Abstract
Purpose
Restless legs syndrome is a movement sleep disorder that may be linked to dopaminergic dysfunction and in which vitamin D may play a role. This 12-week randomized, placebo-controlled trial elucidated the efficacy of vitamin D supplements in decreasing restless legs syndrome symptom severity.
Methods
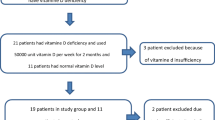
Thirty-five subjects with restless legs syndrome, diagnosed using the International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group criteria, were enrolled. The subjects were randomized to orally receive either vitamin D (50,000 IU caplets) or a placebo. All medications were administered weekly using a direct observation technique. Clinical assessments, including those for restless legs syndrome severity, were conducted at baseline and the end of the study using the International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group rating scale. The serum vitamin D levels and bone profiles were measured at baseline and every 4 weeks. The primary endpoint was the change in the restless legs syndrome severity score from baseline to week 12. There were 17 and 18 patients in the vitamin D and placebo groups, respectively.
Results
The groups did not differ with respect to age, sex, restless legs syndrome severity, or vitamin D levels. Participants in the vitamin D group showed no significant change in the mean restless legs syndrome severity score compared with the placebo group.
Conclusions
The results suggest that vitamin D supplementation does not improve restless legs syndrome symptoms.
Clinical trial registration number
ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02256215 (available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02256215).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RP, Picchietti D, Hening WA, Trenkwalder C, Walters AS, Montplaisi J, Restless Legs Syndrome Diagnosis and Epidemiology workshop at the National Institutes of Health, International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group (2003) Restless legs syndrome: diagnostic criteria, special considerations, and epidemiology. A report from the Restless Legs Syndrome Diagnosis and Epidemiology workshop at the National Institutes of Health. Sleep Med 4:101–119
Allen RP, Walters AS, Montplaisir J, Hening W, Myers A, Bell TJ, Ferini-Strambi L (2005) Restless legs syndrome prevalence and impact: REST general population study. Arch Intern Med 165:1286–1292
Allen RP, Bharmal M, Calloway M (2011) Prevalence and disease burden of primary restless legs syndrome: results of a general population survey in the United States. Mov Disord 26:114–120
Berger K, Kurth T (2007) RLS epidemiology—frequencies, risk factors and methods in population studies. Mov Disord 22:S420–S423
Wali SO, Abaalkhail B (2015) Prevalence of restless legs syndrome and associated risk factors among middle-aged Saudi population. Ann Thorac Med 10:193–198
Chokroverty S, Jankovic J (1999) Restless legs syndrome: a disease in search of identity. Neurology 5:907–910
Turjanski N, Lees AJ, Brooks DJ (1999) Striatal dopaminergic function in restless legs syndrome: 18F-dopa and 11C-raclopride PET studies. Neurology 52:932–937
Montplaisir J, Nicolas A, Denesle R, Gomez-Mancilla B (1999) Restless legs syndrome improved by pramipexole: a double-blind randomized trial. Neurology 52:938–943
Prakash S, Bhanvadia RJ, Shah ND (2010) Restless legs syndrome with carbamazepine-induced osteomalacia: causal or casual association. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 32:228.e1–228.e3
Wetter TC, Stiasny K, Winkelmann J, Buhlinger A, Brandenburg U, Penzel T, Medori R, Rubin M, Oertel WH, Trenkwalder C (1999) A randomized controlled study of pergolide in patients with restless legs syndrome. Neurology 52:944–950
Baksi SN, Hughes MJ (1982) Chronic vitamin D deficiency in the weanling rat alters catecholamine metabolism in the cortex. Brain Res 242:387–390
Ibi M, Sawada H, Nakanishi M, Kume T, Katsuki H, Kaneko S, Shimohama S, Akaike A (2001) Protective effects of 1,25-(OH)2D3 against the neurotoxicity of glutamate and reactive oxygen species in mesencephalic culture. Neuropharmacology 40:761–771
Garcion E, Sindji L, Leblondel G, Brachet P, Darcy F (1999) 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 regulates the synthesis of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and glutathione levels in rat primary astrocytes. J Neurochem 73:859–866
Nakamura K, Wang W, Kang UJ (1997) The role of glutathione in dopaminergic neuronal survival. J Neurochem 69:1850–1858
Cui X, Pelekanos M, Liu PY, Burne THJ, McGrath JJ, Eyles DW (2013) The vitamin D receptor in dopamine neurons; its presence in human substantia nigra and its ontogenesis in rat midbrain. Neuroscience 236:77–87
Orme RP, Bhangal MS, Fricker RA (2013) Calcitriol imparts neuroprotection in vitro to midbrain dopaminergic neurons by upregulating GDNF expression. PLoS One 8:e62040
Balaban H, Yıldız ÖK, Çil G, Şentürk İA, Erselcan T, Bolayır E, Topaktaş S (2012) Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in restless legs syndrome patients. Sleep Med 13:953–957
Allen RP, Picchietti DL, Garcia-Borreguero D, Ondo WG, Walters AS, Winkelman JW, Zucconi M, Ferri R, Trenkwalder C, Lee HB, International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group (2014) Restless legs syndrome/Willis–Ekbom disease diagnostic criteria: updated International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group (IRLSSG) consensus criteria—history, rationale, description, and significance. Sleep Med 15:860–873
Wali S et al (2017) The effect of vitamin D replacement therapy in restless legs syndrome: a randomized trial. CHEST 152(4):A1069
Walters AS, LeBrocq C, Dhar A, Hening W, Rosen R, Allen RP, Trenkwalder C, International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group (2003) Validation of the International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group rating scale for restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med 4:121–132
Van Schoor NM, Lips P (2011) Worldwide vitamin D status. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 25:671–680
Lips P (2004) Which circulating level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D is appropriate? J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 89-90:611–614
Abetz L, Arbuckle R, Allen RP, Garcia-Borreguero D, Hening W, Walters AS, Mavraki E, Kirsch JM (2006) The reliability, validity and responsiveness of the International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group rating scale and subscales in a clinical-trial setting. Sleep Med 7:340–349
Ondo WG, Grieger F, Moran K, Kohnen R, Roth T (2016) Post hoc analysis of data from two clinical trials evaluating the minimal clinically important change in international restless legs syndrome sum score in patients with restless legs syndrome (Willis–Ekbom disease). J Clin Sleep Med 12:63–70
Oran M, Unsal C, Albayrak Y, Tulubas F, Oguz K, Avci O, Turgut N, Alp R, Gurel A (2014) Possible association between vitamin D deficiency and restless legs syndrome. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 10:953–958
Wali S, Shukr A, Boudal A et al (2015) The effect of vitamin D supplements on the severity of restless legs syndrome. Sleep Breath 19:579–583 Erratum in: sleep breath 2015, 1:1483
Wali S, Alsafadi S, Abaalkhail B, Ramadan I, Abulhamail B, Kousa M, Alshamrani R, Faruqui H, Faruqui A, Alama M, Hamed M (2018) The association between vitamin D level and restless legs syndrome: a population-based case–control study. J Clin Sleep Med 14:557–564
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the participants of the study. The authors would like to thank Dr. Ohoud Shakroon, Clinical Pharmacist, King Abdulaziz University Hospital, for her substantial assistance in providing the required medications. The authors greatly appreciate Drs. Mohamed Hamed, Khaled Aljammali, and Hanadi Sabbahi for their effort in collecting data. Finally, special thanks to Dr. Ghada Qadi for help with the preparation of the proposal and to Mrs. Walaa Abuzahra, Research Coordinator, Sleep Medicine and Research Center, for her time and effort in coordinating all procedures. The preliminary results of this study were presented at the Chest Annual Meeting 2017 (Wali SO, et al. Control ID 2729173. Presented at CHEST Annual Meeting, Oct 28–Nov 1, 2017, Toronto, ON, Canada).
Funding
This project was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah (grant no. G-1436-140-279). The authors acknowledge DSR with thanks for their technical and financial support. The funding source had no involvement in the study design, manuscript preparation, or decision to submit the article for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept development: S.O.W. Study design: S.O.W. Data acquisition, supervision, data analysis, and interpretation: S.O.W., B.A., F.A. Manuscript preparation: S.O.W., B.A., F.A. Critical revision of the manuscript: S.O.W., S.R.P.-P. Prior to submission, all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval and consent for participation
The study was approved by the Human Institutional Ethics Committee of King Abdulaziz University Hospital (Approval No. HA-02-J-008). Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wali, S.O., Abaalkhail, B., Alhejaili, F. et al. Efficacy of vitamin D replacement therapy in restless legs syndrome: a randomized control trial. Sleep Breath 23, 595–601 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-018-1751-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-018-1751-2