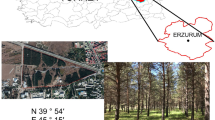
Abstract
In order to determine the heavy metal amounts of white birch afforestation, cobalt (Co), chrome (Cr), arsenic (As) and cadmium (Cd) and manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), nickel (Ni), and lead (Pb) concentrations were calculated within the scope of this study. And it is seen that heavy metal concentrations in soil and plant tissues varied. The highest concentration of heavy metals in soil was discovered in Mn, while the lowest concentration was observed in Cd. Heavy metal concentrations follow this order of Mn > Zn > Cr > Ni > Co > Pb > As > Cd in soil. Simultaneously, soil pollution was assessed, and no significant amount of pollution was discovered in the research area’s soil. PI values varied between 0.41 and 2.15. The PLI value was determined as 1.46. The average concentrations in plant parts were branch > bark > leaf, with Mn having the greatest concentration in the branch part. In comparison to plant parts, bioaccumulation factors (BAFs) were found in Cd at the highest bark layer. Cd > Pb > Zn > As > Ni > Mn > Cr > Co order was followed according to the mean BAF values. It is believed that using White birch barks as a biomonitoring tool may be useful, particularly in monitoring increases in Cd concentrations in urban settings. Additionally, to maximize heavy metal retention, it is advised to use hyperaccumulator plant combinations according to local climatic conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
The data that support the findings of this study are available from “Water, Air, and Soil Pollution” but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of Water, Air, and Soil Pollution.
References
Abacı Bayar, A. A., & Yılmaz, K. (2020). Adıyaman, Kahramanmaraş ve Hatay sulak alani topraklarinda bazi ağir metal kirliliğinin değerlendİrİlmesİ. Black Sea Journal of Agriculture, 3(2), 7.
Ahmadi, M., Jorfi, S., Azarmansuri, A., Jaafarzadeh, N., Mahvi, A. H., Soltani, R. D. C., … Akhbarizadeh, R. (2017). Zoning of heavy metal concentrations including Cd, Pb and As in agricultural soils of Aghili plain, Khuzestan province, Iran. Data in brief, 14, 20–27.
Alloway, B. J. (2012). Heavy metals in soils: trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability (Vol. 22): Springer Science & Business Media.
Aničić, M., Spasić, T., Tomašević, M., Rajšić, S., & Tasić, M. (2011). Trace elements accumulation and temporal trends in leaves of urban deciduous trees (Aesculus hippocastanum and Tilia spp.). Ecological Indicators, 11(3), 824–830.
Aricak, B., Cetin, M., Erdem, R., Sevik, H., & Cometen, H. (2020). The usability of Scotch pine (Pinus sylvestris) as a biomonitor for traffic-originated heavy metal concentrations in Turkey. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 29(2).
Bilgili, A., & Çomaklı, E. (2021). Evaluation of the relationship between root nutrients and root biomass in lands under different management practices. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193(12), 1–11.
Chen, Z., Tsai, C., & Tsui, C. (1999). Proposed regulation of soil pollutants in Taiwan soils. Paper presented at the Proceedings of 6th workshop on soil pollution and prevention: Soil remediation techniques on Soils Contaminated by Organic Pollutants. Taipei, Taiwan.
Comakli, E., Bingöl, M. S., & Çomakli, T. (2018). Determining the some heavy metal content of Pinus sylvestris needles and soil in the urban forest by the side of the road. Alinteri Journal of Agriculture Science, 33(2), 209–214.
Çomaklı, E., & Bingöl, M. S. (2021). Heavy metal accumulation of urban Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) plantation. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 193(4), 192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-08921-6
Czaja, M., Kołton, A., Baran, A., Muszyńska, E., & Muras, P. (2015). Physiological responses of Betula pendula Roth growing in polluted areas. Ecological Questions, 22, 39–46.
Dadea, C., Bacchiocchi, S., Rocca, N. L., Mimmo, T., Russo, A., & Zerbe, S. (2016). Heavy metal accumulation in urban soils and deciduous trees in the City of Bolzano, N Italy. Waldökologie Landschaftsforschung und Naturschutz (Forest Ecology, Landscape Research and Nature Protection), 15, 35–42.
Dmuchowski, W., Gozdowski, D., Baczewska, A. H., & Brągoszewska, P. (2013). Evaluation of various bioindication methods of measuring zinc environmental pollution. International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 51(3–4), 238–254.
Dmuchowski, W., Gozdowski, D., Brągoszewska, P., Baczewska, A. H., & Suwara, I. (2014). Phytoremediation of zinc contaminated soils using silver birch (Betula pendula Roth). Ecological Engineering, 71, 32–35.
Eränen, J. (2008). Rapid evolution towards heavy metal resistance by mountain birch around two subarctic copper–nickel smelters. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 21(2), 492–501.
Faria, J. M., Teixeira, D. M., Pinto, A. P., Brito, I., Barrulas, P., Alho, L., & Carvalho, M. (2020). Toxic levels of manganese in an acidic Cambisol alters antioxidant enzymes activity, element uptake and subcellular distribution in Triticum aestivum. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 193, 110355.
Fuganti, A., Morteani, G., Bazzoli, G., Cocco, S., Santuliana, E., & Visintainer, M. (2005). L’arsenico nelle rocce, nelle acque superficiali e nelle acque sotterranee della valle dell’Adige fra Mezzolombardo e Mattarello e presso Roveré della luna (Trento). Atti della accademia roveretana degli agiati. Classe Di Scienze Matematiche, Fisiche e Naturali, 5, 59–94.
Gorlach, E., & Gambuś, F. (2000). Potencjalnie toksyczne pierwiastki śladowe w glebach (nadmiar, szkodliwość i przeciwdziałanie). Zeszyty Problemowe Postępów Nauk Rolniczych, 472, 275–296.
Ha, J., & Martinez, H. (2018). Influence of environmental pollution on leaf properties of urban trees in China and USA: A comparative study using stomatal density. Asian J Plant Sci Res, 8, 1–7.
Hassan, M. U., Chattha, M. U., Khan, I., Chattha, M. B., Aamer, M., Nawaz, M., … Khan, T. A. (2019). Nickel toxicity in plants: reasons, toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and remediation possibilities—a review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(13), 12673–12688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04892-x
Hrdlicka, P., Kula, E., & Zabecka, J. (2001). Zawartosc wybranych pierwiastkow w lisciach brzozy [Betula verrucosa Ehrh.] rosnacej na terenach znajdujacych sie pod wplywem imisji przemyslowych w okolicy Olkusza. Sylwan, 145(01), 101–110.
Janjić, N., Hasanagić, D., & Maksimović, T. (2017). Stomatal apparatus response of Tilia cordata (Mill.) and Betula pendula (Roth.) to air quality conditions in the City of Banja Luka (Bosnia and Herzegovina). Biologia Serbica, 39(2).
Kabata-Pendias, A., & Mukherjee, A. B. (2007). Trace elements from soil to human: Springer Science & Business Media.
Kabata-Pendias, A., & Pedias, H. (1999). Biogeochemia pierwiastków śladowych. PWN, Warszawa. Karczewska A. 2003. Perspektywy zastosowania fitoremediacji w rekultywacji gleb zanieczyszczonych metalami ciężkimi. Ochrona Środowiska i Zasobów Naturalnych, 25/26, 27–54.
Kalashnikova, I. V., Migalina, S. V., Ronzhina, D. A., Ivanov, L. A., & Ivanova, L. A. (2021). Functional response of Betula species to edaphic and nutrient stress during restoration of fly ash deposits in the Middle Urals (Russia). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(10), 12714–12724.
Kandziora-Ciupa, M., Nadgórska-Socha, A., Ciepał Ryszard, R., & Janowicz, I. (2015). Heavy metals content and biochemical indicators in birch leaves from polluted and clean areas.
Kavcı, E. (2021). Adsorption of Direct Red 243 dye onto clay: Kinetic study and isotherm analysis. Desalination and Water Treatment, 212, 452–461.
Kirkey, F. M., Matthews, J., & Ryser, P. (2012). Metal resistance in populations of red maple (Acer rubrum L.) and white birch (Betula papyrifera Marsh.) from a metal-contaminated region and neighbouring non-contaminated regions. Environmental Pollution, 164, 53–58.
Kul, S., Gül, V., & Cengiz, İ. (2021). Toprak ve Bitkilerde Ağır Metal Kirliliğinin Araştırılması: Bayburt İli Örneği. Journal of Anatolian Environmental and Animal Sciences, 6(2), 195–203.
Li, J., Jia, Y., Dong, R., Huang, R., Liu, P., Li, X., … Chen, Z. (2019). Advances in the mechanisms of plant tolerance to manganese toxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(20), 5096.
Liu, J., Liu, R., Yang, Z., & Kuikka, S. (2021). Quantifying and predicting ecological and human health risks for binary heavy metal pollution accidents at the watershed scale using Bayesian Networks. Environmental Pollution, 269, 116125.
Mentese, S., & Böbrek, O. (2020). Madencilik faaliyetlerinin topraktaki ağır metaller (as, cd, co, fe ve ni) üzerine etkisi: Orhaneli ve Büyükorhan (Bursa) örneği. Ege Coğrafya Dergisi, 29(1), 45–56.
Mertens, J., Luyssaert, S., & Verheyen, K. (2005). Use and abuse of trace metal concentrations in plant tissue for biomonitoring and phytoextraction. Environmental Pollution, 138(1), 1–4.
Mishra, S., Bharagava, R. N., More, N., Yadav, A., Zainith, S., Mani, S., & Chowdhary, P. (2019). Heavy metal contamination: an alarming threat to environment and human health. In Environmental biotechnology: For sustainable future (pp. 103–125): Springer.
Mmolawa, K. B., Likuku, A. S., & Gaboutloeloe, G. K. (2011). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in soils along major roadside areas in Botswana. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 5(3), 186–196.
Nadgórska-Socha, A., Kandziora-Ciupa, M., Trzęsicki, M., & Barczyk, G. (2017). Air pollution tolerance index and heavy metal bioaccumulation in selected plant species from urban biotopes. Chemosphere, 183, 471–482.
De Nicola, F., Spagnuolo, V., Baldantoni, D., Sessa, L., Alfani, A., Bargagli, R., … Giordano, S. (2013). Improved biomonitoring of airborne contaminants by combined use of holm oak leaves and epiphytic moss. Chemosphere, 92(9), 1224–1230.
Nock, C. A., Paquette, A., Follett, M., Nowak, D. J., & Messier, C. (2013). Effects of urbanization on tree species functional diversity in eastern North America. Ecosystems, 16(8), 1487–1497.
Nowak, D. J., Crane, D. E., & Stevens, J. C. (2006). Air pollution removal by urban trees and shrubs in the United States. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 4(3–4), 115–123.
Ozturk, A., Yarci, C., & Ozyigit, I. I. (2017). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in Istanbul using plant (Celtis australis L.) and soil assays. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, 31(5), 948–954.
Parrotta, L., Guerriero, G., Sergeant, K., Cai, G., & Hausman, J.-F. (2015). Target or barrier? The cell wall of early-and later-diverging plants vs cadmium toxicity: Differences in the response mechanisms. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6, 133.
Petrova, S., Yurukova, L., & Velcheva, I. (2014a). Atm spheric Pollution Research. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 5, 196–202.
Petrova, S., Yurukova, L., & Velcheva, I. (2014b). Possibilities of using deciduous tree species in trace element biomonitoring in an urban area (Plovdiv, Bulgaria). Atmospheric Pollution Research, 5(2), 196–202.
Petrushkevych, Y., & Korshykov, I. (2020). Ecological and biological characteristics of Betula pendula in the conditions of urban environment. Regulatory Mechanisms in Biosystems, 11(1), 29–36.
Radomirović, M., Ćirović, Ž., Maksin, D., Bakić, T., Lukić, J., Stanković, S., & Onjia, A. (2020). Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil at a former painting industry facility. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 8(177). https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2020.560415
Rana, V., & Maiti, S. K. (2018). Differential distribution of metals in tree tissues growing on reclaimed coal mine overburden dumps, Jharia coal field (India). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(10), 9745–9758. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1254-5
Remon, E., Bouchardon, J.-L., Le Guédard, M., Bessoule, J.-J., Conord, C., & Faure, O. (2013). Are plants useful as accumulation indicators of metal bioavailability? Environmental Pollution, 175, 1–7.
Samecka-Cymerman, A., Stankiewicz, A., Kolon, K., & Kempers, A. (2009). Self-organizing feature map (neural networks) as a tool to select the best indicator of road traffic pollution (soil, leaves or bark of Robinia pseudoacacia L.). Environmental Pollution, 157(7), 2061–2065.
Schreck, E., Laplanche, C., Le Guédard, M., Bessoule, J.-J., Austruy, A., Xiong, T., … Dumat, C. (2013). Influence of fine process particles enriched with metals and metalloids on Lactuca sativa L. leaf fatty acid composition following air and/or soil-plant field exposure. Environmental pollution, 179, 242–249.
Severoglu, Z., Ozyigit, I. I., Dogan, I., Kurmanbekova, G., Demir, G., Yalcin, I. E., & Kari, G. K. (2015). The usability of Juniperus virginiana L. as a biomonitor of heavy metal pollution in Bishkek City, Kyrgyzstan. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, 29(6), 1104–1112.
Sevik, H., Cetin, M., Ozel, H. B., Akarsu, H., & Cetin, I. Z. (2020). Analyzing of usability of tree-rings as biomonitors for monitoring heavy metal accumulation in the atmosphere in urban area: a case study of cedar tree (Cedrus sp.). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(1), 1–11.
Shahid, M., Dumat, C., Khalid, S., Schreck, E., Xiong, T., & Niazi, N. K. (2017). Foliar heavy metal uptake, toxicity and detoxification in plants: A comparison of foliar and root metal uptake. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 325, 36–58.
Steinnes, E., Lukina, N., Nikonov, V., Aamlid, D., & Røyset, O. (2000). A gradient study of 34 elements in the vicinity of a copper-nickel smelter in the Kola Peninsula. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 60(1), 71–88.
Sürücü, A., & Elaltuntaş, E. (2018). Cobalt, chromium, copper and manganese pollution in the soil near the Bingöl-Erzurum Highway. 1. Paper presented at the International gap agriculture & livestock congress.
Szwalec, A., Mundała, P., Kędzior, R., & Pawlik, J. (2020). Monitoring and assessment of cadmium, lead, zinc and copper concentrations in arable roadside soils in terms of different traffic conditions. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(3), 1–12.
Tomašević, M., & Aničić, M. (2010). Trace element content in urban tree leaves and SEM-EDAX characterization of deposited particles. Facta Universitatis-Series: Physics, Chemistry and Technology, 8(1), 1–13.
Tomašević, M., Aničić, M., Jovanović, L., Perić-Grujić, A., & Ristić, M. (2011). Deciduous tree leaves in trace elements biomonitoring: A contribution to methodology. Ecological Indicators, 11(6), 1689–1695.
Turkyilmaz, A., Sevik, H., Cetin, M., & Ahmaida Saleh, E. A. (2018). Changes in heavy metal accumulation depending on traffic density in some landscape plants. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 27(5).
Wang, Y., Duan, X., & Wang, L. (2020). Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in soils influenced by industrial enterprise distribution: case study in Jiangsu Province. Science of the Total Environment, 710, 134953.
Xiong, T.-T., Leveque, T., Austruy, A., Goix, S., Schreck, E., Dappe, V., … Dumat, C. (2014). Foliar uptake and metal (loid) bioaccessibility in vegetables exposed to particulate matter. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36(5), 897–909.
Yalcin, I. E., Ozyigit, I. I., Dogan, I., Demir, G., & Yarci, C. (2020). Using the Turkish red pine tree to monitor heavy metal pollution. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 29(5), 3881–3889.
Zhang, H., Zhang, L.-L., Li, J., Chen, M., & An, R.-D. (2020). Comparative study on the bioaccumulation of lead, cadmium and nickel and their toxic effects on the growth and enzyme defence strategies of a heavy metal accumulator, Hydrilla verticillata (Lf) Royle. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1–13.
Žibret, G., Van Tonder, D., & Žibret, L. (2013). Metal content in street dust as a reflection of atmospheric dust emissions from coal power plants, metal smelters, and traffic. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(7), 4455–4468.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çomaklı, E., Bingöl, M.S. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Accumulations in Plant Organs and Soil White Birch (Betula verrucosa Ehrh.) Plantation. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 515 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05473-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05473-w