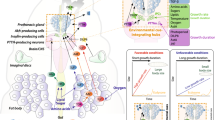
Abstract
Introduction
Metamorphosis is a complicated process in which cell proliferation, differentiation, and death are orchestrated to form the mature structures of insects. In Drosophila, this process is controlled by ecdysone, a steroid hormone responsible for tissue remodeling and organogenesis that gives rise to the adult fly.
Objective
By using a metabolomics approach, this study aimed to elucidate global changes in the central metabolic pathways in Drosophila throughout metamorphosis and then further examine the effects of temperature and origin on metabolic profiles.
Methods
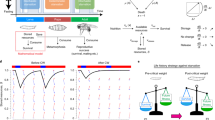
Targeted and non-targeted metabolic profiling of time-course samples from Drosophila were constructed to cover a wide range of cellular metabolites during metamorphosis.
Results
This was the first wide-scale metabolomics study of Drosophila metamorphosis focusing on central metabolism. The abundance of detected metabolites changed drastically and correlated strongly with the development of Drosophila pupae. In non-stress conditions, temperature affected the developmental time, but the metabolic state at a certain stage of metamorphosis remained stable. Between D. melanogaster Canton S and Oregon R, similar metabolic profiles throughout metamorphosis was observed. However, there were still differences in purine and pyrimidine metabolism at an early stage in the pupal period, which was matched by differences in ecdysteroid levels.
Conclusion
This study supported the strength of metabolomics in the field of developmental biology. The results provided a general view on the metabolic profile of Drosophila during metamorphosis, which provides basic 3 knowledge for future metabolomics studies using Drosophila.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrell, I. P. S., & Lundquist, A. M. (1973). Chapter 4—physiological and biochemical changes during insect development. In M. Rockstein. (Ed.), The physiology of insecta (Second Edition). New York: Academic Press.
Aguila, J. R., Suszko, J., Gibbs, A. G. & Hoshizaki, D. K. (2007). The role of larval fat cells in adult Drosophila melanogaster. Journal of Experimental Biology, 210, 956–963.
An, P. N., Yamaguchi, M., Bamba, T., & Fukusaki, E. (2014). Metabolome analysis of Drosophila melanogaster during embryogenesis. PLoS One, 9, e99519.
Andres, A. J., Fletcher, J. C., Karim, F. D., & Thummel, C. S. (1993). Molecular analysis of the initiation of insect metamorphosis: A comparative study of Drosophila ecdysteroid-regulated transcription. Developmental Biology, 160, 388–404.
Baehrecke, E. H. (1996). Ecdysone signaling cascade and regulation of Drosophila metamorphosis. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 33, 231–244.
Bainbridge, S. P., & Bownes, M. (1981). Staging the metamorphosis of Drosophila melanogaster. Journal of Embryology and Experimental Morphology, 66, 57–80.
Chiang, H. C. (1963). Tactic reactions of young adults of Drosophila melanogaster. The American Midland Naturalist, 70, 329–338.
Chintapalli, V. R., Al Bratty, M., Korzekwa, D., Watson, D. G., & Dow, J. A. (2013). Mapping an atlas of tissue-specific Drosophila melanogaster metabolomes by high resolution mass spectrometry. PLoS One, 8, e78066.
Davis, M. B., & Li, T. (2013). Genomic analysis of the ecdysone steroid signal at metamorphosis onset using ecdysoneless and EcRnull Drosophila melanogaster mutants. Genes Genomics, 35, 21–46.
Dempo, Y., Ohta, E., Nakayama, Y., Bamba, T., & Fukusaki, E. (2014). Molar-based targeted metabolic profiling of cyanobacterial strains with potential for biological production. Metabolites, 4, 499–516.
Duffy, J. B. (2002). GAL4 system in Drosophila: a fly geneticist’s Swiss army knife. Genesis (New York, N. Y.: 2000), 34, 1–15.
Eriksson, L., Jaworska, J., Worth, A. P., Cronin, M. T., Mcdowell, R. M., & Gramatica, P. (2003). Methods for reliability and uncertainty assessment and for applicability evaluations of classification- and regression-based QSARs. Environmental health perspectives, 111, 1361–1375.
Gilbert, L. I., & Schneiderman, H. A. (1961). Some biochemical aspects of insect metamorphosis. American Zoologist, 1, 11–51.
Hariharan, R., Hoffman, J. M., Thomas, A. S., Soltow, Q. A., Jones, D. P., & Promislow, D. E. (2014). Invariance and plasticity in the Drosophila melanogaster metabolomic network in response to temperature. BMC Systems Biology, 8, 139.
Hashim, Z., Mukai, Y., Bamba, T., & Fukusaki, E. (2014). Metabolic profiling of retrograde pathway transcription factors rtg1 and rtg3 knockout yeast. Metabolites, 4, 580–598.
Hoffman, J. M., Soltow, Q. A., Li, S., Sidik, A., Jones, D. P., & Promislow, D. E. (2014). Effects of age, sex, and genotype on high-sensitivity metabolomic profiles in the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster. Aging Cell, 13, 596–604.
Howe, E., Holton, K., Nair, S., Schlauch, D., Sinha, R., & Quackenbush, J. (2010). MeV: MultiExperiment viewer. In M. F. Ochs, J. T. Casagrande & R. V. Davuluri. (Eds.), Biomedical informatics for cancer research. Berlin: Springer.
Kamleh, M. A., Hobani, Y., Dow, J. A. T., Zheng, L., & Watson, D. G. (2009). Towards a platform for the metabonomic profiling of different strains of Drosophila melanogaster using liquid chromatography–Fourier transform mass spectrometry. FEBS Journal, 276, 6798–6809.
Kawase, N., Tsugawa, H., Bamba, T. & Fukusaki, E. (2014). Different-batch metabolome analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae based on gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 117, 248–255.
Laye, M. J., Tran, V., Jones, D. P., Kapahi, P., & Promislow, D. E. (2015). The effects of age and dietary restriction on the tissue-specific metabolome of Drosophila. Aging Cell, 14, 797–808.
Lee, Y., & Montell, C. (2013). Drosophila TRPA1 functions in temperature control of circadian rhythm in pacemaker neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 33, 6716–6625.
Lindsley, D. L., Grell, E. H., & Bridges, C. B. (1972). Genetic variations of Drosophila melanogaster. Washington, D.C: Carnegie institution of Washington.
Linford, N. J., Bilgir, C., Ro, J., & Pletcher, S. D. (2013). Measurement of lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster. The Journal of Visualized Experiments. doi:10.3791/50068.
Merkey, A. B., Wong, C. K., Hoshizaki, D. K., & Gibbs, A. G. (2011). Energetics of metamorphosis in Drosophila melanogaster. Journal of Insect Physiology, 57, 1437–1445.
Mitchell, C. L., Yeager, R. D., Johnson, Z. J., D’annunzio, S. E., Vogel, K. R., & Werner, T. (2015). Long-term resistance of Drosophila melanogaster to the mushroom toxin alpha-amanitin. PLoS One, 10, e0127569.
Nation, J. L. (2008). Insect physiology and biochemistry, Second Edition. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Putri, S. P., Nakayama, Y., Matsuda, F., Uchikata, T., Kobayashi, S., Matsubara, A. & Fukusaki, E. (2013). Current metabolomics: practical applications. The Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 115, 579–589.
Rajamohan, A., & Sinclair, B. J. (2009). Hardening trumps acclimation in improving cold tolerance of Drosophila melanogaster larvae. Physiological Entomology, 34, 217–223.
Reed, L. K., Lee, K., Zhang, Z., Rashid, L., Poe, A., Hsieh, B., Deighton, N., Glassbrook, N., Bodmer, R., & Gibson, G. (2014). Systems genomics of metabolic phenotypes in wild-type Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics, 197, 781–793.
Salmon, A. B., Marx, D. B., & Harshman, L. G. (2001). A cost of reproduction in Drosophila melanogaster: stress susceptibility. Evolution, 55, 1600–1608.
Scott Chialvo, C. H., Che, R., Reif, D., Motsinger-Reif, A., & Reed, L. K. (2016). Eigenvector metabolite analysis reveals dietary effects on the association among metabolite correlation patterns, gene expression, and phenotypes. Metabolomics, 12, 167.
St Johnston, D. (2002). The art and design of genetic screens: Drosophila melanogaster. Nature Reviews Genetics, 3, 176–188.
Tennessen, J. M., Baker, K. D., Lam, G., Evans, J., & Thummel, C. S. (2011). The Drosophila estrogen-related receptor directs a metabolic switch that supports developmental growth. Cell Metabolism, 13, 139–148.
Tennessen, J. M., Bertagnolli, N. M., Evans, J., Sieber, M. H., Cox, J., & Thummel, C. S. (2014). Coordinated metabolic transitions during Drosophila embryogenesis and the onset of aerobic glycolysis. G3 (Bethesda), 4, 839–850.
Theodosiou, N. A., & Xu, T. (1998). Use of FLP/FRT system to study Drosophila development. Methods (San Diego, Calif.), 14, 355–365.
Tortoriello, G., Rhodes, B. P., Takacs, S. M., Stuart, J. M., Basnet, A., Raboune, S., Widlanski, T. S., Doherty, P., Harkany, T., & Bradshaw, H. B. (2013). Targeted lipidomics in Drosophila melanogaster identifies novel 2-monoacylglycerols and N-acyl amides. PLoS One, 8, e67865.
Tsugawa, H., Tsujimoto, Y., Arita, M., Bamba, T., & Fukusaki, E. (2011). GC/MS based metabolomics: development of a data mining system for metabolite identification by using soft independent modeling of class analogy (SIMCA). BMC Bioinformatics, 12, 131.
Vaiserman, A. M., Zabuga, O. G., Kolyada, A. K., Pisaruk, A. V., & Kozeretska, I. A. (2013). Reciprocal cross differences in Drosophila melanogaster longevity: an evidence for non-genomic effects in heterosis phenomenon? Biogerontology, 14, 153–163.
Warren, J. T., Yerushalmi, Y., Shimell, M. J., O’connor, M. B., Restifo, L. L., & Gilbert, L. I. (2006). Discrete pulses of molting hormone, 20-hydroxyecdysone, during late larval development of Drosophila melanogaster: correlations with changes in gene activity. Developmental Dynamics, 235, 315–326.
Wheelock, Å. & Wheelock, C. E (2013). Trials and tribulations of ‘omics data analysis: assessing quality of SIMCA-based multivariate models using examples from pulmonary medicine. Molecular BioSystems, 9, 2589–2596.
Wigglesworth, V. B. (2012). The principles of insect physiology. Berlin: Springer.
Williams, S., Dew-Budd, K., Davis, K., Anderson, J., Bishop, R., Freeman, K., Davis, D., Bray, K., Perkins, L., Hubickey, J., & Reed, L. K. (2015). Metabolomic and gene expression profiles exhibit modular genetic and dietary structure linking metabolic syndrome phenotypes in Drosophila. G3 (Bethesda), 5, 2817–2829.
Xia, J., Sinelnikov, I. V., Han, B., & Wishart, D. S. (2015). MetaboAnalyst 3.0—making metabolomics more meaningful. Nucleic Acids Research, 43, W251–W257.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Bloomington Stock Center and Prof. Mi-Ae Yoo for fly stocks. This study was partially supported by Grants-in-Aid from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Core-to-Core Program, B. Asia-Africa Science Platforms. Phan Nguyen Thuy An is supported financially by The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan. This study represents a portion of the dissertation submitted by Phan Nguyen Thuy An to Osaka University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for her Ph.D.
Author contributions
P.N.T.A., M.Y., and E.F. conceived, designed and analyzed the experiments. P.N.T.A. and M.Y. performed the experiments. P.N.T.A. wrote the paper. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Funding
This study is partially supported by Grants-in-Aid from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Core-to-Core Program, B. Asia-Africa Science Platforms.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, P.N.T., Yamaguchi, M. & Fukusaki, E. Metabolic profiling of Drosophila melanogaster metamorphosis: a new insight into the central metabolic pathways. Metabolomics 13, 29 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1167-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1167-1