Abstract
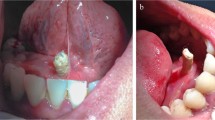
Sialolithiasis is a common salivary pathology, and an uncommon complication of sialadenitis and sialolithiasis is the formation of fistulous tracts to other compartments. Submandibular gland sialo-oral fistulae are not particularly remarkable, given the location of the gland and Wharton’s duct, but submandibular sialolith-associated fistulae to other cervico-facial compartments (transcervical sialo-cutaneous and sialo-pharyngeal fistulae) are much less common. We report herein an unusual case of a 49-year-old obese man with sialo-cutaneous fistula containing a large, ectopic sialolith in subcutaneous tissue that was expected to undergo spontaneous elimination, but revealed hidden Eagle syndrome featuring an ipsilateral enlarged, elongated styloid process. Furthermore, we offer a thorough review of the literature regarding sialo-fistulae and highlight the relationship between an abnormal styloid process and submandibular sialadenitis with sialolithiasis and new tract formation based on computed tomography.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ledesma-Montes C, Garces-Ortiz M, Salcido-Garcia JF. Giant sialolith: case report and review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;65:128.
Oteri G, Procopio R, Cicciu M. Giant salivary gland calculi (GSGC): report of two cases. Open Dent J. 2011;5:90–5.
Lustmann J, Regev E, Melamed Y. Sialolithiasis: a survey on 245 patients and a review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1990;19:135–8.
Bodner L. Giant salivary gland calculi: diagnostic imaging and surgical management. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;94:320–3.
Abdeen BE, Khen MA. An unusual large submandibular gland calculus: a case report. Smile Dental J. 2010;5:14–7.
Kraaij S, Karagozoglu KH, Forouzanfar T, Veerman EGI, Brand HS. Salivary stones: symptoms, aetiology, biochemical composition and treatment. Br Dent J. 2014;217(11):E23.
Cherrick HM, Wood N. Pits, fistulae and draining lesions. In: Wood N, Goaz PW, editors. Differential diagnosis of oral and maxillofacial lesions, 5th ed. Missouri: Mosby; 1997. p.217–24.
Kumar RVK, Devireddy SK, Gali RS, Chaithanyaa N, Chakravarthy C, Kumarvelu C. Cutaneous sinuses of cervicofacial region: a clinical study of 200 cases. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2012;11:411–5.
Siddiqui SJ. Sialolithiasis: an unusually large submandibular salivary stone. Br Dent J. 2002;193:89–91.
Leite TC, Blei V, de Oliveira DP, Robaina TF, Rangel Janini ME, Meirelles V Jr. Giant asymptomatic sialolithiasis. Int J Oral Med Sci. 2011;10:175–8.
Williams MF. Sialolithiasis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1999;32:819–34.
Sutay S, Erdag TK, Ikiz AO, Guneri EA. Large submandibular gland calculus with perforation of the floor of the mouth. Otolaryngol Neck Surg. 2003;128(4):587–8.
Rauso R, Gherardini G, Biondi P, Tartaro G, Colella G. A case of a giant submandibular gland calculus perforating the floor of the mouth. Ear Nose Throat J. 2012;91:E-25–7.
Kasat V, Mahindra U, Saluja H. Giant sialolith in the Wharton’s duct causing sialo-oral fistula: a case report and review of literature. J Orofac Sci. 2012;4(2):137.
Kurtoglu G, Durmusoglu M, Ecevit MC. Submandibular sialolithiasis perforating the floor of mouth: a case report. Turkish Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015;53:35–7.
Parkar MI, Vora MM, Bhanushali D. A large sialolith perforating the Wharton’s duct: review of literature and a case report. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2012;11:477–82.
Kieliszak CR, Gill A, Faiz M, Joshi AS. Submandibular ductal fistula: an obstacle to sialendoscopy. JAMA Otolaryngol Neck Surg. 2015;141(4):373–6.
Karengera D, Yousefpour A, Reychler H. Unusual elimination of a salivary calculus. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1998;27:224–5.
Drage NA, Brown JE, Makdissi J, Townend J. Migrating salivary stones: report of three cases. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;43:180–2.
Almasri MA. Management of giant intraglandular submandibular sialolith with neck fistula. Ann Dent. 2005;12(1):41–6.
Salikumar K, Gopakumar KP, Divya GM, Sindhu BS. An unusual sequel of submandibular gland calculus—a case report. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;58:303–4.
Rangappa V, Soumya M, Steenivas V. Salivary fistula with a calculus! Int J Head Neck Surg. 2014;5:96–8.
Singh R, Bhagat S, Singh B. Submandibular gland sialolithiasis presenting as fistula in the neck a case report. Austin J Otolaryngol. 2015;2:1040.
Kusunoki T, Homma H, Kidokoro Y, Yanai A, Hara S, Kobayashi Y, To M, Wada R, Ikeda K. Cervical fistula caused by submandibular sialolithiasis. Clin Pract. 2017;7(4):985–8.
Pirkl I, Filipovic B, Goranovic T, Simunjak B. Large tonsillolith associated with the accessory duct of the ipsilateral submandibular gland: support for saliva stasis hypothesis. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2015;44(8):20150090.
Panuganti BA, Baldassarre RL, Bykowski J, Husseman J. Chronic sialadenitis with sialolithiasis associated with parapharyngeal fistula and tonsillolith. Radiol Case Rep. 2017;12:519–22.
Jayachandran S, Bakyalakshmi K, Singh K. Giant submandibular sialolith presenting with sialocutaneous and sialo-oral fistula—a case report and review of literature. J Indian Acad Oral Med Radiol. 2011;23:491–4.
Gaur U, Choudhry R, Anand C, Choudhry S. Submandibular gland with multiple ducts. Surg Radiol Anat. 1994;16:439–40.
Gododia A, Seith A, Neyaz Z, Sharma R, Thakkar A. Magnetic resonance identification of an accessory submandibular duct and gland: an unusual variant. J Laryngol Otol. 2007;121:e18.
Kuroyanagi N, Kinoshita H, Machida J, Suzuki S, Yamada Y. Accessory duct in the submandibular gland. Asian J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;19:110–2.
Eagle WW. Symptomatic elongated styloid process: report of two cases of styloid process-carotid artery syndrome with operation. Arch Otolaryngol. 1949;49:490–501.
Keur JJ, Campbell JP, McCarthy JF, Ralph WJ. The clinical significance of the elongated styloid process. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1986;61:399–404.
Murtagh RD, Caracciolo JT, Fernandez G. CT findings associated with Eagle syndrome. Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22:1401–2.
Norman JED. The natural history of lithogenesis and sialolithiasis, acute sial sepsis and sialoadenitis. In: Norman JED, McGurk M, editors. Color atlas and text of the salivary glands. Diseases, disorders and surgery. London: Mosby-Wolfe; 1995. p. 252–262.
Som PM, Curtin HD. Parapharyngeal and masticator space lesions. In: Som PM, Curtin HD, editors. Head and neck imaging. 5th ed. St Louis: Mosby; 2011. p. 2388–2390.
Fanibunda K, Lovelock DJ. Calcified styloid ligament: unusual pressure symptoms. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1997;26:249–51.
Salmons S, Bannister LH. 7.Muscle/12.Alimentary system. In: Williams PL, Bannister LH, Berry MM, Collins P, Dyson M, Dussek JE, Ferguson MWJ, editors. Gray’s anatomy. 38th ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1995. p. 806–1692.
Steinmann EP. Styloid syndrome in abscess of an elongated process. Acta Otolaryngol. 1968;66:347–56.
Nitipong P, Promporn S, Daych C, Charles LH. Unveiling the hidden Eagle: acute parotitis-induced Eagle syndrome. North Am J Med Sci. 2014;6(2):102–4.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Private University Research Branding Project from MEXT of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors M. Wakoh, TK. Goto, T. Shibahara, K Matsuzaka and T Kamio declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions. Informed consent was obtained from a patient for being included in the study. Additional informed consent was obtained from a patient for which identifying information is included in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wakoh, M., Goto, T.K., Matsuzaka, K. et al. Sialo-cutaneous fistula with ectopic submandibular gland sialolith, revealing a hidden ipsilateral enlarged and elongated styloid process: a consideration based on CT findings. Oral Radiol 37, 336–344 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-020-00481-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-020-00481-8