Abstract
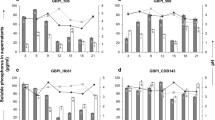
A phosphate solubilizing bacterium ZB was isolated from the rhizosphere soil of Araucaria, which falls into the species Pantoea agglomerans. Optimization for phosphate solubilization by strain ZB was performed. At optimum culture conditions, the isolate showed great ability of solubilizing different insoluble inorganic phosphate sources viz. Ca3(PO4)2 (TCP), Hydroxyapatite (HP), CaHPO4, AlPO4, FePO4 along with rock phosphates (RPs). Inoculation with planktonic cells was found to enhance dissolved phosphorous as compared to that achieved by symplasma inoculation. Besides inoculation with different status of cells, pre-incubation could also exert a great effect on phosphate solubilization ability of P. agglomerans. When isolate ZB was cultured with glucose as carbon sources, phosphorous was more efficiently dissolved from HP and RP without pre-incubation in comparison to that obtained with pre-cultivation. Pre-cultivation, however, was more suitable for P solubilization than no pre-cultivation when bacteria were grown with xylose. A positive correlation was detected between the production of organic acids and phosphate solubilization. P. agglomerans ZB possessed many plant growth promotion traits such as N2 fixation and production of indole 3-acetic acid, phytase, alkaline phosphatase. Pot experiment showed inoculation with single isolate ZB or biofertilizer prepared from semi-solid fermentation of isolate ZB with spent mushroom substrate (SMS) compost could enhance plant growth with respect to number of leaves, plant leave area, stem diameter, root length, root dry mass, shoot dry mass and biomass when compared to the abiotic control, revealing strain ZB could be a promising environmental-friendly biofertilizer to apply for agricultural field.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alori ET, Glick BR, Babalola OO (2017) Microbial phosphorus solubilization and its potential for use in sustainable agriculture. Front Microbiol 8:971. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00971
Bakhshandeh E, Rahimian H, Pirdashti H, Nematzadeh GA (2014) Phosphate solubilization potential and modeling of stress tolerance of rhizobacteria from rice paddy soil in northern Iran. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30(9):2437–2447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1669-1
Bashan Y, Kamnev AA, de-Bashan LE (2013) A proposal for isolating and testing phosphate-solubilizing bacteria that enhance plant growth. Biol Fertil Soils 49(1):1–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-012-0756-4
Bhatia S, Sharma DK (2010) Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene, its alkylated derivatives and crude oil by a newly isolated strain Pantoea agglomerans D23W3. Biochem Eng J 50(3):104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2010.04.001
Brenner DJ, Kieg NR, Staley JT, Garrity GM (2001) Bergey's Manual® of systematic bacteriology, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 713–720. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-28022-7
Chi R, Xiao C, Gao H (2006) Bio-leaching of phosphorous from rock phosphate containing pyrites by Acidithiobacillus ferroxidans. Miner Eng 19(9):979–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2005.10.003
Coutinho FP, Felix WP, Yano-Melo AM (2012) Solubilization of phosphates in vitro by Aspergillus spp. and Penicillium spp. Ecol Eng 42(9):85–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.02.002
Duan JY, Yi T, Lu ZY, Shen DL, Feng YJ (2007) Rice endophyte Pantoea agglomerans YS19 forms multicellular symplasmata via cell aggregation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 270(2):220–226. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00677.x
Dutkiewicz J, Mackiewicz B, Lemieszek MK, Golec M, Milanowski J (2015) Panotoea agglomerans: a marvelous bacterium of evil and good: Part I: Deleterious effects: Dust-borne endotoxins and allergens-focus on cotton dust. Ann Agric Environ Med 22(4):576–588. https://doi.org/10.5604/12321966.1185757
Gadd GM (1999) Fungal production of citric and oxalic acid: importance in metal speciation, physiology and biogeochemical processes. Adv Microb Physiol 41:47–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2911(08)60165-4
Ghosh R, Barman S, Mukherjee R, Mandal NC (2016) Role of phosphate solubilizing Burkholderia spp. for successful colonization and growth promotion of Lycopodium cernuum L. (Lycopodiaceae) in lateritic belt of Birbhum district of West Bengal, India. Microbiol Res 183:80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2015.11.011
Gupta P, Kumar V (2017) Value added phytoremediation of metal stressed soils using phosphate solubilizing microbial consortium. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2176-3
Iyer B, Rajput MS, Rajkumar S (2017) Effect of succinate on phosphate solubilization in nitrogen fixing bacteria harbouring chick pea and their effect on plant growth. Microbiol Res 202:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2017.05.005
Jung I, Park DH, Park K (2002) A study of the growth condition and solubilization of phosphate from hydroxyapatite by Pantoea agglomerans. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 7(4):201–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932970
Kaur G, Reddy MS (2013) Phosphate solubilizing rhizobacteria from an organic farm and their influence on the growth and yield of maize (Zea mays L). J Gen Appl Microbiol 59(4):295–303. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.59.295
Khan MS, Zaidi A, Wani PA (2007) Role of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms in sustainable agriculture- a review. Agron Sustain Dev 27(1):29–43. https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2006011
Kim KY, McDonald GA, Jordan D (1997) Solubilization of hydroxyapatite by Enterobacter agglomerans and cloned Escherichia coli in culture medium. Biol Fertil Soils 24(4):347–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050256
Li LL, Lv ZS, Yuan XL (2013) Effect of L-glycine on bio-leaching of collophanite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 85(7):156–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.07.002
Li LL, Lv ZS, Zuo ZY, Yang ZH, Yuan XL (2016) Effect of energy source and leaching method on bio-leaching of rock phosphates by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 164:238–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2016.06.018
Li LL, Zuo ZY, Lv ZS, Yang ZH, Qi XR, Zhou WT, Guan HY, Liu YN, Mao W (2018) Isolation and characterization of Acidithiobacillus caldus TST3 and the effect of pre-cultivation on its dissolution of phosphorous from rock phosphates. Hydrometallurgy 177:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2018.02.010
Ma Q, Yang Z, Pu M, Peti W, Wood TK (2011) Engineering a novel c-di-GMP-binding protein for biofilm dispersal. Environ Microbiol 13(3):631–642. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02368.x
Priha O, Sarlin T, Blomberg P, Wendling L, Mäkinen J, Arnold M, Kinnunen P (2014) Bioleaching phosphorus from fluorapatites with acidophilic bacteria. Hydrometallurgy 150:269–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.08.002
Sahay R, Patra DD (2014) Identification and performance of sodicity tolerant phosphate solubilizing bacterial isolates on Ocimum basilicum in sodic soil. Ecol Eng 71:639–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.08.007
Son HJ, Park GT, Cha MS, Heo MS (2006) Solubilization of insoluble inorganic phosphates by a novel salt- and pH-tolerant Pantoea agglomerans R-42 isolated from soybean rhizosphere. Biores Technol 97(2):204–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.02.021
Walterson AM, Stavrinides J (2015) Pantoea: insights into a highly versatile and diverse genus within the Enterobacteriaceae. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39(6):968–984. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuv027
Wei YQ, Zhao Y, Shi MZ, Cao ZY, Lu Q, Yang TX, Fan YY, Wei ZM (2018) Effect of organic acids production and bacterial community on the possible mechanism of phosphorous solubilization during composting with enriched phosphate-solubilizing bacteria inoculation. Biores Technol 247:190–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.092
Xiang WL, Liang HZ, Liu S, Luo F, Tang J, Li MY, Che ZM (2011) Isolation and performance evaluation of halotolerant phosphate solubilizing bacteria from the rhizospheric soils of historic Dagong Brine Well in China. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27(11):2629–2637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0736-0
Xiao CQ, Chi RA, Huang XH, Zhang WX, Qiu GZ, Wang DZ (2008) Optimization for rock phosphate solubilization by phosphate-solubilizing fungi isolated from phosphate mines. Ecol Eng 33(2):187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2008.04.001
Yazdani R, Safaie N, Shams-Bakhsh M (2018) Association of Pantoea ananatis and Pantoea agglomerans with leaf spot disease on ornamental plants of Araceae Family. Eur J Plant Pathol 150(1):167–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-017-1264-z
Yu X, Jiang J, Liang C, Zhang X, Wang J, Shen D, Feng Y (2016) Indole affects the formation of multicellular aggregate structures in Pantoea agglomerans YS19. J Gen Appl Microbiol 62(1):31–37. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.62.31
Zhu HJ, Sun LF, Zhang YF, Zhang XL, Qiao JJ (2012) Conversion of spent mushroom substrate to biofertilizer using a stress-tolerant phosphate-solubilizing Pichia farinose FL7. Biores Technol 111:410–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.02.042
Zhu HJ, Liu JH, Sun LF, Hu ZF, Qiao JJ (2013) Combined alkali and acid pretreatment of spent mushroom substrate for reducing sugar and biofertilizer production. Biores Technol 136:257–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.02.121
Acknowledgements
The present work was financed by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21376184), Foundation from Educational Commission of Hubei Province of China (Grant No. D20191101), Natural Science Foundation of Hubei province of China (2009CDA006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Chen, R., Zuo, Z. et al. Evaluation and improvement of phosphate solubilization by an isolated bacterium Pantoea agglomerans ZB. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 36, 27 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2744-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2744-4