Abstract
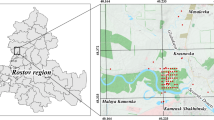
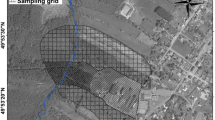
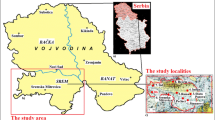
The quantification of heavy metal contents in soils and their sources are essential for contamination monitoring and the assessment of the potential risks to the ecosystems. This study aims to investigate the source of heavy metals and other elements in soils from a uranium-phosphate deposit using integrated multivariate and geostatistics techniques. For this, 50 soil samples in Itataia deposit, Northeastern, Brazil, were collected at 0–0.2-m depth for the determination of U, Fe, Al, Mn, Ti, Zn, Cu, Ni, Mo, Co, Cr, Cd, Pb, As, Se, V, B, and Zr. The Pb, Se, Ni, Cr, As, and Mo mean contents were closer or exceeded The Brazilian Environmental Council (CONAMA) prevention values for soils. Uranium content was about 500 times higher than the mean levels reported for Brazilian soils. The cluster analysis indicates three geochemical groups based on different contamination levels. The first principal component was associated with lithological origin, the second principal component may be related to anthropogenic sources, and the third and fourth principal components indicated a joined source (natural and anthropogenic), indicating different sources of contamination. Mo was not related to other heavy metals, being found independent in the area. The accumulation of heavy metals in soils is associated not only with the parent material but also with the minerals of the soil. In the area of study, calcareous soils favored alkaline conditions that influenced the dynamics of heavy metals. The multivariate and geostatistical analyses were able to provide preliminary information regarding the metal contents in soil for environmental management.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano, D. C. (2001). Trace elements in the terrestrial environment: biogeochemistry, bioavailability, and risks of metals. Springer.
Ai, S., Liu, B., Yang, Y., Ding, J., Yang, W., Bai, X., Naeem, S., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Temporal variations and spatial distributions of heavy metals in a wastewater-irrigated soil-eggplant system and associated influencing factors. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 153, 204–221.
Angeiras, A. G. (1988). Geology and metallogeny of the Northeastern Brazil uranium-phosphorus province emphasizing the Itataia deposit. Ore Geology Reviews, 3, 211–225.
Bech, J., Suarez, M., Reverter, F., Tume, P., Sánchez, P., Bech, J., & Lansac, A. (2010). Selenium and other trace elements in phosphate rock of bayovar–sechura (Peru). Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 107, 136–145.
Biondi, C. M., Nascimento, C. W. A., Neta, A. B. F., & Ribeiro, M. R. (2011). Teores de Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu, Ni e Co em solos de referência de Pernambuco. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 35, 1057–1066.
Chai, Y., Guo, J., Chai, S., Cai, J., Xue, L., & Zhang, Q. (2015). Source identification of eight heavy metals in grassland soils by multivariate analysis from the Baicheng–Songyuan area, Jilin Province, Northeast China. Chemosphere, 134, 67–75.
Chen, Y. M., Gao, J. B., Yuan, Y. Q., Ma, J., & Yu, S. (2016). Relationship between heavy metal contents and clay mineral properties in surface sediments: implications for metal pollution assessment. Continental Shelf Research, 124, 125–133.
Conama - Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente. (2009). Conama, no 420/2009. http://wwwMma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi=620. Accessed 18 June 2016.
Crannell, S. B. (2000). Heavy metal stabilization in municipal solid waste combustion bottom ash using soluble phosphate. Waste Management, 20, 135–148.
Cunha, C. S. M., Hernandez, F. F. F., da Silva, F. N., Ortiz Escobar, M. E., Magalhães, D. R., & dos Anjos, D. C. (2014). Relação entre solos afetados por sais e concentração de metais pesados em quatro perímetros irrigados no Ceará. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental, 18, S80–S85.
Cunha, C.S.M., Silva, Y. J.A. B. da, Ortiz Escobar, M.E., Nascimento, C.W.A do. (2018). Spatial variability and geochemistry of rare earth elements in soils from the largest uranium-phosphate deposit of Brazil. Environmental geochemistry and health, 40, 1629-1643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0077-0
Azevedo, F. A. de, Chasin, A. A. da M. (2004). As bases toxicológicas da ecotoxicologia. Editora Rima.
Eich-Greatorex, S., Krogstad, T., & Sogn, T. A. (2010). Effect of phosphorus status of the soil on selenium availability. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 173, 337–344.
Embrapa – Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária.(2011). Centro nacional de pesquisas de solos. Manual de métodos de análises de solos. 2nd .ed. Rio de Janeiro: Embrapa solos.
Fendorf, S., Michael, H. A., & Van Geen, A. (2010). Spatial and temporal variations of groundwater arsenic in south and Southeast Asia. Science, 328, 1123–1127.
Goh, K. H., & Lim, T. T. (2004). Geochemistry of inorganic arsenic and selenium in a tropical soil: effect of reaction time, pH and competitive anions on arsenic and selenium adsorption. Chemosphere, 55, 849–859.
Goldschmidt, V. M. (1958). Geochemistry. London. oxford university press.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., Anderson, R. E., & Tatham, R. L. (2009). Análise multivariada de dados (6th ed.). Porto alegre: bookman.
Haribala, Hu, B. Wang, C Gerilemandahu, Xu, X., Zhang, S., Bao, S., Li, Y. (2016). Assessment of radioactive materials and heavy metals in the surface soil around uranium mining area of Tongliao,China Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 130, 185–192.
IBGE. Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (2018). Mapa Recursos Naturais, Informações ambientais, Pedologia. Portal de Mapas do IBGE. Pedologia: Carta SA-24 – Fortaleza. Escala 1:250000. Updated in Aug./2018. Available in: https://geoftp.ibge.gov.br/informacoes_ambientais/pedologia/vetores/escala_250_mil/recorte_milionesimo/SA24_pedo.zip. Accessed: 10 May 2019.
INB - Indústrias Nucleares do Brasil. 2010. Available in: http://www.inb.gov.br/inb/WebForms/default.aspx. Accessed: 10 January 2015.
IUSS-Working Group WRB. (2014). World reference base for soil resources 2014. World Soil Resources Report No. 106.
Jansson-Charrier, M., Guibal, E., Roussy, J., Delanghe, B., & Le Cloirec, P. (1996). Vanadium (IV) sorption by chitosan: kinetics and equilibrium. Water Research, 30, 465–475.
Kabata-Pendias, A., & Pendias, H. (2001). Trace elements in soils and plants (3rd ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: Crc Press.
Kelepertzis, E. (2014). Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils of mediterranean: insights from Argolida basin, Peloponnese, Greece. Geoderma, 222, 82–90.
Kwon, J. C., Nejad, Z. D., Jung, M. C. (2017). Arsenic and heavy metals in paddy soil and polished rice contaminated by mining activities in Korea. 148, 92–100.
Lee, Y. J. (2010). Spectroscopic investigation of arsenate and selenate incorporation into hydroxylapatite. Current Applied Physics, 10, 158–163.
Little, M. G., & Lee, C. T. A. (2010). Sequential extraction of labile elements and chemical characterization of a basaltic soil from Mt. Meru, Tanzania. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 57, 444–454.
Liu, R., Men, C., Liu, Y., Yu, W., Xu, F., & Shen, Z. (2016). Spatial distribution and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in Yangtze estuary sediment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 110, 564–571.
Lopes Filho, A. F. (1977). Bases de estudos hidrogeológicos para a região de Itatira. Nota técnica. Fortaleza: Nuclebrás/DRM.
Lv, J. (2019). Multivariate receptor models and robust geostatistics to estimate source apportionment of heavy metals in soils. Environmental pollution, 244,72-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.147
Mendonça, J. C. J. S., Campos, M., Braga, A. P. G., Souza, E. M., Favali, J. C., & Leal, J. R. L. V. (1985). Jazida de urânio de Itataia-Ceara. In Principais depositos minerais do Brasil, I (pp. 121–131). Departamento Nacional de Producao Mineral-DNPM/Companhia Vale do Rio Doce-CVRD.
Naeem, A., Westerhoff, P., & Mustafa, S. (2007). Vanadium removal by metal (hydr) oxide adsorbents. Water Research, 41, 1596–1602.
Nannoni, F., & Protano, G. (2016). Chemical and biological methods to evaluate the availability of heavy metals in soils of the Siena urban area (Italy). Science of the Total Environment, 568, 1–10.
Nickel, S., Hertel, A., Pesch, R., Schroder, W., Steinnes, E., & Uggerud, H. T. (2014). Modelling and mapping spatio-temporal trends of heavy metal accumulation in moss and natural surface soil monitored 1990 - 2010 throughout Norway by multivariate generalized linear models and geostatistics. Atmospheric Environment, 99, 85–93.
NIST - National Institute of Standards and Technology Standard. (2003). Reference material - SRM 2709 addendum issue date: 18 July 2003.
Obiora, S. C., Chukwu, A., & Davies, T. C. (2016). Heavy metals and health risk assessment of arable soils and food crops around Pb - Zn mining localities in Enyigba, Southeastern Nigeria. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 116, 182–189.
Paschoa, A. S., & Godoy, J. M. (2002). The areas of high natural radioactivity and TENORM wastes. International Congress Series, 1225, 3–8.
Perez, D. V. (1998). Total concentration of uranium and thorium in some Brazilian soils. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 33, 1417–1423.
Preston, W., Nascimento, C. W. A., Biondi, C. M., Souza Junior, V. S., Silva, W. R., & Ferreira, H. A. (2014). Valores de referência de qualidade para metais pesados em solos do Rio Grande do Norte. Revista brasileira de ciências do solo, 38, 2041–2051.
RIMA - Relatório de Impacto Ambiental. Projeto Santa Quitéria - Santa Quitéria, CE. 2014. http://www.consorciosantaquiteria.com.br/arquivos/rima.pdf. Accessed: 24 June 2016.
Rodrigues, U.M.T.(2008) Meio ambiente, ecossistemas, caatinga. Available in: http://www.mre.gov.br/cdbrasil/itamaraty/web/port/meioamb/ecossist/caatinga/index.htm. Accessed: 13 May 2008.
Sadeghi, A., Graff, C. D., Starr, J., McCarty, G., Codling, E., & Sefton, K. (2006). Spatial variability of soil phosphorous levels before and after poultry litter application. Soil Science, 171, 850–857.
Schaller, J., Weiske, A., & Dudel, E. G. (2011). Effects of gamma-sterilization on doc, uranium and arsenic remobilization from organic and microbial rich stream sediments. Science of the Total Environment, 409, 3211–3214.
Shi, J., Wang, H., Xu, J., Wu, J., Liu, X., Zhu, H., & Yu, C. (2007). Spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils: a case study of Changxing, China. Environmental Geology, 52, 1–10.
Silva, F. B., Nascimento, C. W. A., Araújo, P. R., da Silva, L. H., & da Silva, R. F. (2016). Assessing heavy metal sources in sugarcane Brazilian soils: an approach using multivariate analysis. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 457.
Sipos, P., Nemeth, T., May, Z., & Szalai, Z. (2011). Accumulation of trace elements in Fe-rich nodules in a neutral-slightly alkaline floodplain soil. Carpathian journal of earth and environmental sciences, 6, 13–22.
USEPA - US Environmental Protection Agency. (1998.). Method 3050 b. http://www.epa.gov/sw-846/pdfs/3050b.pdf. 29 July 2015.
Veríssimo, C. U. V., Santos, R. V., Parente, C. V., de Oliveira, C. G., Cavalcanti, J. A. D., & Neto, J. A. N. (2016). The Itataia phosphate-uranium deposit (Ceara, Brazil) new petrographic, geochemistry and isotope studies. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 70, 115–144.
Yang, J., Wang, M., Jia, Y., Gou, M., & Zeyer, J. (2017). Toxicity of vanadium in soil on soybean at different growth stages. Environmental Pollution, 231, 48–58.
Yu, R. L., Yuan, X., Zhao, Y., Hu, G., & Tu, X. (2008). Heavy metal pollution in interdital sediments from Quanzhou Bay, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 20, 664–669.
Zwonitzer, J. C., Pierzynsky, G. M., & Hettiarachchi, G. M. (2003). Effects of phosphorus additions on lead, cadmium, and zinc bioavailabilities in metal-contaminated soil. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 143, 193–209.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to CAPES (Brazilian Federal Agency for Support and Evaluation of Graduate Education) for granting the scholarship of the first author, to the “Pró-Integração” project 55/2013 for partially funding this research and to Industrias Nucleares do Brasil for allowing the sampling. The authors also would like to acknowledge anonymous reviewers for helpful comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cunha, C.S.M., Hernandez, R.D.Z., Hernandez, F.F.F. et al. Assessment of Heavy Metal Sources in Soils from a Uranium-Phosphate Deposit Using Multivariate and Geostatistical Techniques. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 168 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4207-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4207-9