Abstract
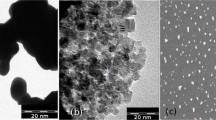
The present study reveals a simple, non-toxic and eco-friendly method for the “green” synthesis of Ag-NPs using hydroponic and soil medicinal plant Stevia rebaudiana extracts, the characterization of biosynthesized nanoparticles, as well as the evaluation of their antibacterial activity. Transmission electronic microscopy (TEM) and Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) analysis confirmed that biosynthesized Ag-NPs are in the nano-size range (50–100 nm) and have irregular morphology. Biogenic NPs demonstrate antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli BW 25,113, Enterococcus hirae ATCC 9790, and Staphylococcus aureus MDC 5233. The results showed a more pronounced antibacterial effect on E. coli growth rate, in comparison with Gram-positive bacteria, which is linked to the differences in the structure of bacterial cell wall. Moreover, the Ag-NPs not only suppressed the growth of bacteria but also changed the energy-dependent H+-fluxes across the bacterial membrane. The change of H+-fluxes in presence of H+-translocating systems inhibitor, N,N’-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD), proves the effect of Ag-NPs on the structure and permeability of the bacterial membrane. Overall, our findings indicate that the Ag-NPs synthesized by medicinal plant Stevia extracts may be an excellent candidate as an alternative to antibiotics against the tested bacteria.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaszadegan A, Ghahramani Y, Gholami A et al (2015) The effect of charge at the surface of silver nanoparticles on antimicrobial activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria: a preliminary study. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/720654
Aghajanyan A, Movsisyan Z, Trchounian A (2017) Antihyperglycemic and antihyperlipidemic activity of hydroponic Stevia rebaudiana aqueous extract in hyperglycemia induced by immobilization stress in rabbits. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9251358
Aghajanyan A, Gabrielyan L, Schubert R, Trchounian A (2020) Silver ion bioreduction in nanoparticles using Artemisia annua L. extract: characterization and application as antibacterial agents. AMB Express 10:66. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-020-01002-w
Baruah D, Yadav RNS, Yadav A, Das AM (2019) Alpinia nigra fruits mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial and photocatalytic activities. J Photochem Photobiol B 201:111649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111649
Bonilla-Gameros L, Chevallier P, Sarkissian A, Mantovani D (2020) Silver-based antibacterial strategies for healthcare-associated infections: processes, challenges, and regulations. An integrated review. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 24:102142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2019.102142
Botha TL, Elemike EE, Horn S, Onwudiwe DC, Giesy JP, Wepener V (2019) Cytotoxicity of Ag, Au and Ag-Au bimetallic nanoparticles prepared using golden rod (Solidago canadensis) plant extract. Sci Rep 9:4169. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40816-y
Clemente C, Angelini LG, Ascrizzi R, Tavarini S (2021) Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni) as a multifunctional and sustainable crop for the mediterranean climate. Agriculture 11:123. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11020123
Eid AM, Fouda A, Niedbala G et al (2020) Endophytic Streptomyces laurentii mediated green synthesis of Ag-NPs with antibacterial and anticancer properties for developing functional textile fabric properties. Antibiotics 9:641. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9100641
El-Gendy AO, Samir A, Ahmed E, Enwemeka CS, Mohamed T (2021) The antimicrobial effect of 400 nm femtosecond laser and silver nanoparticles on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. J Photochem Photobiol B 223:112300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2021.112300
Fadeel B, Alexiou C (2020) Brave new world revisited: focus on nanomedicine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 533:36–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.08.046
Gabrielyan L, Trchounian A (2019) Antibacterial activities of transient metals nanoparticles and membranous mechanisms of action. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35:162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2742
Gabrielyan L, Badalyan H, Gevorgyan V, Trchounian A (2020) Comparable antibacterial effects and action mechanisms of silver and iron oxide nanoparticles on Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Sci Rep 10:13145. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70211-x
Gevorgyan S, Schubert R, Yeranosyan M et al (2021) Antibacterial activity of royal Jelly-mediated green synthesized silver nanoparticles. AMB Express 11:51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-021-01213-9
Guzman M, Dille J, Godet S (2012) Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 8:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2011.05.007
Jadoun S, Arif R, Jangid NK, Meena RK (2020) Green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19:355–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01074-x
Kazmi A, Khan MA, Mohammad S et al (2019) Elicitation directed growth and production of steviol glycosides in the adventitious roots of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Ind Crops Prod 139:111530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111530
Khalandi B, Asadi N, Milani M et al (2017) A review of potential role of silver nanoparticles and possible mechanisms of their action on bacteria. Drug Res (stuttg) 67:70–76. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-113383
Lashin I, Founda A, Gobouri AA et al (2021) Antimicrobial and in vitro cytotoxic efficacy of biogenic silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) fabricated by callus extract of Solanum incanum L. Biomolecules 11:341. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11030341
Manosalva N, Tortella G, Diez MC et al (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: effect of synthesis reaction parameters on antimicrobial activity. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35:88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2664-3
Mba IE, Nweze EI (2021) Nanoparticles as therapeutic options for treating multidrug-resistant bacteria: research progress, challenges, and prospects. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 37:108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-03070-x
Mehwish HM, Liu G, Rajoka MSR et al (2021a) Therapeutic potential of Moringa oleifera seed polysaccharide embedded silver nanoparticles in wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol 184:144–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.202
Mehwish HM, Rajoka MSR, Xiong Y et al (2021b) Green synthesis of a silver nanoparticle using Moringa oleifera seed and its applications for antimicrobial and sun-light mediated photocatalytic water detoxification. J Evir Chem Engin 9(4):105290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105290
Mobaraki F, Momeni M, Jahromi M et al (2022) Apoptotic, antioxidant and cytotoxic properties of synthesized AgNPs using green tea against human testicular embryonic cancer stem cells. Process Biochem 119:106–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2022.05.021
Muraro PCL, Pinheiro LDSM, Chuy G et al (2022) Silver nanoparticles from residual biomass: Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity. J Biotechnol 343:47–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2021.11.003
Prata C, Zambonin L, Rizzo B et al (2017) Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni possess insulin-mimetic and antioxidant activities in rat cardiac fibroblasts. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3724545
Raghunath A, Perumal E (2017) Metal oxide nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: a promise for the future. Int J Antimicrob Agents 49:137–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.11.011
Rai M, Ingle AP, Trzcinska-Wencel J et al (2021) Biogenic silver nanoparticles: what we know and what do we need to know? Nanomaterials 11:2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112901
Roy A, Bulut O, Some S, Mndal AK, Yilmaz MD (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle: biomolecule-nanoparticle organizations targeting antimicrobial activity. RSC Adv 9:2673–2702. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA08982E
Taghavizadeh Yazdi ME, Darroudi M, Amiri MS et al (2022) Antimycobacterial, anticancer, antioxidant and photocatalytic activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Berberis integerrima. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci 46:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-021-01226-w
Wang L, Hu C, Shao L (2017) The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: present situation and prospects for the future. Int J Nanomed 12:1227–1249. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S121956
Zou X, Tan QW, Goh BH, Lee LH, Tan KL, Ser HL (2020) “Sweeter” than its name: anti-inflammatory activities of Stevia rebaudiana. All Life 13:286–309. https://doi.org/10.1080/26895293.2020.1771434
Funding
This work was supported by the Science Committee of RA, in the frames of the research project № 21T-1F179 (to L.G.), and Basal support from Science Committee, Ministry of Education, Science, Culture and Sport of RA. The authors acknowledge the use of the XBI biolab at European XFEL GmbH (Germany). The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Sci. Mikayel Babakhanyan and Dr. Lusya Hovhannisyan (Davtyan Institute of Hydroponics Problems, NAS, Yerevan, Armenia) for supplied plant material.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.T. performed the experiments with the antibacterial activity of NPs and determination of H+-fluxes; A.A. prepared the Ag-NPs, participated in the experiments with NPs antibacterial activity and performed the data processing; R.S. provided characterization of Ag-NPs; A.A. and L.G. wrote the manuscript; K.T. was involved in the discussion of results, edited the manuscript; L.G. coordinated the research, designed the study, edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Timotina, M., Aghajanyan, A., Schubert, R. et al. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using extracts of Stevia rebaudiana and evaluation of antibacterial activity. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 196 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03393-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03393-3