Abstract
Background
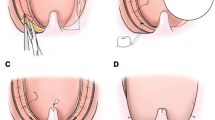
Another transoral tongue base surgical procedure for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is described. The procedure was named as the “Robo-Cob” technique because it is similar to transoral robotic surgery (TORS) but using a coblation technology to manage tongue base hypertrophy in patients with OSA especially in countries where TORS is not an available option for such benign conditions.
Methods
The technique is described step by step. The new surgical technique was carried out in 25 adult OSA patients with mean age of 41.36 ± 8.72 years (average 23–56) with confirmed tongue base hypertrophy by preoperative drug-induced sleep endoscopy (DISE). Coblation was used to resect, not ablate, the tongue base with similar technique as described in TORS.
Results
The Robo-Cob technique is proved to be feasible and effective in all cases either alone or when combined with other procedures in multilevel surgery settings. There were no significant intraoperative or postoperative complications. No tracheostomy was done in any patient. Objective clinical improvement was confirmed by polysomnography 3 months postoperatively with significant decrease in mean AHI from 33.84 ± 10.54 to 11.52 ± 5.42 (P < 0.005). Moreover, this technique provided tongue base tissue specimen that allowed measurement of its volume that ranged from 10 to 22 cc (mean 14.96 ± 3.62 cc) to monitor extent of tissue resection.
Conclusion
The added value of using coblation in resection, not ablation, is being quicker, and being able to provide tissue specimen to measure its volume to judge resection limits.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee EJ, Cho JH (2019) Meta-analysis of obstruction site observed with drug-induced sleep endoscopy in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Laryngoscope 129:1235–1243. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.27320
Vicini C, Dallan I, Canzi P, Frassineti S, La Pietra MG, Montevecchi F (2010) Transoral robotic tongue base resection in obstructive sleep apnoea-hypopnoea syndrome: a preliminary report. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 72(1):22–27
Stuck BA, Maurer JT, Verse T, Hormann K (2002) Tongue base reduction with temperature-controlled radiofrequency volumetric tissue reduction for treatment of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Acta Otolaryngol 122(5):531–536
MacKay SG, Carney AS, Woods C, Antic N, McEvoy RD, Chia M et al (2013) Modified uvulopalatopharyngoplasty and coblation channeling of the tongue for obstructive sleep apnea: a multi-centre Australian trial. J Clin Sleep Med 9(2):117–124
Chabolle F, Wagner I, Blumen MB, Sequert C, Fleury B, De Dieuleveult T (1999) Tongue base reduction with hyoepiglottoplasty: a treatment for severe obstructive sleep apnea. Laryngoscope 109(8):1273–1280
Vicini C, Dallan I, Canzi P, Frassineti S, Nacci A, Seccia V, Panicucci E, Grazia la Pietra M, Montevecchi F, Tschabitscher M (2012) Transoral robotic surgery of the tongue base in obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome: anatomic considerations and clinical experience. Head Neck 34(1):15–22
Cammaroto G, Montevecchi F, D'Agostino G, Zeccardo E, Bellini C, Galletti B, Shams M, Negm H, Vicini C (2017) Tongue reduction for OSAHS: TORSs vs coblations, technologies vs techniques, apples vs oranges. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274(2):637–645
Li HY, Lee LA, Kezirian EJ (2016) Coblation endoscopic lingual lightening (CELL) for obstructive sleep apnea. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273(1):231–236
Li HY, Lee LA, Kezirian EJ (2016) Efficacy of Coblation endoscopic lingual lightening in multilevel surgery for obstructive sleep apnea. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 142(5):438–443
Robinson S, Ettema SL, Brusky L, Woodson BT (2006) Lingual tonsillectomy using bipolar radiofrequency plasma excision. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134(2):328–330
Maturo SC, Mair EA (2006) Coblation lingual tonsillectomy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135(3):487–488
Hoff PT, D'Agostino MA, Thaler ER (2015) Transoral robotic surgery in benign diseases including obstructive sleep apnea: safety and feasibility. Laryngoscope 125(5):1249–1253
Vicini C, Montevecchi F, Campanini A, Dallan I, Hoff PT, Spector ME, Thaler E, Ahn J, Baptista P, Remacle M, Lawson G, Benazzo M, Canzi P (2014) Clinical outcomes and complications associated with TORS for OSA: a benchmark for evaluating an emerging surgical technology in a targeted application for benign disease. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 76(2):63–69
Cho H-J, Park D-Y, Min HJ, Chung HJ, Lee J-G, Kim C-H (2016) Endoscope-guided coblator tongue base resection using an endoscope-holding system for obstructive sleep apnea. Head Neck 38:635–639. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.24252
Funding
This study received no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Presentation at a conference:
This paper was presented as oral presentation during:
• The First International Egyptian Laryngological & Sleep surgery society congress ELSSS, January 2018
• 8th Emirates Rhinology & Otology Congress EROC, January 2018
• RhinoEgypt, March 2018
• AlexORL, April 2019
• RhinoEgypt, March 2018
• 9th Emirates Rhinology & Otology Congress EROC, January 2019
• AlexORL, April 2019
• 106th Italian Society of Otolaryngology, June 2019
This paper was presented as poster presentation during:
• American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head&Neck Surgery Meeting, September 2018
• 5th Congress of European ORL-HNS, July 2019
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahgat, A., Bahgat, Y. Robo-Cob technique; transoral endoscopic coblation tongue base resection in obstructive sleep apnea patients. Sleep Breath 25, 411–415 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-020-02101-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-020-02101-5