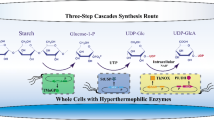
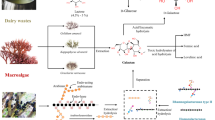
Abstract
D-glucuronic acid is a kind of glucose derivative, which has excellent properties such as anti-oxidation, treatment of liver disease and hyperlipidemia, and has been widely used in medicine, cosmetics, food and other fields. The traditional production methods of D-glucuronic acid mainly include natural extraction and chemical synthesis, which can no longer meet the growing market demand. The production of D-glucuronic acid by biocatalysis has become a promising alternative method because of its high efficiency and environmental friendliness. This review describes different production methods of D-glucuronic acid, including single enzyme catalysis, multi-enzyme cascade, whole cell catalysis and co-culture, as well as the intervention of some special catalysts. In addition, some feasible enzyme engineering strategies are provided, including the application of enzyme immobilized scaffold, enzyme mutation and high-throughput screening, which provide good ideas for the research of D-glucuronic acid biocatalysis.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request from the authors.
References
Amaniampong PN, Karam A, Trinh QT et al (2017) Selective and catalyst-free oxidation of D-glucose to D-glucuronic acid induced by high-frequency ultrasound. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40650
Anuar MSK, Hashim AM, Ho CL et al (2023) Synergism: biocontrol agents and biostimulants in reducing abiotic and biotic stresses in crop. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03579-3
Arewång CJ, Lahmann M, Oscarson S, Tidén AK (2007) Synthesis of urine drug metabolites: glucuronic acid glycosides of phenol intermediates. Carbohyd Res 342(7):970–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2007.01.014
Bedford CT (1998) Glucuronic acid conjugates. J Chromatogr 717(1–2):313–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4347(98)00328-4
Besnard J, Okumoto S (2014) Glutamine flux imaging using genetically encoded sensors. J V Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/51657
Bezborodov AM, Zagustina NA (2016) Enzymatic biocatalysis in chemical synthesis of pharmaceuticals (review). Appl Biochem Microbiol 52(3):237–249. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683816030030
Carr AC, Frei B (1999) Toward a new recommended dietary allowance for vitamin C based on antioxidant and health effects in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 69(6):1086–1107
Chen JY, Guo XN, Zhu M et al (2019) Polysaccharide monooxygenase-catalyzed oxidation of cellulose to glucuronic acid-containing cello-oligosaccharides. Biotechnol Biofuels. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-019-1384-0
Chow J, Perez-Garcia P, Dierkes R, Streit WR (2023) Microbial enzymes will offer limited solutions to the global plastic pollution crisis. Microb Biotechnol 16(2):195–217. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.14135
de Carvalho C (2011) Enzymatic and whole cell catalysis: finding new strategies for old processes. Biotechnol Adv 29(1):75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.09.001
Denooy AEJ, Besemer AC, Vanbekkum H (1995) Highly selective nitroxyl radical-mediated oxidation of primary alcohol groups in water-soluble glucans. Carbohyd Res 269(1):89–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6215(94)00343-E
Doong SJ, Gupta A, Prather KLJ (2018) Layered dynamic regulation for improving metabolic pathway productivity in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(12):2964–2969. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1716920115
Dueber JE, Wu GC, Malmirchegini GR et al (2009) Synthetic protein scaffolds provide modular control over metabolic flux. Nat Biotechnol 27(8):753-U107. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1557
Fana SE, Fazaeli A, Aminian M (2023) Directed evolution of cholesterol oxidase with improved thermostability using error-prone PCR. Biotech Lett 45(9):1159–1167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-023-03401-y
Feng TT, Wang ZQ, Li HW et al (2023) Whole-cell biotransformation for simultaneous synthesis of allitol and D-gluconic acid in recombinant Escherichia coli. J Biosci Bioeng 135(6):433–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2023.03.004
Fernandes CD, Oechsler BF, Sayer C et al (2022) Recent advances and challenges on enzymatic synthesis of biobased polyesters via polycondensation. Eur Polym J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2022.111132
Ghadam FMJ, Faramarzi M, Panahi HA, Parsa SAM (2023) Glucuronic acid-conjugated smart cellulose nanocrystals as novel carrier for gemcitabine delivery. Mater Chem Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126862
Han J, Luo P, Wang L et al (2020) Construction of a multienzymatic cascade reaction system of coimmobilized hybrid nanoflowers for efficient conversion of starch into gluconic acid. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(13):15023–15033. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b21511
Hirao H (2011) The effects of protein environment and dispersion on the formation of ferric-superoxide species in myo-inositol oxygenase (MIOX): a combined oniom(DFT:MM) and energy decomposition analysis. J Phys Chem B 115(38):11278–11285. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp2057173
Ho A, Sinick J, Esko T et al (2019) Circulating glucuronic acid predicts healthspan and longevity in humans and mice. Aging-Us 11(18):7694–7706. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102281
Hüttner S, Klaubauf S, de Vries RP et al (2017) Characterisation of three fungal glucuronoyl esterases on glucuronic acid ester model compounds. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(13):5301–5311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8266-9
Jaime-Acuña OE, Zamora JL, Raymond-Herrera O (2021) Photoconversion of glucose to glucuronic acid over plasmonic M-CdS/MOR (M = Ag, Au) nanocomposites. Sustain Chem Pharm. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2020.100351
Jiang L, Song XG, Li YF et al (2018) Programming integrative extracellular and intracellular biocatalysis for rapid, robust, and recyclable synthesis of trehalose. ACS Catal 8(3):1837–1842. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.7b03445
Jug U, Glavnik V, Kranjc E, Vovk I (2018) High-performance thin-layer chromatography and high-performance thin-layer chromatography-mass spectrometry methods for the analysis of phenolic acids. J Planar Chromatogr Modern Tlc 31(1):13–22. https://doi.org/10.1556/1006.2018.31.1.2
Kohn R, Kovac P (1978) Dissociation-constants of d-galacturonic and d-glucuronic acid and their o-methyl derivatives. Chem Zvesti 32(4):478–485
Koko MYF, Mu WM, Hassanin HAM et al (2020) Archaeal hyperthermostable mannitol dehydrogenases: a promising industrial enzymes for D-mannitol synthesis. Food Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109638
Kornauth C, Pemovska T, Vladimer GI et al (2022) Functional precision medicine provides clinical benefit in advanced aggressive hematologic cancers and identifies exceptional responders. Cancer Discov 12(2):372–387. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0538
Kucinska-Lipka J, Gubanska I, Strankowski M et al (2017) Synthesis and characterization of cycloaliphatic hydrophilic polyurethanes, modified with L-ascorbic acid, as materials for soft tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl 75:671–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.02.052
Laisne A, Ewald M, Ando T et al (2011) Self-assembly properties and dynamics of synthetic proteo-nucleic building blocks in solution and on surfaces. Bioconjug Chem 22(9):1824–1834. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc2002264
Leal JM, Suárez LV, Jayabalan R et al (2018) A review on health benefits of kombucha nutritional compounds and metabolites. Cyta-J of Food 16(1):390–399. https://doi.org/10.1080/19476337.2017.1410499
Li W, Xu SG, Xu X (2022) Valorisation of corncob residue towards the sustainable production of glucuronic acid. Catalysts. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121603
Liu ZJ, Cao S, Liu M, Kang W et al (2019) Self-assembled multienzyme nanostructures on synthetic protein scaffolds. ACS Nano 13(10):11343–11352. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b04554
Liu J, Wu P, Yan SH et al (2021) Spin-regulated inner-sphere electron transfer enables efficient o-o bond activation in nonheme diiron monooxygenase MIOX. ACS Catal 11(10):6141–6152. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.1c00898
Moon TS, Yoon SH, Lanza AM et al (2009) Production of glucaric acid from a synthetic pathway in recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(3):589–595. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00973-08
Nguyen NK, Nguyen HT, Le PH (2015a) Effects of Lactobacillus casei and alterations in fermentation conditions on biosynthesis of glucuronic acid by a dekkera bruxellensis-gluconacetobacter intermedius kombucha symbiosis model system. Food Biotechnol 29(4):356–370. https://doi.org/10.1080/08905436.2015.1092446
Nguyen NK, Nguyen PB, Nguyen HT, Le PH (2015b) Screening the optimal ratio of symbiosis between isolated yeast and acetic acid bacteria strain from traditional kombucha for high-level production of glucuronic acid. Lwt-Food Sci Technol 64(2):1149–1155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.07.018
Ning XJ, Ying YH, Lin TL (2020) Adsorption behavior of glucuronic acid on pyrite surface: an electrochemical and dft study. Archiv Metall Mater 65(1):433–440. https://doi.org/10.24425/amm.2020.131746
Oyekunle DT, Gendy EA, Ifthikar J, Chen ZQ (2022) Heterogeneous activation of persulfate by metal and non-metal catalyst for the degradation of sulfamethoxazole: a review. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135277
Park E, Kim M, Shin JS (2010) One-pot conversion of l-threonine into l-homoalanine: biocatalytic production of an unnatural amino acid from a natural one. Adv Synth Catal 352(18):3391–3398. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201000601
Pitt N, Duane RM, O’Brien A et al (2004) Synthesis of a glucuronic acid and glucose conjugate library and evaluation of effects-on endothelial cell growth. Carbohyd Res 339(11):1873–1887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2004.05.024
Qu G, Li AT, Acevedo-Rocha CG et al (2020) The crucial role of methodology development in directed evolution of selective enzymes. Angew Chem Int Ed 59(32):13204–13231. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201901491
Ricciutelli M, Caprioli G, Cortese M et al (2014) Simultaneous determination of taurine, glucuronolactone and glucuronic acid in energy drinks by ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (triple quadrupole). J Chromatogr A 1364:303–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.08.083
Richel A, Laurent P, Wathelet B et al (2010) Microwave-assisted synthesis of D-glucuronic acid derivatives using cost-effective solid acid catalysts. Tetrahedron Lett 51(10):1356–1360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.12.065
Rogers JK, Church GM (2016) Genetically encoded sensors enable real-time observation of metabolite production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113(9):2388–2393. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1600375113
Rommelaere S, Millet V et al (2013) PPARalpha regulates the production of serum Vanin-1 by liver. FEBS Lett 587(22):3742–3748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2013.09.046
Sarkaya P, Akan E, Kinik O (2021) Use of kombucha culture in the production of fermented dairy beverages. Lwt-Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110326
Shiue E, Prather K (2014) Improving D-glucaric acid production from myo-inositol in E. coli by increasing MIOX stability and myo-inositol transport. Metab Eng 22:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2013.12.002
Tanchuk VY, Tanin VO, Vovk AI, Poda G (2016) A new, improved hybrid scoring function for molecular docking and scoring based on autodock and autodock vina. Chem Biol Drug Des 87(4):618–625. https://doi.org/10.1111/cbdd.12697
Teng F, You R, Hu M et al (2019) Production of D-glucuronic acid from myo-inositol using Escherichia coli whole-cell biocatalyst overexpressing a novel myo-inositol oxygenase from Thermothelomyces thermophile. Enzyme Microb Technol 127:70–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2019.04.013
Wang HM, Loganathan D (1991) Determination of the pka of glucuronic-acid and the carboxy groups of heparin by c-13-nuclear-magnetic-resonance spectroscopy. Biochem J 278:689–695. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2780689
Wang YC, Yu O (2012) Synthetic scaffolds increased resveratrol biosynthesis in engineered yeast cells. J Biotechnol 157(1):258–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.11.003
Wei YS, Zhu BW, Yao Z et al (2023) Biochemical characterization and elucidation of the action mode of a GH16 family k-carrageenase for efficient preparation of carrageenan oligosaccharides. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03668-3
Willson M, Callens M, Kuntz DA et al (1993) Synthesis and activity of inhibitors highly specific for the glycolytic-enzymes from trypanosoma-brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol 59(2):201–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-6851(93)90218-M
Wojcieszak R, Cuccovia IM, Silva MA et al (2016) Selective oxidation of glucose to glucuronic acid by cesium-promoted gold nanoparticle catalyst. J Mol Catal A Chem 422:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2016.02.008
Wu JX, Yuan H, Zhang P et al (2016) Synthesis of glucuronic acid by heterogeneous selective oxidation with active MnO2 characterized generally. React Kinet Mech Catal 117(1):319–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-015-0930-4
Wu TF, Liu CM et al (2022) Enzymatic synthesis, characterization and properties of the protein-polysaccharide conjugate: a review. Food Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131332
Xiong Y, Patana AS, Miley MJ et al (2008) The first aspartic acid of the DQxD motif for human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A10 interacts with UDP-glucuronic acid during catalysis. Drug Metab Dispos 36(3):517–522. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.107.016469
Yigit B, Taslimi P, Celepci DB et al (2023) Novel PEPPSI-type N-heterocyclic carbene palladium(II) complexes: synthesis, characterization, in-silico-studies and enzyme inhibitory properties against some metabolic enzymes. Inorg Chim Acta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2022.121239
Yuan H, Liu HQ, Du ZP et al (2012) Synthesis of glucuronic acid from methyl glucoside by heterogeneous selective catalytic oxidation. Chem Eng J 207:72–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.07.010
Zhang J, Wang M, Gao ZR et al (2022) Importance of species heterogeneity in supported metal catalysts. J Am Chem Soc 144(11):5108–5115. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.2c00202
Zheng S, Hou J, Zhou Y et al (2018) One-pot two-strain system based on glucaric acid biosensor for rapid screening of myo-inositol oxygenase mutations and glucaric acid production in recombinant cells. Metab Eng 49:212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.08.005
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key R and D Program of China (2022YFC3401301), National Natural Science Foundation of China (22078151, 22178169) and Jiangsu Natural Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (BK20220052).
Funding
Funding was provide by National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2022YFC3401301), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 22178169, 22078151), Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK20220052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HH: Investigation, writing—original draft. LJ, JW, JY, WY, WY: Investigation. JY, JW: Supervision. ZW: Supervision, Writing—review and editing. XF: Investigation, Supervision, Writing—review and editing. ZW: Resources, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, H., Li, J., Jiang, W. et al. Strategies for the biological synthesis of D-glucuronic acid and its derivatives. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 40, 94 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-024-03900-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-024-03900-8