Abstract
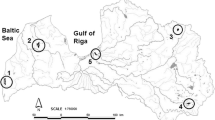
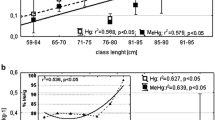
The aim of the study was to determine the impact trace metals, mainly toxic ones, on the condition of eel (Anguilla anguilla) inhabiting four regions of Poland. Metal concentrations in eel muscle tissues were studied as functions of size, region, and season 2011–2012. The levels of metals were also used for risk assessment on consumer health. Copper and zinc occurred at concentrations that could only have positive impacts on eel condition. Low levels of cadmium and lead did not impair the condition of the fish. However, mercury occurred at high levels and increased with fish length and season. The mercury levels in eels were compared with the threshold of toxicity (500–1,200 μg kg−1), which can cause changes in biochemical processes and impair fish reproduction. The concentration of mercury was 1,010 μg kg−1 in one specimen of the 120 samples examined, and in 16 specimens, it exceeded 500 μg kg−1. The toxic effects of the mercury could have been attenuated by the selenium in the muscles of the eel, especially in the muscles of smaller specimens in which the Se/Hg molar ratio was higher than 1 with a positive correlation between these two elements. In larger specimens measuring in excess of 70 cm, this coefficient was below 1, and the mercury to selenium correlation was negative, which meant that the protective effects of selenium were weaker. The mercury in the muscles of large specimens at levels exceeding 500 μg kg−1 could have weakened eel condition and also posed a threat to consumer health. The cadmium and lead in the muscles of the eel did not affect the condition of the fish. Mercury weakened the condition of large eel, A. anguilla. Selenium protected small- and medium-sized eel against the toxic effects of mercury.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ankarberg E, Bjerselius R, Aune M, Darnerud PL, Larsson L, Andersson A, Tysklind M, Bergek S, Lundstedt-Enkel K, Karlsson L, Törnkvist A, Glynn A (2004) Study of dioxin and dioxin-like PCB levels in fatty fish from Sweden 2000-2002. Organohalogen Compd 66:2035–2039
Barska I, Skrzyński I (2003) Contents of methylmercury and total mercury in Baltic Sea fish and fish products. Bull Sea Fish Inst 3(160):3–16
Bartel R, Bieniasz K, Epler P (1998) Move the fish by hydroelectric turbine on the River Wieprza Darłów. Annu Sci Pol Angling Assoc 11:87–90
Belpaire C, Goemans G (2007) Eels: contaminant cocktails pinpointing environmental contamination. ICES J Mar Sci 64:1423–1436
Bidone ED, Castilhos ZC, Santos TJS, Souza TMC, Lacerda LD (1997) Fish contamination and human exposure to mercury in Tartarugalzinho River, Northern Amazon, Brazil: a screening approach. Water Air Soil Pollut 97:9–15
Burger J, Gochfeld M (2013) Selenium and mercury molar ratios in commercial fish from New Jersey and Illinois: variation within species and relevance to risk communication. Food Chem Toxicol 57:235–245
Burger J, Gaines KF, Boring CS, Stephens WL Jr, Snodgrass J, Gochfeld M (2001) Mercury and selenium in fish from the Savannah River: species, trophic level, and location differences. Environ Res 87:108–118
Chen MH, Shih CC, Chou CL, Chou LS (2002) Mercury organic mercury and selenium in small cetaceans in Taiwanese waters. Mar Pollut Bull 45:237–245
Cid BP, Boia C, Pombo L, Rebelo E (2001) Determination of trace metals in fish species of the Ria de Aveiro (Portugal) by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem 75:93–100
Crump KL, Trudeau VL (2009) Mercury-induced reproductive impairment in fish. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:895–907
Dietz R, Sonne K, Basu N, Braune B, O'Hara T, Letcher RJ, Scheuhammer T et al (2013) What are the toxicological effects of mercury in Arctic biota? Sci Total Environ 443:775–790
Drevnick PE, Sandheinrich MB, Oris JT (2006) Increased ovarian follicular apoptosis in fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas) exposed to dietary methylmercury. Aquat Toxicol 79:49–54
EFSA (2010) Scientific opinion. Scientific Opinion on Lead in Food EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). EFSA Journal 8(4): 1570 http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/1570.pdf (Accessed 02 January 2014)
EFSA (2012) Scientific opinion on the risk for public health related to the presence of mercury and methylmercury in food (CONTAM). EFSA Journal 10(12): 2985 http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/2985.pdf (Accessed 02 January 2014)
Egeland GM, Middaugh JP (1997) Balancing fish consumption benefits with mercury exposure. Science 278:1904–1906
Ferrante MC, Clausi MT, Meli R, Fusco G, Naccari C, Lucisano A (2010) Polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in European eel (Anguilla anguilla) from the Garigliano River (Campania region, Italy). Chemosphere 78:709–716
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) (2011) Scientific opinion. Statement on tolerable weekly intake for cadmium EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). EFSA Journal 9(2): 1975 http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/1975.pdf (Accessed 02 January 2014)
Ganther HE, Goudie C, Sunde ML, Kopecky MJ, Wagner R, Sang-Hwang OH, Hoekstra WG (1972) Selenium relation to decreased toxicity of methylmercury added to diets containing tuna. Science 72:1122–1124
Gochfeld M, Burger J (2005) Good fish/bad fish: a composite benefit–risk by dose curve. Neurotoxicology 26:511–520
Green NW, Knutzen J (2003) Organohalogens and metals in marine fish and mussels and some relationships to biological variables at reference localities in Norway. Mar Pollut Bull 46:362–377
Guimaraes L, Gravato C, Santos J, Monteiro LS, Guilhermino L (2009) yellow eel (Anguilla anguilla) development in NW Portuguese estuaries with different contamination levels. Ecotoxicology 18:385–402
Hammerschmidt CR, Fitzgerald WF (2006) Bioaccumulation and trophic transfer of methylmercury in Long Island sound. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 51:416–424
Has-Schön E, Bogut I, Strelec I (2006) Heavy metal profile in five fish species included in human diet, domiciled in the end flow of River Neretva (Croatia). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 50:545–551
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (1999) Biogeochemistry of trace elements. Strontium. Biogeochemia Pierwiastków śladowych. PWN Warszawa, pp. 134-140 (in Polish)
Kaneko JJ, Ralston NVC (2007) Selenium and mercury in pelagic fish in the central north Pacific near Hawaii. Biol Trace Elem Res 119:242–254
Karl H, Bladt A, Rottler H, Ludwigs R, Mathar W (2010) Temporal trends of PCDD, PCDF and PCB levels in muscle meat of herring from different fishing grounds of the Baltic Sea and actual data of different fish species from the Western Baltic Sea. Chemosphere 78:106–112
Kim JG, Birks E, Heisinger JF (1977) Protective action of selenium against mercury in northern creek chubs. B Environ Contam Toxicol 17:132–136
Klaper R, Rees CB, Drevnick P, Weber D, Sandheinrich M, Caravan MJ (2006) Gene expression changes related to endocrine function and decline in reproduction in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) after dietary methylmercury exposure. Environ Health Perspect 11:1337–1343
Knutzen J, Bjerkeng BN, Schlabach M (2003) Polychlorinated dibenzofurans/dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDF/PCDDs) and other dioxin-like substances in marine organisms from the Grenland fjords, S. Norway, 1975–2001: present contamination levels, trends and species specific accumulation of PCDF/PCDD congeners. Chemosphere 52:745–760
Lange TR, Royals HE, Connor LL (1994) Mercury accumulation in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) in a Florida Lake. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 27:466–471
Maes J, Belpaire C, Goemans G (2008) Spatial variations and temporal trends between 1994 and 2005 in polychlorinated biphenyls, organochlorine pesticides and heavy metals in European eel (Anguilla anguilla L.) in Flanders, Belgium. Environ Pollut 153:223–237
Neto AF, Costa JL, Costa MJ, Pereira ME, Duarte A, Caçador I, Domingos I (2011) Accumulation of metals in Anguilla anguilla from the Tagus estuary and relationship to environmental contamination. J Appl Ichthyol 27(5):265–272
Ouédraogo O, Amyot, M (2013) Mercury, arsenic and selenium concentrations in water and fish from sub-Saharan semi-arid freshwater reservoirs (Burkina Faso) 444: 243-254
Peterson SA, Ralston NVC, Whanger PD, Oldfield JE, Mosher WD (2009) Selenium and mercury interactions with emphasis on fish tissue. Environ Bioindic 4:318–334
Pinho AP, Guimaraes JRD, Marins AS, Costa PAS, Olavo G, Valentin J (2002) Environ Res 89:250–258
Polak-Juszczak L (2009) Temporal trends in the bioaccumulation of trace metals in herring, sprat, and cod from the southern Baltic Sea in the 1994–2003 period. Chemosphere 76:1334–1339
Polak-Juszczak L (2012) Bioaccumulation of mercury in the trophic chain of flatfish from the Baltic Sea. Chemosphere 89:585–591
Ponce RA, Bartell SM, Wong EY, LaFlamme D, Carrington C, Lee RC, Patrick DI, Faustman EM, Bolger M (2000) Use of quality-adjusted life year weights with dose–response models for public health decisions: a case study of the risks and benefits of fish consumption. Risk Anal 20:529–542
Ralston NVC, Raymond LJ (2010) Dietary selenium’s protective effects against methylmercury toxicity. Toxicology 278:112–123
Ralston NVC, Ralston CR, Blackwell JL, Raymond LJ (2008) Dietary and tissue selenium in relation to methylmercury toxicity. Neurotoxicology 29:802–811
Raymond LJ, Ralston NVC (2004) Mercury: selenium interactions and health implications. SMDJ Seychelles Med Dental J 7:72–77
Raymond LJ, Ralston NVC (2009) Selenium’s importance in regulatory issues regarding mercury. Fuel Process Technol 90:1333–1338
Rezayi M, Esmaeli AS, Valinasab T (2011) Mercury and selenium content in Otolithes rubber and Psettodes erumei from Khuzestan Shore, Iran. B Environ Contam Toxicol 86:511–514
Ribeiro CAO, Vollaire Y, Sánchez-Chardi A, Roche H (2005) Bioaccumulation and the effects of organochlorine pesticides, PAH and heavy metals in Eel (Anguilla anguilla) at the Camargue Nature Reserve, France. Aquat Toxicol 74:53–69
Rice G, Swartout J, Mahaffey K, Schoeny R (2000) Derivation of US EPS’s oral reference dose (RfD) for methylmercury. Drug Chem Toxicol 23:41–54
Ringdal O, Julshamn K (1985) Effect of selenite on the uptake of methylmercury in cod (Gadus morhua). B Environ Contam Toxicol 35:335–344
Sandheinrich MB, Miller KM (2006) Effects of dietary methylmercury on reproductive behavior of fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas). Environ Toxicol Chem 25:3053–3057
Sandheinrich MB, Wiener JG (2010) Methylmercury in freshwater fish: recent advances in assessing toxicity of environmentally relevant exposures, Beyer N., Meador J., (Ed.) Environmental contaminants in wildlife: interpreting tissue concentrations, 2nd edition (2010), Taylor and Francis Publishers, Boca Raton, Florida. http://www.newmoa.org/prevention/mercury/conferences/sciandpolicy/presentations/Sandheinrich_Session6A.pdf (Accessed 02 January 2014)
Scheuhammer AM, Wong AHK, Bond D (1998) Mercury and selenium accumulation in common loons (Gavia immer) and common mergansers (Mergus merganser) from Eastern Canada. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:197–201
Sormo EG, Ciesielski TM, Overjordet JB, Lierhagen S, Eggen GS, Berg T, Jenssen BM (2011) Selenium moderates mercury toxicity in free-ranging fish. Environ Sci Technol 45:6561–6566
Stachel B, Christoph EH, Götz R, Herrmann T, Krüger F, Kühn T, Lay J et al (2007) Dioxins and dioxin-like PCBs in different fish from the River Elbe and its tributaries, Germany. J Hazard Mater 148:199–209
Szlinder-Richert J, Udydus Z, Pelczarski W (2010) Organochlorine pollutants in European eel (Anguilla anguilla) from Poland. Chemosphere 80(2):93–99
Wang A, Barber D, Pfeiffer CJ (2001) Protective effects of selenium against mercury toxicity in cultured Atlantic spotted dolphin (Stenella plagiodon) renal cells. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 41:403–409
WHO, World Health Organization (1989) Mercury-Environmental Aspects. WHO, Geneva, Switzerland
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Henner Hollert
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polak-Juszczak, L., Robak, S. Mercury toxicity and the protective role of selenium in eel, Anguilla anguilla . Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 679–688 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3382-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3382-x