganisms, and triggered the lignocellulose decomposition.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aira M, Domínguez J (2011) Earthworm effects without earthworms: inoculation of raw organic matter with worm-worked substrates alters microbial community functioning. PLoS One 6:1–8
Aira M, Monroy F, Domínguez J (2006) Eisenia foetida (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae) activates fungal growth, triggering cellulose decomposition during vermicomposting. Microb Ecol 52(4):738–747
Aira M, Monroy F, Domínguez J (2007a) Earthworms strongly modify microbial biomass and activity triggering enzymatic activities during vermicomposting independently of the application rates of pig manure. Sci Total Environ 385:252–261
Aira M, Monroy F, Domínguez J (2007b) Eisenia fetida (Oligochaeta: Lumbricidae) modifies the structure and physiological capabilities of microbial communities improving carbon mineralization during vermicomposting of pig manure. Microb Ecol 54:662–671
Aira M, Monroy F, Domínguez J (2008) Detritivorous earthworms directly modify the structure, thus altering the functioning of a microdecomposer food web. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2511–2516
Bellemain E, Carlsen T, Brochmann C, Coissac E, Taberlet P, Kauserud H (2010) ITS as an environmental DNA barcode for fungi: an in silico approach reveals potential PCR biases. BMC Microbiol 10:189
Bhat SA, Singh J, Vig AP (2015) Potential utilization of bagasse as feed material for earthworm Eisenia fetida and production of vermicompost. SpringerPlus 4:11
Brown GG, Doube B (2004) Functional interactions between earthworms, microorganisms, organic matter and plants. In: Edwards CA (ed) Earthworm ecology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 213–240
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Tumbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336
Castillo JM, Romero E, Nogales R (2013) Dynamics of microbial communities related to biochemical parameters during vermicomposting and maturation of agroindustrial lignocellulose wastes. Bioresour Technol 146:345–354
Cheng CL, Chang JS (2011) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic feedstock by novel cellulases originating from Pseudomonas sp. CL3 for fermentative hydrogen production. Bioresour Technol 102:8628–8634
DeAngelis KM, Allgaier M, Chavarria Y, Fortney JL, Hugenholtz P, Simmons B, Sublette K, Silver WL, Hazen TC (2011) Characterization of trapped lignin degrading microbes in tropical forest soil. PLoS One 6(4), e19306
Ernst G, Henseler I, Felten D, Emmerling C (2009) Decomposition and mineralization of energy crop residues governed by earthworms. Soil Biol Biochem 41(7):1548–1554
Feng YJ, Yu YL, Wang X, Qu YP, Li DM, He WH, Kim BH (2011) Degradation of raw corn stover powder (RCSP) by an enriched microbial consortium and its community structure. Bioresour Technol 102:742–747
Fernández-Gómez MJ, Nogales R, Insam H, Romero E, Goberna M (2010) Continuous-feeding vermicomposting as a recycling management method to revalue tomato-fruit wastes from greenhouse crops. Waste Manag 30:2461–2468
Fernández-Gómez MJ, Nogales R, Insam H, Romero E, Goberna M (2012) Use of DGGE and COMPOCHIP for investigating bacterial communities of various vermicomposts produced from different wastes under dissimilar conditions. Sci Total Environ 414:664–671
Fracchia L, Dohrmann AB, Martinotti MG, Tebbe CC (2006) Bacterial diversity in a finished compost and vermicompost: differences revealed by cultivation-independent analyses of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA genes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:942–952
Garg P, Gupta A, Satya S (2006) Vermicomposting of different types of waste using Eisenia foetida: a comparative study. Bioresour Technol 97:391–395
Garg VK, Suthar S, Yadav A (2012) Management of food industry waste employing vermicomposting technology. Bioresour Technol 126:437–443
Gómez-Brandón M, Domínguez J (2014) Recycling of solid organic wastes through vermicomposting: microbial community changes throughout the process and use of vermicompost as a soil amendment. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 44:1289–1312
Gómez-Brandón M, Lazcano C, Lores M, Domínguez J (2010) Detritivorous earthworms modify microbial community structure and accelerate plant residue decomposition. Appl Soil Ecol 44(3):237–244
Gómez-Brandón M, Lores M, Domínguez J (2013) Changes in chemical and microbiological properties of rabbit manure in a continuous-feeding vermicomposting system. Bioresour Technol 128:310–316
Gopalakrishnan S, Vadlamudi S, Bandikinda P, Sathya A, Vijayabharathi R, Rupela O, Kudapa H, Katta K, Varshney RK (2014) Evaluation of Streptomyces strains isolated from herbal vermicompost for their plant growth-promotion traits in rice. Microbiol Res 169:40–48
Guo HG, Liu RY, Yu ZS, Zhang HX, Yun JL, Li YM, Liu X, Pan JG (2012) Pyrosequencing reveals the dominance of methylotrophic methanogenesis in a coal bed methane reservoir associated with Eastern Ordos Basin in China. Int J Coal Geol 93:56–61
Hayawin ZN, Khalil HPSA, Jawaid M, Ibrahim MH, Astimar AAA (2010) Exploring chemical analysis of vermicomposting of various oil palm fibre wastes. Environmentalist 30:273–278
Huang K, Li FS, Wei YF, Chen XM, Fu XY (2013) Changes of bacterial and fungal community compositions during vermicomposting of vegetable wastes by Eisenia foetida. Bioresour Technol 150:235–241
José Molina M, Desamparados SM, Ingelmo F, Llinares J (2013) Stabilisation of sewage sludge and vinasse bio-wastes by vermicomposting with rabbit manure using Eisenia fetida. Bioresour Technol 137:88–97
Karimi K, Zamani A (2013) Mucor indicus: Biology and industrial application perspectives: a review. Biotechnol Adv 31:466–481
Karthika A, Seethadevi G, Vasanthy M, Swabna V, Susila S, Vivekanadhan M (2015) Potentiality of Eisenia fetida to degrade disposable paper cups-an ecofriendly solution to solid waste pollution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(4):2868–2876
Krištüfek V, Ravasz K, Pizl V (1993) Actinomycete communities in earthworm guts and surrounding soil. Pedobiologia 37:379–384
Lavelle P, Decaens T, Aubert M, Barot S, Blouin M, Bureau F, Margerie P, Mora P, Rossi JP (2006) Soil invertebrates and ecosystem services. Eur J Soil Biol 42:3–15
McLellan SL, Huse SM, Mueller-Spitz SR, Andreishcheva EN, Sogin ML (2010) Diversity and population structure of sewage-derived microorganisms in wastewater treatment plant influent. Environ Microbiol 12(2):378–392
Monroy F, Aira M, Domínguez J (2009) Reduction of total coliform numbers during vermicomposting is caused by short-term direct effects of earthworms on microorganisms and depend on the dose of application of pig slurry. Sci Total Environ 407:5411–5416
Moody SA, Briones MJI, Pierce TG, Dighton J (1995) Selective consumption of decomposting wheat straw by earthworms. Soil Biol Biochem 27:1209–1213
Nakagawa T, Ikehata R, Uchino M, Miyaji T, Takano K, Tomizuka N (2006) Cold-active acid β-galactosidase activity of isolated psychrophilic-basidiomycetous yeast Guehomyces pullulans. Microbiol Res 161:75–79
Nguyen TLT, Hermansen JE, Mogensen L (2013) Environmental performance of crop residues as an energy source for electricity production: the case of wheat straw in Denmark. Appl Energy 104:633–641
Okeke BC, Liu J (2011) Characterization of a defined cellulolytic and xylanolytic bacterial consortium for bioprocessing of cellulose and hemicelluloses. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 163:869–881
Paoletti MG (1999) The role of earthworms for assessment of sustainability and as bioindicators. Agric Ecosyst Environ 74:137–155
Parachin NS, Siqueira S, Faria FPD, Torres FAG, Moraes LMPD (2009) Xylanases from Cryptococcus flavus isolate I-11: enzymatic profile, isolation and heterologous expression of CfXYN1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Catal B Enzym 59:52–57
Pathma J, Sakthivel N (2013) Molecular and functional characterization of bacteria isolated from straw and goat manure based vermicompost. Appl Soil Ecol 70:33–47
Peng F, Peng P, Xu F, Sun RC (2012) Fractional purification and bioconversion of hemicelluloses. Biotechnol Adv 30:879–903
Pinto PA, Dias AA, Fraga I, Marques G, Rodrigues MAM, Colaco J, Sampaio A, Bezerra RMF (2012) Influence of ligninolytic enzymes on straw saccharification during fungal pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 111:261–267
Qian PY, Wang Y, Lee OO, Lau SC, Yang J, Lafi FF, Wong TY (2011) Vertical stratification of microbial communities in the Red Sea revealed by 16S rDNA pyrosequencing. ISME J 5(3):507–518
Qiu MH, Zhang RF, Xue C, Zhang SS, Li SQ, Zhang N, Shen QR (2012) Application of bio-organic fertilizer can control Fusarium wilt of cucumber plants by regulating microbial community of rhizosphere soil. Biol Fertil Soils 48:807–816
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41(D1):D590–D596
Raphael K, Velmourougane K (2011) Chemical and microbiological changes during vermicomposting of coffee pulp using exotic (Eudrilus eugeniae) and native earthworm (Perionyx ceylanesis) species. Biodegradation 22(3):497–507
Roesch LF, Fulthorpe RR, Riva A, Casella G, Hadwin AK, Kent AD, Triplett EW (2007) Pyrosequencing enumerates and contrasts soil microbial diversity. ISME J 1(4):283–290
Saha BC (2004) Production, purification and properties of endoglucanase from a newly isolated strain of Mucor circinelloides. Process Biochem 39:1871–1876
Sangwan P, Kaushik CP, Garg VK (2008) Feasibility of utilization of horse dung spiked filter cake in vermicomposters using exotic earthworm Eisenia foetida. Bioresour Technol 99:2442–2448
Saratale GD, Saratale RG, Oh SE (2012) Production and characterization of multiple cellulolytic enzymes by isolated Streptomyces sp. MDS. Biomass Bioenerg 47:302–315
Sen B, Chandra TS (2009) Do earthworms affect dynamics of functional response and genetic structure of microbial community in lab-scale composting system? Bioresour Technol 100:804–811
Suthar S (2008) Bioconversion of post harvest crop residues and cattle shed manure into value-added products using earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae Kinberg. Ecol Eng 32:206–214
Suthar S, Gairola S (2014) Nutrient recovery from urban forest leaf litter waste solids using Eisenia fetida. Ecol Eng 71:660–666
Suthar S, Sharma P (2013) Vermicomposting of toxic weed—Lantana camara biomass: chemical and microbial properties changes and assessment of toxicity of end product using seed bioassay. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 95:179–187
Suthar S, Mutiyar P, Singh S (2012) Vermicomposting of milk processing industry sludge spiked with plant wastes. Bioresour Technol 116:214–219
Suthar S, Kumar K, Mutiyar PK (2015) Nutrient recovery from compostable fractions of municipal solid wastes using vermitechnology. J Mater Cycles Waste Manage 17(1):174–184
Thongekkaew J, Ikeda H, Masaki K, Iefuji H (2013) Fusion of cellulose binding domain from Trichoderma reesei CBHI to Cryptococcus sp. S-2 cellulase enhances its binding affinity and its cellulolytic activity to insoluble cellulosic substrates. Enzym Microb Technol 52:241–246
Tiwari R, Singh S, Shukla P, Nain L (2014) Novel cold temperature active β-glucosidase from Pseudomonas lutea BG8 suitable for simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. RSC Adv 4:58108–58115
Van Soest PJ, Robertson JB, Lewis BA (1991) Methods for dietary fibre, neutral detergent fibre, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J Dairy Sci 74(10):3583–3597
Vig AP, Singh J, Wani SH, Dhaliwal SS (2011) Vermicomposting of tannery sludge mixed with cattle dung into valuable manure using earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny). Bioresour Technol 102(17):7941–7945
Williamson PR (1994) Biochemical and molecular characterization of the diphenol oxidase of Cryptococcus neoformans: identification as a laccase. J Bacteriol 176(3):656–664
Yasir M, Aslam Z, Kim SW, Lee SW, Jeon CO, Chung YR (2009) Bacterial community composition and chitinase gene diversity of vermicompost with antifungal activity. Bioresour Technol 100:4396–4403
Yuan XF, Wen BT, Ma XG, Zhu WB, Wang XF, Chen SJ, Cui ZJ (2014) Enhancing the anaerobic digestion of lignocellulose of municipal solid waste using a microbial pretreatment method. Bioresour Technol 154:1–9
Zainudin MHM, Hassan MA, Tokura M, Shirai Y (2013) Indigenous cellulolytic and hemicellulolytic bacteria enhanced rapid co-composting of lignocellulose oil palm empty fruit bunch with palm oil mill effluent anaerobic sludge. Bioresour Technol 147:632–635
Zhang Y, Wang X, Hu M, Li PF (2015) Effect of hydraulic retention time (HRT) on the biodegradation of trichloroethylene wastewater and anaerobic bacterial community in the UASB reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:1977–1987
Zhao LM, Wang YY, Yang J, Xing MY, Li XW, Yi DH, Deng DH (2010) Earthworm-microorganism interactions: a strategy to stabilize domestic wastewater sludge. Water Res 44:2572–2582
Zhu XD, Williamson PR (2004) Role of laccase in the biology and virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans. FEMS Yeast Res 5:1–10
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Project (20110723), the National Natural Science Foundation of China Project (31101337), the Open Fund of Key Laboratory for Biodiversity Science and Ecological Engineering, Ministry of Education, Beijing Normal University, and “985 Project” of Jilin University. The authors express their gratitude to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Q. et al. Earthworms modify microbial community structure and accelerate maize stover decomposition during vermicomposting. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 17161–17170 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4955-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4955-z