Abstract
Introduction
The ability of urinary metabolomics to detect meaningful, tissue-specific, biological effects (i.e., toxicity, disease) is compounded by high background variability. We hypothesize that sensitivity can be enhanced by imposing a tissue-targeted metabolic stressor.
Objective
We tested whether the sensitivity of metabolomics to assess kidney function is improved under the diuretic stress of furosemide.
Methods
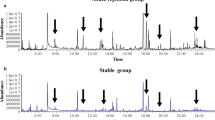
To mildly compromise kidney, rats were given a sub-acute dose of d-serine. Then at 24 h postdose, we administered vehicle solution (control) or the diuretic drug, furosemide, and conducted NMR-based urinary metabolomics.
Results
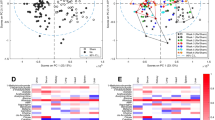
Principal Components and OPLS discriminant analyses showed no effects on urinary profiles in rats receiving d-serine alone. However, the effects of d-serine were observable under furosemide-induced stress, as urinary profiles classified separately from rats receiving furosemide alone or vehicle-treated controls (p < 0.001). Furthermore, this profile was uniquely different from a co-treatment effect observed following co-administration of d-serine + furosemide. We identified 24 metabolites to classify the effects of furosemide in normal rats vs. d-serine-compromised rats. Most notably, a furosemide-induced increase in urinary excretion of α-ketoglutarate, creatinine, trigonelline, and tryptophan in control rats, was significantly reduced in d-serine exposed rats (p < 0.05). Interestingly, increased tryptophan metabolism has been shown to correlate with the severity of kidney transplant failure and chronic kidney disease.
Conclusions
We attribute these effects to differences in kidney function, which were only detectable under the stress imposed by furosemide. This technique may extend to other organ systems and may provide improved sensitivity for assessment of tissue function or early detection of disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We “spiked” a urine sample with furosemide at a concentration equivalent to that which would be expected assuming that the entire furosemide dose was excreted into urine within 24 h postdose (~0.3 mM). The observable furosemide signals were very weak, and in experimental animal samples the signals were barely detectable and did not interfere with our analyses, as none were chosen as salient features for class discrimination. Detection of furosemide metabolites was ignored since >80% is known to be excreted as the parent compound.
References
Anderson, P. E., Mahle, D. A., Doom, T. E., Reo, N. V., DelRaso, N. J., & Raymer, M. L. (2011). Dynamic adaptive binning: An improved quantification technique for NMR spectroscopic data. Metabolomics, 7, 179–190.
Assfalg, M., Bertini, I., Colangiuli, D., et al. (2008). Evidence of different metabolic phenotypes in humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 105, 1420–1424.
Bell, J. D., Sadler, P. J., Morris, V. C., & Levander, O. A. (1991). Effect of aging and diet on proton NMR-spectra of rat urine. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 17, 414–422.
Bollard, M. E., Stanley, E. G., Lindon, J. C., Nicholson, J. K., & Holmes, E. (2005). NMR-based metabolomics approaches for evaluating physiological influences on biofluid composition. NMR in Biomedicine, 18, 143–162.
Brandacher, G., Cakar, F., Winkler, C., et al. (2007). Non-invasive monitoring of kidney allograft rejection through IDO metabolism evaluation. Kidney International, 71, 60–67.
Brenner, B. M., Keimowitz, R. I., Wright, F. S., & Berliner, R. W. (1969). An inhibitory effect of furosemide on sodium reabsorption by the proximal tubule of the rat nephron. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 48, 290–300.
Burke, T. J., Robinson, R. R., & Clapp, J. R. (1972). Determination of the effect of furosemide on the proximal tubule. Kidney International, 1, 12–18.
Carone, F. A., & Ganote, C. E. (1975). d-Serine nephrotoxicity. The nature of proteinuria, glucosuria, and aminoaciduria in acute tubular necrosis. Archives of Pathology, 99, 658–662.
Chen, L., & Burka, L. T. (2007). Chemical and enzymatic oxidation of furosemide: formation of pyridinium salts. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 20, 1741–1744.
Christensen, S., Steiness, E., & Christensen, H. (1986). Tubular sites of furosemide natriuresis in volume-replaced and volume-depleted conscious rats. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 239, 211–218.
Connor, S. C., Wu, W., Sweatman, B. C., et al. (2004). Effects of feeding and body weight loss on the 1H-NMR based urine metabolic profiles of male Wistar Han rats: implications for biomarker discovery. Biomarkers: Biochemical Indicators of Exposure, Response, and Susceptibility to Chemicals, 9, 156–179.
Costa, M., Marchetti, M., Balaszczuk, A., & Arranz, C. (2001). Effects of l-arginine and furosemide on blood pressure and renal function in volume-exapnded rats. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, 28, 528–532.
Cvetanovic, I., Renade, V., Molnar, J., Whelton, A., & Somberg, J. (2007). The evaluation of the diuretic action of parenteral formulations of metolazone. American Journal of Therapeutics, 14, 25–29.
DelRaso, N., Mauzy, C., & Rietcheck, R. (2009a). Biomarkers of exposure to toxic substances Volume I: Global experimental design: biomarker discovery for early prediction of organ-selective toxicity Air Force Research Laboratory Technical Report. Vol AFRL-RH-WP-TR-2009-0102.
DelRaso, N. J., Rietcheck, R., & Mahle, D. (2009b). Metabonomics biomarkers to liver and organ damage: Biomarker discovery for early prediction of organ-selective toxicity. In AFRL-RH-WP-TR-2009-0105 (ed). vol 4.
Dieterle, F., Ross, A., Schlotterbeck, G., & Senn, H. (2006). Probabilistic quotient normalization as robust method to account for dilution of complex biological mixtures. Application in 1H NMR metabonomics. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 4281–4290.
Gao, H., Dong, B., Liu, X., Xuan, H., Houang, Y., & Lin, D. (2008). Metabonomic profiling of renal cell carcinoma: High-resolution proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of human serum with multivariate data analysis. Analytica Chemica Acta, 624, 269–277.
Gao, H., Lu, Q., Liu, X., et al. (2009). Application of 1H NMR-based metabonomics in the study of metabolic profiling of human hepatocellular carcinoma and liver cirrhosis. Cancer Science, 100, 782–785.
Genote, C. E., Peterson, D. R., & Carone, F. E. (1974). The nature of d-serine-induced nephrotoxicity. American Journal of Pathology, 77, 269–282.
Habold, C., Chevalier, C., Dunnel-Erb, S., Foltzer-Jourdainne, C., Le Maho, Y., & Lignor, J. H. (2004). Effects of fasting and refeeding on jejunal morphology and cellular activity in rats in relation to depletion of body stores. Scandnavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 6, 531–539.
Hansen, L. L., Schilling, A. R., & Wiederholt, M. (1981). Effect of calicium, furosemide and chlorothiazine on net volume reabsorption and basolateral membrane potential of distal tubule. Pflugers Archiv European. Journal of Physiology, 389, 121–126.
Ho, K. M., & Power, B. M. (2010). Benefits and risks of furosemide in acute kidney injury. Anaesthesia, 65, 283–293.
Holmes, E., Nicholls, A. W., Lindon, J. C., et al. (2000). Chemometric models for toxicity clarification based on NMR spectra of biofluids. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 13, 471–478.
Holmes, E., Nicholson, J. K., & Tranter, G. (2001). Metabonomic characterization of genetic variations in toxicological and metabolic responses using probabilistic neural networks. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 14, 182–191.
Hwang, G.-S., Yang, J.-Y., Ryu, D. H., & Kwon, T.-H. (2010). Metabolic profiling of kidney and urine in rats with lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus by 1H NMR-based metabonomics. American Journal of Physiology: Renal Physiology 298, F461–F470.
Iyalomhe, G., Omogbai, E., Ozolua, R., & Iyalomhe, O. (2008). Effects of hydrochlorothiazide and furosemide on creatinine clearance in some hypertensive Nigerians. African Journal of Biotechnology, 7, 848–851.
Jung, J., Park, M., Park, H. J., et al. (2010). 1H NMR-based metabolic profiling of naproxen-induced toxicity in rats. Toxicology Letters, 200, 1–7.
Kale, V. P., Joshi, G. S., Parikshit, B., & Jain, M. R. (2009). Effect of fasting duration on clinical pathology results in Wistar rats. Veterinary Clinical Pathology, 38, 361–366.
Khan, A., Low H., & Efendic, S. (1985). Effects of fasting and refeeding on the activity of hepatic glucose-6-phosphatase in rats. Acta Physiologica Scandinavia, 124, 591–596.
Kind, T., Tolstikov, V., Fiehn, O., & Weiss, R. H. (2007). A comprehensive urinary metabolomics approach for identifying kidney cancer. Analytical Biochemistry, 363, 185–195.
Klawitter, J., Bendrick-Peart, J., Rudolph, B., et al. (2009). Urine metabolites reflect time-dependent effects of cyclosporine and sirolimus on rat kidney function. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 22, 118–128.
Klawtter, J., Haschke, M., Kahle, C., et al. (2010). Toxicodynamic effects of ciclosporin are reflected by metabolite profiles in the urine of healthy individuals after a single dose. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 70, 241–251.
Kochhar, S., Jacobs, D. M., Ramadan, Z., Berruex, F., Fuerholz, A., & Fay, L. B. (2006). Probing gender-specific metabolism differences in humans by nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics. Analytical Biochemistry, 352, 274–281.
Koyner, J., Davison, D., Brasha-Mitchell, E., et al. (2015). Furosemide stress test and biomarkers for the prediction of AKI severity. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 26, 2023–2031.
Krug, A. W., Volker, K., Dntzler, W. H., Silbernagl, S. (2007). Why d-serine is nephrotoxic and α-aminoisobutyric acid protective?. American Journal of Physiology: Renal Physiology, 293, F382–F390.
Kutina, A. V., Zakharov, V. V., & Natochin, Y. V. (2008). Excretion of proteins by rat kidney during various types of diuresis. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 146, 671–674.
Lahdou, I., Sadeghi, M., Daniel, V., et al. (2010). Increased pretransplantation plasma kynurenine levels do not protect from but predict acute kidney allograph rejection. Human Immunology, 71, 1067–1072.
Lassnigg, A., Donner, E., Grubhofer, G., Presterl, E., Druml, W., & Hiesmayr, M. (2000). Lack of renoprotective effects of dopamine and furosemide during cardiac surgery. Journal of American Society of Nephrology, 11, 97–104.
LeBrun, M., Grenier, L., Bergeron, M. G., Thibault, L., Labrecque, G., & Beauchamp, D. (1999). Effect of fasting on temporal variation in the nephrotoxicity of Amphotericin B in rats. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 43, 520–524.
Lenaerts, K., Sokotovic, M., Bouwman, F. G., Lamers, W. H., Mariman, E. C., & Renes, J. (2006). Stavation induces phase-specific changes in the proteome of mouse small intestine. Journal of Proteome Research, 5, 2113–2122.
Lenz, E., Bright, J., Wilson, I., et al. (2004a). Metabonomics, dietary influences and cultural differences: A 1H NMR-based study of urine samples obtained from healthy British and Swedish subjects. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 36, 841–849.
Lenz, E., Bright, J., Wilson, I., Morgan, S., & Nash, A. (2003). A 1H NMR-based metabonomic study of urine and plasma samples obtained from healthy human subjects. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 33, 1103–1115.
Lenz, E. M., Bright, J., Knight, R., Wilson, I. D., & Major, H. (2004b). Cyclosporin A-induced changes in endogenous metabolites in rat urine: A metabonomic investigation using high field 1H NMR spectroscopy, HPLC-TOF/MS and chemometrics. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 35, 599–608.
Lindon, J. C., E. Holmes, & J. K. Nicholson (2003). So what is the deal with the metabolomics?. Analytical Chemistry, 75, 385A–391A.
Lindon, J. C., Holmes, E., & Nicholson, J. K. (2004). Toxicological applications of magnetic resonance. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, 45, 109–143.
Lindon, J. C., Nicholson, J. K., Holmes, E., & Everett, J. R. (2000). Metabolomics: Metabolic Processes Studied by NMR Spectroscopy of Biofluids. Concepts in Magnetic Resonance, 12, 289–300.
Lombardi, R., Ferreiro, A., & Servetto, C. (2003). Renal function after cardiac surgery: Adverse effect of furosemide. Renal Failure, 25, 775–786.
Maclntyre, D., Jimenez, B., Lewintre, E. J., et al. (2010). Serum metabolome analysis by 1H NMR reveals differences between chronic lymphocytic leukemia molecular subgoups. Leukemia: Official Journal of the Leukemia Society of America, Leukemia Research Fund, U. K, 24, 788–797.
Mahesh, B., Yim, B., Robson, D., Pillai, R., Ratnatunga, C., & Pigott, D. (2008). Does furosemide prevent renal dysfunction in high-risk cardiac surgical patients? Results of a double-blinded prospective randomised trial. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, 33, 370–376.
Mahle, D. A., Anderson, P. E., DelRaso, N. J., Raymer, M. L., Neuforth, A. E., & Reo, N. V. (2011). A generalized model for metabolomics analyses: application to dose and time dependent toxicity. Metabolomics, 7, 206–216.
Martin, F. P. J., Collino, S., & Rezzi, S. (2011). 1 H NMR-based metabonomic applications to decipher gut microbial metabolic influence on mammalian health. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry, 49, S47–S54.
Munn, D., Zhou, M., Attwood, J., Bondarev, I., Conway, S., & Marshall, B. (1998). Prevention of allogeneic fetal rejection by tryptophan catabolism. Science, 281, 1191–1193.
Myles, P., Buckland, M., Schenk, N., et al. (1993). Effect of ‘renal-dose’ dopamine on renal function following cardiac surgery. Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, 21, 56–61.
Ng, D. J. Y., & Pasikanti, K. K. (2011). Trend analysis of metabonomics and systematic review of metabonomics-derived cancer marker metabolites. Metabolomics, 7, 155–178.
Nicholls, A. W., Holmes, E., Lindon, J. C., et al. (2001). Metabonomic investigation into Hydrazine toxicity in the rat. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 14, 975–987.
Nicholls, A. W., Mortishire-Smith, R. J., & Nicholson, J. K. (2003). NMR spectroscopic-based metabolomics studies of urinary metabolite variation in acclimatizing germ-free rats. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 16, 1395–1404.
Nicholson, J. K., Lindon, J. C., & Holmes, E. (1999). ‘Metabonomics’: Understanding the metabolic response of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica; The Fate of Foreign Compounds in Biological Systems, 29, 1181–1189.
Nicholson, J. K., & Wilson, I. D. (1989). High resolution proton NMR spectroscopy of biological fluids. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, 449–501.
Nowland, M. H., Hugunin, K. M. S. & Rogers, K. L. (2011). Effects of short-term fasting in male Sprague–Dawley rats. Comparative Medicine, 61, 138–144.
Oberleithner, H., Guggino, W., & Giebisch, G. (1983). The effect of furosemide on lumunal sodium, chloride and potassium transport in the early distal tubule of Amphiuma kidney. Effects of potassium adaptation. Pflugers Archiv European. Journal of Physiology, 396, 27–33.
Odunsi, K., Wollman, R. M., Ambrosone, C. B., et al. (2005). Detection of epithelial ovarian cancer using 1H-NMR-based metabonomics. International Journal of Cancer, 113, 782–788.
Pichette, V., & Du Souich, P. (1996). Role of the kidneys in the metabolism of furosemide: Its inhibition by probenecid. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 7, 345–349.
Pichette, V., Geadah, D., & du Souich, P. (1999). Role of plasma protein binding on renal metabolism and dynamics of furosemide in the rabbit. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 27, 81–85.
Psihogios, N. G., Gazi, I. F., Elisaf, M. S., Seferiadis, K. I., & Bairaktari, E. T. (2008). Gender-related and age-related urinalysis of healthy subjects by NMR-based metabolomics. NMR in Biomedicine, 21, 195–207.
Robertson, D. G. (2005). Metabonomics in toxicology: A review. Toxicological Sciences, 85, 809–822.
Robertson, D. G., Reily, M. D., Sigler, R. E., Wells, D. F., Paterson, D. A., & Braden, T. K. (2000). Metabonomics: Evaluation of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and pattern recognition technology for rapid in vivo screening of liver and kidney toxicants. Toxicological Sciences, 57, 326–337.
Robertson, D. G., Ruepp, S., Stryker, S. A., et al. (2011). Metabolomic and transcriptomic changes induced by overnight (16 h) fasting in male and female Sprague–Dawley rats. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 24, 481–487.
Rozman, K. K., & Doull, J. (1998). General principles of toxicology. In J. Rose (Ed.) Environmental toxicology: Current development (pp. 1–11). Amsterdam: Gordon and Breach Science Publishers.
Savorani, F., Rasmussen, M. A., Mikkelsen, M. S., & Engelsen, S. B. (2013). A primer to nutritional metabolomics by NMR spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Research International, 54, 1131–1145.
Schefold, J. C., Zeden, J. P., Fotopoulou, C., et al. (2009). Increased indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) activity and elevated serum levels of tryptophan catabolites in patients with chronic kidney disease: A possible link between chonric inflammation and uraemic symptoms. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation: Official Publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association: European Renal Association, 24, 1901–1908.
Seely, J. F., & Dirks, J. H. (1977). Site of action of diuretic drugs. Kidney International, 11, 1–8.
Sieber, M., Hoffmann, D., Adler M., et al. (2009). Comparative analysis of novel noninvasive renal biomarkers and metabonomic changes in a rat model of gentamicin nephrotoxicity. Toxicological Sciences, 109, 336–349.
Silbernagl, S., Volker, K., & Dantzler, W. H. (1999). d-Serine is reabsorbed in rat renal pars rectal. American Journal of Pathology, 276, F857–F863.
Smilde, A., Westerhuis, J., Hoefsloot, H., et al. (2010). Dynamic metabomoic data analysis: A tutorial review. Metabolomics, 6, 3–17.
Solanky, K., Bailey, N., Beckwith-Hall, B., et al. (2003). Application of biofluid 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabonomic techniques for the analysis of the biochemical effects of dietary isoflavones on human plasma profile. Analytical Biochemistry, 323, 197–204.
Solanky, K., Bailey, N., Beckwith-Hall, B., et al. (2005). Biofluid 1H NMR-based metabonomic techniques in nutrition research: Metabolic effects of dietary isoflavones in humans. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 16(4), 236–244.
Sumner, L., Amberg, A., Barrett, D., et al. (2007). Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics, 3, 211–221.
Sun, J., Schnackenberg, L. K., Holland, R. D., et al. (2008). Metabonomics evaluation of urine from rats given acute and chronic doses of acetominophen using NMR and UPLC/MS. Journal of Chromatography B: Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 871, 328–340.
Terness, P., Bauer, T., Rose, L., et al. (2002). Inhibition of allogeneic T-cell proliferation by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-expressing dendritic cells: Medication of suppression by tryptophan metabolites. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 196, 447–457.
Tiziani, S., Lopes, V., & Gunther, U. L. (2009). Early stage diagnosis of oral cancer using 1H NMR-based metabolomics. Neoplasia (New York, N. Y.), 11, 269–276.
Tonomura, Y., Tsuchiya, N., Torii, M., & Uehara, T. (2010). Evaluation of the usefulness of urinary biomarkers fro nephrotoxicity in rats. Toxicology, 273, 53–59.
Vavrincova-Yaghi, D., Seelen, M. A., Kema, I. P., et al. (2015). Early posttransplant tryptophan metabolism predicts long-term outcome of human kidney transplantation. Transplantation, 99, e97–e104.
Viant, M. R., Rosenblum, E. S., & Tjeerdema, R. S. (2003). NMR-based metabolomics: A powerful approach for characterizing the effects of environmental stressors on organism health. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 4982–4989.
Walsh, M., Brennan, L., Malthouse, J., Roche, H., & Gibney, M. (2006). Effect of acute dietary standardization on the urinary, plasma, and salivary metabolomic profiles of healthy humans. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 84, 531–539.
Wei, L., Liao, P., Wu, H., et al. (2009). Metabolic profiling studies on the toxicological effects of realgar in rats by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Toxicological and Applied Pharmacology, 234, 314–325.
Wider, G., Baumann, R., Nagayama, K., Ernst, R. R., & Wuthrich, K. (1981). Strong spin-spin coupling in the two-dimentional J-resolved 360-MHz spectra of the common amino acids. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 42, 73–87.
Williams, R. E., Jacobson, M., & Lock, E. A. (2003). 1H NMR pattern recognition and 31P NMR studies with d-serine in rat urine and kidney, time- and dose-related metabolic effects. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 16, 1207–1216.
Williams, R. E., & Lock, E. A. (2004). d-Serine-induced nephrotoxicity: Possible interaction with tyrosine metabolism. Toxicology, 201, 231–238.
Williams, R. E., Major, H., Lock, E. A., Lenz, E. M., & Wilson, I. D. (2005). d-Serine-induced nephrotoxicity: A HPLC-TOF/MS-based metabolomics approach. Toxicology, 207, 179–190.
Wise, E., & Elwyn, D. (1966). Hyperaminoaciduria in rats following d-serine administration. Proceedings of the Society of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 121, 982–986.
Wittner, M., Stefano, D., Wangemann, P., & Greger, R. (1991). How do loop diuretics act? Drugs, 41, 1–13.
Won, A. J., Kim, S., Kim, Y. G., et al. (2016). Discovery of urinary metabolmic biomarkers for early detection of acute kidney injury. Molecular BioSystems, 12, 133–144.
Xu, J., Yang, S., Cai, S., Dong, J., Li, X., & Chen, Z. (2010). Identification of biochemical changes in lactovegetarian urine using 1H NMR spectroscopy and pattern recognition. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 396, 1451–1463.
Xu, J., Zhang, J., Dong, J., Cai, S., Yang, J., & Chen, Z. (2009). Metabolomics studies and intact hepatic and renal cortical tissues from diabetic db/db mice using high-resolution magic-angle spinning 1H NMR spectroscopy. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 393, 1657–1668.
Yang, Y., Li, C., Nie, X., et al. (2007). Metabonomic studies of human hepatocellular carcinoma using high-resolution magic-angle spinning 1H NMR spectroscopy in conjunction with multivariate data analysis. Journal of Proteome Research, 6, 2605–2614.
Yap, I. K. S., Clayton, T. A., Tang, H., et al. (2006). An integrated metabonomic approach to describe temporal metabolic disregulation induced in the rat by the model hepatotoxin Allyl Formate. Journal of Proteome Research, 5, 2675–2684.
Zuppi, C., Messana, I., Forni, F., Ferrari, F., Cristina, R., & Giardina, B. (1998). Influence of feeding on metabolite excretion evidenced by urine 1H NMR spectral profiles: A comparison between subjects living in Rome and subjects living at arctic latitudes (Svaldbard). Clinica Chimica Acta, 278, 75–79.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Ohio Third Frontier, Research Challenge Fund (NVR), and funds provided by the Air Force Research Laboratory, 711th Human Performance Wing, Human Effectiveness Directorate, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, OH (DRM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Research involving Human and animal rights
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution at which the studies were conducted.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sibomana, I., DelRaso, N.J., Mattie, D. et al. Furosemide enhances the sensitivity of urinary metabolomics for assessment of kidney function. Metabolomics 13, 24 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1162-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1162-6