Abstract
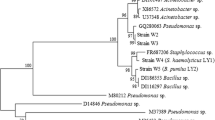
Four aerobic bacterial strains capable of utilizing di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) as the sole source of carbon and energy were isolated from river sediments. Based on the morphology, biochemical characterization, and 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, they were identified as Gordonia sp. The optimal conditions for DBP degradation by these strains were found to be pH 7.0, 30°C, and stirring at 175 rpm. These four strains could degrade, respectively, 96, 98, 98, and 78% of DBP (400 mg l−1) as well as dimethyl phthalate (DMP), diethyl phthalate (DEP), di-n-octyl phthalate (DOP), di-isooctyl phthalate (DIOP), and di-isononyl phthalate (DINP). Furthermore, partial sequences of the gene for 3,4-phthalate dioxygenase were obtained from all four strains. To our knowledge, this is the first time that the 3,4-phthalate dioxygenase gene has been successfully cloned from Gordonia sp.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arenskotter M, Broker D, Steinbuchel A (2004) Biology of the metabolically diverse genus Gordonia. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3195–3204
Asaoka K, Hagihara K, Kabaya H, Sakamoto Y, Katayama H, Yano K (2000) Uptake of phthalate esters, di-(n-butyl)phthalate and di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate, as environmental chemicals in monkeys in Japan. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 64:679–685
Bento M, Camargo A, Okeke C, Frankenberger T (2005) Comparative bioremediation of soils contaminated with diesel oil by natural attenuation, biostimulation and bioaurmention. Bioresour Technol 96:1049–1055
Chao WL, Cheng CY (2007) Effect of introduced phthalate-degrading bacteria on the diversity of indigenous bacterial communities during di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) degradation in a soil microcosm. Chemosphere 67:482–488
Chao WL, Lin CM, Shiung II, Kuo YL (2006) Degradation of di-butyl-phthalate by soil bacteria. Chemosphere 63:1377–1383
Chatterjee S, Tapan KD (2003) Metabolism of butyl benzyl phthalate by Gordonia sp. strain MTCC 4818. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 30:36–43
Chatterjee S, Mallick S, Tapan KD (2005) Pathways in the degradation of hydrolyzed alcohols of butyl benzyl phthalate in metabolically diverse Gordonia sp. strain MTCC 4818. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 9:110–120
Eaton RW (2001) Plasmid-encoded phthalate catabolic pathway in Arthrobacter keyseri 12B. J Bacteriol 183:3689–3703
Fang HHP, Liang DW, Zhang T (2007) Aerobic degradation of diethyl phthalate by Sphingomonas sp. Bioresour Technol 98:717–720
Fang C, Yao J, Zheng Y, Jiang C, Hu L, Wu Y, Shen D (2010) Dibutyl phthalate degradation by Enterobacter sp. T5 isolated from municipal solid waste in landfill bioreactor. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 64:442–446
Gu JG, Han BP, Duan SS, Zhao ZY, Wang YP (2009) Degradation of the endocrine-disrupting dimethyl phthalate carboxylic ester by Sphingomonas yanoikuyae DOS01 isolated from the South China Sea and the biochemical pathway. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 63:450–455
Habe H, Miyakoshi M, Chung J, Kasuga K, Yoshida T, Nojiri H, Omori T (2003) Phthalate catabolic gene cluster is linked to the angular dioxygenase gene in Terrabacter sp. strain DBF63. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61:44–54
Hashizume K, Nanya J, Toda C, Yasui T, Nagano H, Kojima N (2002) Phthalate esters detected in various water samples and biodegradation of the phthalates by microbes isolated from river water. Biol Pharm Bull 25:209–214
Liang DW, Zhang T, Fang HHP, He JZ (2008) Phthalates biodegradation in the environment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80:183–198
Lu Y, Tang F, Wang Y, Zhao JH, Zeng X, Luo QF, Wang L (2009) Biodegradation of dimethyl phthalate, diethyl phthalate and Di-n-butyl phthalate by Rhodococcus sp. L4 isolated from activated sludge. J Hazard Mater 168:938–943
Roslev P, Vorkamp K, Aarup J, Frederiksen K (2007) Degradation of phthalate esters in an activated sludge wastewater treatment plant. Water Res 41:969–976
Staples CA, Peterson DR, Parkerton TF, Adams WJ (1997) The environmental fate of phthalate esters: a literature review. Chemosphere 35:667–749
Sung HH, Kao WY, Su YJ (2003) Effects and toxicity of phthalate esters to hemocytes of giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquatic Toxicol 64:25–37
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Wu X, Liang R, Dai Q, Jin D, Wang Y, Chao W (2009) Complete degradation of di-n-octyl phthalate by biochemical cooperation between Gordonia sp. strain JDC-2 and Arthrobacter sp. strain JDC-32 isolated from activated sludge. J Hazard Mater 176:262–268
Xu XR, Lia HB, Gu JD (2005) Biodegradation of an endocrine-disrupting chemical di-n-butyl phthalate ester by Pseudomonas uorescens B-1. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 55:9–15
Xu HL, Li WJ, Liu ZH, Jiang CL (2007) Actinomycete systematic—principle, methods and practice. Science press, Beijing
Zeng F, Cui KY, Li XD, Fu JM, Sheng GY (2004) Biodegradation kinetics of phthalate esters by Pseudomonas fluoresences FS1. Process Biochem 39:1125–1129
Acknowledgments
This investigation was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30770388).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Wang, Y., Dai, Q. et al. Isolation and characterization of four di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP)-degrading Gordonia sp. strains and cloning the 3,4-phthalate dioxygenase gene. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27, 2611–2617 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0734-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0734-2