Abstract
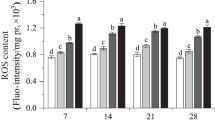
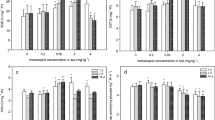
The aim of this study was to evaluate the toxicological responses of earthworm (Eisenia fetida) induced by field-contaminated, metal-polluted soils. Biochemical responses and DNA damage of earthworm exposed to two multi-metal-contaminated soils in a steel industry park and a natural reference soil in Zijin Mountain for 2, 7, 14, and 28 days were studied. Results showed that three enzyme activities, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), acetylcholinesterase (AChE), and cellulase, in earthworm in metal-contaminated soils were significantly different from those of the reference soil. Cellulase and AChE were more sensitive than SOD to soil contamination. The Olive tail moment of the comet assay after 2-day exposure increased 56.5 and 552.0 % in two contaminated soils, respectively, compared to the reference soil. Our findings show that cellulase and DNA damage levels can be used as potential biomarkers for exposure of earthworm to metal-polluted soils.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarenga P, Palma P, Gonçalves AP, Fernandes RM, Varennes A, Vallini G, Duarte E, Cunha-Queda AC (2008) Evaluation of tests to assess the quality of mine-contaminated soils. Environ Geochem Hlth 30(2):95–99. doi:10.1007/s10653-008-9147-z
Barillet S, Buet A, Adam C, Devaux A (2005) Does uranium exposure induce genotoxicity in the teleostean Danio rerio? First experimental results. Radioprotection 40:175–181. doi:10.1051/radiopro:2005s1-028
Basta NT, Ryan JA, Chaney RL (2005) Trace element chemistry in residual-treated soil: key concepts and metal bioavailability. J Environ Qual 34(1):49–63
Beauvais SL, Jones SB, Parris JT, Brewer SK, Little EE (2001) Cholinergic and behavioral neurotoxicity of carbaryl and cadmium to larval rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Ecotox Environ Safe 49(1):84–90. doi:10.1006/eesa.2000.2032
Berthelot Y, Valton É, Auroy A, Trottier B, Robidoux PY (2008) Integration of toxicological and chemical tools to assess the bioavailability of metals and energetic compounds in contaminated soils. Chemosphere 74(1):166–177. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.07.056
Bigorgne E, Cossu-Leguille C, Bonnard M, Nahmani J (2010) Genotoxic effects of nickel, trivalent and hexavalent chromium on the Eisenia fetida earthworm. Chemosphere 80(9):1109–1112. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.05.039
Bonnard M, Devin S, Leyval C, Morel JL, Vasseur P (2010) The influence of thermal desorption on genotoxicity of multipolluted soil. Ecotox Environ Safe 73(5):955–960. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.02.023
Bonnard M, Eom I-C, Morel J-L, Vasseur P (2009) Genotoxic and reproductive effects of an industrially contaminated soil on the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ Mol Mutagen 50(1):60–67. doi:10.1002/em.20436
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilising the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254. doi:10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Calisi A, Lionetto MG, Schettino T (2011) Biomarker response in the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris exposed to chemical pollutants. Sci Total Environ 409(20):4456–4464. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.06.058
Capowiez Y, Rault M, Mazzia C, Belzunces L (2003) Earthworm behaviour as a biomarker—a case study using imidacloprid. Pedobiologia 47(5–6):542–547. doi:10.1078/0031-4056-00226
Chakra Reddy N, Venkateswara Rao J (2008) Biological response of earthworm, Eisenia foetida (Savigny) to an organophosphorous pesticide, profenofos. Ecotox Environ Safe 71(2):574–582. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.01.003
Chang LW, Meier JR, Smith MK (1997) Application of plant and earthworm bioassays to evaluate remediation of a lead-contaminated soil. Arch Environ Con Tox 32(2):166–171. doi:10.1007/s002449900170
Ching EWK, Siu WHL, Lam PKS, Xu LH, Zhang YY, Richardson BJ, Wu RSS (2001) DNA adduct formation and DNA strand breaks in green-lipped mussels (Perna viridis) exposed to benzo[a]pyrene: dose- and time-dependent relationships. Mar Pollut Bull 42(7):603–610. doi:10.1016/s0025-326x(00)00209-5
Collins AR (2004) The comet assay for DNA damage and repair principles, applications, and limitations. Mol Biotechnol 26:249–261. doi:10.1385/MB:26:3:249
Collins AR, Ma AG, Duthie SJ (1995) The kinetics of repair of oxidative DNA-damage (strand breaks and oxidized pyrimidines) in human-cells. Mutat Res-dna Repair 336(1):69–77. doi:10.1016/0921-8777(94)00043-6
Dayton EA, Basta NT, Payton ME, Bradham KD, Schroder JL, Lanno RP (2006) Evaluating the contribution of soil properties to modifying lead phytoavailability and phytotoxicity. Environ Toxicol Chem 25(3):719–725. doi:10.1897/05-307r.1
Dhindsa RS, Plumbdhindsa P, Thorpe TA (1981) Leaf senescence: correlated with increased levels of membrane-permeability and lipid-peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide-dismutase and catalase. J Exp Bot 32(126):93–101. doi:10.1093/jxb/32.1.93
Di Marzio WD, Saenz ME, Lemière S, Vasseur P (2005) Improved single-cell gel electrophoresis assay for detecting DNA damage in Eisenia foetida. Environ Mol Mutagen 46(4):246–252. doi:10.1002/em.20153
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7((2):88. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
Eyambe GS, Goven AJ, Fitzpatrick LC, Venables BJ, Cooper EL (1991) A noninvasive technique for sequential collection of earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) leukocytes during subchronic immunotoxicity studies. Lab Anim-uk 25(1):61–67. doi:10.1258/002367791780808095
Faust F (2004) The use of the alkaline comet assay with lymphocytes in human biomonitoring studies. Mutat Res-rev Mutat 566(3):209–229. doi:10.1016/j.mrrev.2003.09.007
Frasco MF, Fournier D, Carvalho F, Guilhermino L (2005) Do metals inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE)? Implementation of assay conditions for the use of AChE activity as a biomarker of metal toxicity. Biomarkers 10(5):360–375. doi:10.1080/13547500500264660
Gastaldi L, Ranzato E, Caprì F, Hankard P, Pérès G, Canesi L, Viarengo A, Pons G (2007) Application of a biomarker battery for the evaluation of the sublethal effects of pollutants in the earthworm Eisenia andrei. Comp Biochem Phys C 146(3):398–405. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2007.04.014
Hankard PK, Svendsen C, Wright J, Wienberg C, Fishwick SK, Spurgeon DJ, Weeks JM (2004) Biological assessment of contaminated land using earthworm biomarkers in support of chemical analysis. Sci Total Environ 330(1–3):9–20. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2003.08.023
Honsi TG, Hoel L, Stenersen JV (1999) Non-inducibility of antioxidant enzymes in the earthworms Eisenia veneta and E. fetida after exposure to heavy metals and paraquat. Pedobiologia 43(6):652–657
Hu CW, Li M, Cui YB, Li DS, Chen J, Yang LY (2010) Toxicological effects of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles in soil on earthworm Eisenia fetida. Soil Biol Biochem 42:586–591. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.12.007
Key PB, Fulton MH (2002) Characterization of cholinesterase activity in tissues of the grass shrimp (Palaemonetes pugio). Pestic Biochem Phys 72(3):186–192. doi:10.1016/s0048-3575(02)00006-8
Khalil MA, AbdelLateif HM, Bayoumi BM, vanStraalen NM, vanGestel CAM (1996) Effects of metals and metal mixtures on survival and cocoon production of the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa. Pedobiologia 40(6):548–556
Łaszczyca P, Augustyniak M, Babczyńska A, Bednarska K, Kafel A, Migula P, Wilczek G, Witas I (2004) Profiles of enzymatic activity in earthworms from zinc, lead and cadmium polluted areas near Olkusz (Poland). Environ Int 30(7):901–910. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2004.02.006
Li M, Liu Z, Xu Y, Cui Y, Li D, Kong Z (2009) Comparative effects of Cd and Pb on biochemical response and DNA damage in the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Annelida, Oligochaeta). Chemosphere 74(5):621–625. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.10.048
Lourenço JI, Pereira RO, Silva AC, Morgado JM, Carvalho FP, Oliveira JM, Malta MP, Paiva AA, Mendo SA, Gonçalves FJ (2011) Genotoxic endpoints in the earthworms sub-lethal assay to evaluate natural soils contaminated by metals and radionuclides. J Hazard Mater 186(1):788–795. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.073
Luo Y-R, Wang S-H, Yun M-X, Li X-Y, Wang J-J, Sun Z-J (2009) The toxic effects of ionic liquids on the activities of acetylcholinesterase and cellulase in earthworms. Chemosphere 77:313–318. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.07.026
Luo Y, Zang Y, Zhong YA, Kong ZM (1999) Toxicological study of two novel pesticides on earthworm Eisenia foetida. Chemosphere 39(13):2347–2356. doi:10.1016/s0045-6535(99)00142-3
Lutz WK (1998) Dose–response relationships in chemical carcinogenesis: superposition of different mechanisms of action, resulting in linear–nonlinear curves, practical thresholds, J-shapes. Mutat Res-fund Mol M 405(2):117–124. doi:10.1016/s0027-5107(98)00128-6
Maity S, Roy S, Chaudhury S, Bhattacharya S (2008) Antioxidant responses of the earthworm Lampito mauritii exposed to Pb and Zn contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 151(1):1–7. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2007.03.005
Manerikar RS, Apte AA, Ghole VS (2008) In vitro and in vivo genotoxicity assessment of Cr(VI) using comet assay in earthworm coelomocytes. Environ Toxicol Phar 25(1):63–68. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2007.08.009
Nahmani J, Hodson ME, Black S (2007a) Effects of metals on life cycle parameters of the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to field-contaminated, metal-polluted soils. Environ Pollut 149(1):44–58. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.12.018
Nahmani J, Hodson ME, Black S (2007b) A review of studies performed to assess metal uptake by earthworms. Environ Pollut 145(2):402–424. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.04.009
Neuhauser EF, Loehr RC, Milligan DL, Maleck MR (1985) Toxicity of metals to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Biol and Fert Soils 1(3):149–152. doi:10.1007/BF00301782
Novais SC, Gomes SIL, Gravato C, Guilhermino L, De Coen W, Soares AMVM, Amorim MJB (2011) Reproduction and biochemical responses in Enchytraeus albidus (Oligochaeta) to zinc or cadmium exposures. Environ Pollut 159(7):1836–1843. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2011.03.031
Peijnenburg W, Jager T (2003) Monitoring approaches to assess bioaccessibility and bioavailability of metals: matrix issues. Ecotox Environ Safe 56(1):63–77. doi:10.1016/s0147-6513(03)0051-4
Qiao M, Chen Y, Wang C-X, Wang Z, Zhu Y-G (2007) DNA damage and repair process in earthworm after in-vivo and in vitro exposure to soils irrigated by wastewaters. Environ Pollut 148(1):141–147. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.10.033
Rao JV, Kavitha P (2004) Toxicity of azodrin on the morphology and acetylcholinesterase activity of the earthworm Eisenia foetida. Environ Res 96(3):323–327. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2004.02.014
Ribera D, Narbonne JF, Arnaud C, Saint-Denis M (2001) Biochemical responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida andrei exposed to contaminated artificial soil, effects of carbaryl. Soil Biol Biochem 33(7–8):1123–1130. doi:10.1016/s0038-0717(01)00035-9
Romani R, Antognelli C, Baldracchini F, De Santis A, Isani G, Giovannini E, Rosi G (2003) Increased acetylcholinesterase activities in specimens of Sparus auratus exposed to sublethal copper concentrations. Chem-biol Interact 145(3):321–329. doi:10.1016/s0009-2797(03)00058-9
Reinecke SA, Reinecke AJ (2004) The comet assay as biomarker of heavy metal genotoxicity in earthworms. Arch Environ Con Tox 46:208–215. doi:10.1007/s00244-003-2253-0
Saint-Denis M, Narbonne JF, Arnaud C, Ribera D (2001) Biochemical responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida andrei exposed to contaminated artificial soil: effects of lead acetate. Soil Biol Biochem 33(3):395–404. doi:10.1016/s0038-0717(00)00177-2
Saint-Denis M, Narbonne JF, Arnaud C, Thybaud E, Ribera D (1999) Biochemical responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida andrei exposed to contaminated artificial soil: effects of benzo[a]pyrene. Soil Biol Biochem 31(13):1837–1846. doi:10.1016/s0038-0717(99)00106-6
Sarkarati B, Cokugras AN, Tezcan EF (1999) Inhibition kinetics of human serum butyrylcholinesterase by Cd2+, Zn2+ and Al3+: comparison of the effects of metal ions on cholinesterases. Comp Biochem Physiol C-Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 122(2):181–190. doi:10.1016/s0742-8413(98)10102-0
Shi Y, Shi Y, Wang X, Lu Y, Yan S (2007) Comparative effects of lindane and deltamethrin on mortality, growth, and cellulase activity in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Pestic Biochem Phys 89:31–38. doi:10.1016/j.pestbp.2007.02.005
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low-levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175(1):184–191. doi:10.1016/0014-4827(88)90265-0
Spurgeon DJ, Hopkin SP (1995) Extrapolation of the laboratory-based OECD earthworm toxicity test to metal-contaminated field sites. Ecotoxicology 4(3):190–205. doi:10.1007/bf00116481
Spurgeon DJ, Hopkin SP (1996) Effects of variations of the organic matter content and pH of soils on the availability and toxicity of zinc to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Pedobiologia 40(1):80–96
Spurgeon DJ, Hopkin SP, Jones DT (1994) Effects of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc on growth, reproduction and survival of the earthworm Eisenia foetida (savigny)—assessing the environmental-impact of point-source metal contamination in terrestrial ecosystems. Environ Pollut 84(2):123–130. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(94)90094-9
Svendsen C, Spurgeon DJ, Hankard PK, Weeks JM (2004) A review of lysosomal membrane stability measured by neutral red retention: is it a workable earthworm biomarker? Ecotox Environ Safe 57(1):20–29. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2003.08.009
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H, Miyamae Y, Rojas E, Ryu JC, Sasaki YF (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35(3):206–221. doi:10.1002/(sici)1098-2280(2000)35:3<206::aid-em8>3.0.co;2-j
Venkateswara Rao J, Surya Pavan Y, Madhavendra SS (2003) Toxic effects of chlorpyrifos on morphology and acetylcholinesterase activity in the earthworm, Eisenia foetida. Ecotox Environ Safe 54(3):296–301. doi:10.1016/s0147-6513(02)00013-1
Wei B, Yang L (2010) A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem J 94(2):99–107. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2009.09.014
Xia JC (1996) Detailed study of the soil environmental quality standards. China environmental science publisher, Beijing, China (in Chinese)
Xiao N-W, Song Y, Ge F, Liu X-H, Ou-Yang Z-Y (2006a) Biomarkers responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida to acetochlor exposure in OECD soil. Chemosphere 65(6):907–912. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.03.060
Xiao NW, Jing B, Ge F, Liu XH (2006b) The fate of herbicide acetochlor and its toxicity to Eisenia fetida under laboratory conditions. Chemosphere 62(8):1366–1373. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.07.043
Xiao RY, Wang ZJ, Wang CX, Yu G, Zhu YG (2006c) Genotoxic risk identification of soil contamination at a major industrialized city in northeast China by a combination of in vitro and in vivo bioassays. Environ Sci Technol 40(19):6170–6175. doi:10.1021/es0607335
Xie X, Wu Y, Zhu M, Y-k Z, Wang X (2011) Hydroxyl radical generation and oxidative stress in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209). Ecotoxicology 20(5):993–999. doi:10.1007/s10646-011-0645-x
Zatta P, Ibn-Lkhayat-Idrissi M, Zambenedetti P, Kilyen M, Kiss T (2002) In vivo and in vitro effects of aluminum on the activity of mouse brain acetylcholinesterase. Brain Res Bull 59(1):41–45. doi:10.1016/s0361-9230(02)00836-5
Zhang DA (1991) The experimental handbook of biological macromolecule. The press of Jilin University. Changchun, China (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Support Program of Jiangsu Province (No. BE2012737), Public Sector Special Scientific Research Program of the National Environmental Protection Ministry (No. 2011467054), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21077052). The authors are grateful to Richard A. Manderville for his assistance and helpful advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, K., Liu, Z., Li, Y. et al. Toxicological responses of earthworm (Eisenia fetida) exposed to metal-contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 8382–8390 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1689-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1689-7