Abstract
Objective
The objective of our research was to explore the effects of maternal and postpartum chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) exposure on atherosclerosis in adulthood offspring of rats, and the role of Caveolin-1 in the course.
Methods
Sixteen rats were assigned to two groups (n = 8), maternal normoxia and CIH group. After delivery, two male pups per litter were selected and breastfed for 1 month, which then randomly received postpartum normoxia or CIH. Thus, 4 groups were created as follows (n = 8): (1) maternal normoxia and postpartum normoxia group, (2) maternal CIH and postpartum normoxia group, (3) maternal CIH and postpartum CIH group, and (4) maternal normoxia and postpartum CIH group. The offspring were weighed at birth and weaning. After the duration of 12-week experiment, morphological changes, the expression of Caveolin-1 and NF-κB p65 in the aorta were detected.
Results
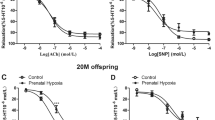
Maternal CIH resulted in significantly lower body weight and thicker intima (P < 0.001). CIH upregulated the expression of Caveolin-1 and NF-κB p65 significantly (P < 0.01). There was a synergistic effect of maternal and postpartum CIH on the thickening of intima (P < 0.05), also on the expression of Caveolin-1 and NF-κB p65 (P < 0.01).
Conclusions
The results demonstrate that maternal CIH exposure causes a postpartum catch-up growth and early atherosclerotic changes followed by upregulating Caveolin-1 expression. Besides, maternal CIH enhances the atherosclerotic changes caused by postpartum CIH. Oxidative stress probably implicates in above effects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lorenzi-Filho G, Drager LF (2009) Obstructive sleep apnea and atherosclerosis: a new paradigm. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 51:400–410
Bonomini F, Tengattini S, Fabiano A et al (2008) Atherosclerosis and oxidative stress. Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi Japanese Journal of Geriatrics 45:287–290
Savransky V, Nanayakkara A, Li J, Bevans S, Smith PL, Rodriguez A, Polotsky VY (2007) Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces atherosclerosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 175:1290–1297
Pien GW, Pack AI, Jackson N, Maislin G, Macones GA, Schwab RJ (2014) Risk factors for sleep-disordered breathing in pregnancy. Thorax 69:371–377
Barker DJP (1995) The wellcome foundation lecture, 1994. The fetal origins of adult disease. Proc Biol Sci 262:37–43
Barker DJ, Osmond C, Simmonds SJ, Wield GA (1993) The relation of small head circumference and thinness at birth to death from cardiovascular disease in adult life. BMJ 306:422–426
Wang Z, Huang Z, Lu G, Lin L, Ferrari M (2009) Hypoxia during pregnancy in rats leads to early morphological changes of atherosclerosis in adult offspring. Am J Phys Heart Circ Phys 296:H1321–H1328
Cohen AW, Hnasko R, Schubert W, Lisanti MP (2004) Role of caveolae and caveolins in health and disease. Physiol Rev 84:1341–1379
Razani B, Woodman SE, Lisanti MP (2002) Caveolae: from cell biology to animal physiology. Pharmacol Rev 54:431–467
Smart EJ, Graf GA, McNiven MA, Sessa WC, Engelman JA, Scherer PE, Okamoto T, Lisanti MP (1999) Caveolins, liquid-ordered domains, and signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol 19:7289–7304
Ingueneau C, Huynh-Do U, Thiers JC, Nègre-Salvayre A, Salvayre R, Vindis C (2008) Caveolin-1 sensitizes vascular smooth muscle cells to mildly oxidized LDL-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 369:889–893
Lin WW, Lin YC, Chang TY, Tsai SH, Ho HC, Chen YT, Yang VC (2006) Caveolin-1 expression is associated with plaque formation in hypercholesterolemic rabbits. J Histochem Cytochem 54:897–904
Schwencke C, Schmeisser A, Walter C et al (2005) Decreased caveolin-1 in atheroma: loss of antiproliferative control of vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res 68:128–135
Roth DM, Patel HH (2011) Role of caveolae in cardiac protection. Pediatr Cardiol 32:329–333
Wang WY, Zeng YM, Chen XY et al (2013) Effect of Telmisartan on local cardiovascular oxidative stress in mouse under chronic intermittent hypoxia condition. Sleep Breath 17:435–435
Chen L, Zadi ZH, Zhang J et al (2017) Intermittent hypoxia in utero damages postnatal growth and cardiovascular function in rats. J Appl Physiol 124:821–830
Iqbal W, Ciriello J (2013) Effect of maternal chronic intermittent hypoxia during gestation on offspring growth in the rat. Am J Obstet Gynecol 209:1–9
Peebles DM (2004) Fetal consequences of chronic substrate deprivation. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 9:379–386
Fagerberg B, Bondjers L, Nilsson P (2004) Low birth weight in combination with catch-up growth predicts the occurrence of the metabolic syndrome in men at late middle age: the atherosclerosis and insulin resistance study. J Intern Med 256:254–259
Bol VV, Delattre AI, Reusens B et al (2009) Forced catch-up growth after fetal protein restriction alters the adipose tissue gene expression program leading to obesity in adult mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 297:291–299
Sasaki S, Yoneda Y, Fujita H, Uchida A, Takenaka K, Takesako T, Itoh H, Nakata T, Takeda K, Nakagawa M (1994) Association of blood pressure variability with induction of atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rats. Am J Hypertens 7:453–459
Michiels C, Minet E, Mottet D, Raes M (2002) Regulation of gene expression by oxygen: NF-kappaB and HIF-1, two extremes. Free Radic Biol Med 33:1231–1242
Libby P (2002) Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 420:868–874
Kavurma MM, Schoppet M, Bobryshev YV, Khachigian LM, Bennett MR (2008) TRAIL stimulates proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells via activation of NF-kappaB and induction of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. J Biol Chem 283:7754–7762
Wu CC, Wang SH, Kuan II, Tseng WK, Chen MF, Wu JC, Chen YL (2009) OxLDL upregulates caveolin-1 expression in macrophages: role for caveolin-1 in the adhesion of oxLDL-treated macrophages to endothelium. J Cell Biochem 107:460–472
Fernández-Hernando C, Yu J, Suárez Y, Rahner C, Dávalos A, Lasunción MA, Sessa WC (2009) Genetic evidence supporting a critical role of endothelial caveolin-1 during the progression of atherosclerosis. Cell Metab 10:48–54
Fernández-Hernando C, Yu J, Dávalos A, Prendergast J, Sessa WC (2010) Endothelial-specific overexpression of caveolin-1 accelerates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Am J Pathol 177:998–1003
Frank PG, Lisanti MP (2004) Caveolin-1 and caveolae in atherosclerosis: differential roles in fatty streak formation and neointimal hyperplasia. Curr Opin Lipidol 15:523–529
Hassan GS, Williams TM, Frank PG, Lisanti MP (2006) Caveolin-1-deficient aortic smooth muscle cells show cell autonomous abnormalities in proliferation, migration, and endothelin-based signal transduction. Am J Phys Heart Circ Phys 290:H2393–H2401
Li G, Xiao Y, Estrella JL, Ducsay CA, Gilbert RD, Zhang L (2003) Effect of fetal hypoxia on heart susceptibility to ischemia and reperfusion injury in the adult rat. J Soc Gynecol Investig 10:265–274
Funding
This works was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Number 81770016), Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (Number 2015J01445), Young people training project from Fujian Province Health System (Number2014JQNJC20), Fund from Quanzhou Science and Technology Bureau (Number2013Z55), and Quanzhou Science and Technology Project (Number 2018N028S).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experiments were conducted in accordance with National Institutes of Health guidelines. The study protocols were approved by the Standing Committee on Ethics and Animal Experimentation at Fujian Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The animal experiments were performed after approval from the Standing Committee on Ethics and Animal Experimentation at Fujian Medical University.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, H., Zeng, Y. & Wang, Z. Maternal chronic intermittent hypoxia in rats causes early atherosclerosis with increased expression of Caveolin-1 in offspring. Sleep Breath 23, 1071–1077 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-019-01781-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-019-01781-y