Abstract
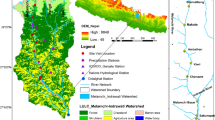
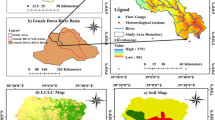
Jordan is an arid country with limited water resources, so there is a chronic need to study and understand its hydrology at the watershed scale which will eventually help in achieving good management for the existing scarce water resources. The studied watershed was the Zarqa River Basin which is considered as the largest watershed in Jordan. The objective of this study was to calibrate the hydrological component of the Hydrological Simulation Program – FORTRAN (HSPF) model for the Zarqa River Basin. The calibrated model could be used in a later stage to examine the impact of different management practices and climate change scenarios on the water resources in the basin. The calibration of the HSPF water quantity parameters was aided by GIS and by the automatic calibration model (PEST). The automatic calibration was done for the years 1988–1991 and the validation was done for the years 1996–1998. The coefficient of determination, R 2 for the calibration and verification years of the monthly flows was 0.81 and 0.76, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Abed N, Whiteley H (2002) Calibration of the hydrological simulation program fortran (HSPF) model using automatic calibration and GIS. J Hydrol Process 16:3169–3188
Al-Abed N, Abdullah F, Abu Khyarah A (2005) GIS-hydrological models for managing water resources in the Zarqa River basin. Environ Geol 47:405–411
Albek M, Öğütveren U, Albek E (2004) Hydrological modeling of Seydi Suyu watershed (Turkey) with HSPF. J Hydrol 285:260–271
Al-Haddadin M (2002) Drought assessment and management for selected water resources basins in jordan using Geographic Information System (GIS). MS thesis, Civil Engineering Department, Jordan University for Science and Technology
Bahremand A, De Smedt F (2007) Distributed hydrological modeling and sensitivity analysis in Torysa Watershed, Slovakia. Water Resour Manag DOI 10.1007/s11269-007-9168-x
Bicknell BR, Imhoff JC, Kittle JL, Jobes TH, Donigian AS (2001) Hydrological simulation program – Fortran: user’s manual for version 12, EPA Contract no. 68-C-98-010
Doherty J (1994) PEST: a unique computer program for model-independent parameter optimisation. Watermark, Washington, DC
Doherty J (2002) PEST: model-independent parameter estimation user manual, 5th edn. Watermark, Washington, DC
Donigian AS, Crawford NH (1976) Modelling NonPoint pollution from the land surface. Environmental Research Laboratory, Office of Research and Development. US Environmental Protection Agency, EPA-600/3-76-083
Donigian AS, Imhoff JC, Bicknell BR, Kittle JL (1984) Application guide for Hydrological Simulation Program – Fortran (HSPF). US Environmental Protection Agency, EPA-600/3-84-065
HARZA Engineering Company, Arabtech Consulting Engineers (1989) Storage facilities in the Jordan Valley, Amman, Jordan, pp 306
Hydrocomp (1996) Hydrologic Journal. Available at: http://www.hydrocomp.com
Kavetski D, Kuczera G, Franks S (2006) Calibration of conceptual hydrological models revisited. 1. Overcoming numerical artefacts. J Hydrol 320:173–186
Linsley RK, Kohler MA, Paulhus JLH (1986) Hydrology for engineers. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 339–356
Moor LW, Chew CY, Smith RH, Sahoo S (1992) Modelling of best management practices on North Reelfoot Creek, Tennessee. Water Environ Res 64(3):241–247 May/June
MWI (2002) Ministry of Water and Irrigation, Annual Report, Amman, Jordan
MWI, JICA (2000) Jordan master plan
Refsgaard JC (1997) Parameterisation, calibration and validation of distributed hydrological models. J Hydrol 198:69–97
RIVIX (2005) RiverTools users manual. Rivix, LLC
Smith B (1994) Preliminary investigations into the vulnerability of groundwater resources to contamination by natural series radio nuclides in areas associated with sedimentary phosphate. British Geological Survey Technical Report WC/94/14C, Overseas Geology Series, BGS, Key worth
Sorooshian SD, Gupta VK (1995) Model calibration. In: Singh VP (ed) Computer models of watershed hydrology. Water Resources Publication, Highlands Ranch, CO
World Bank (1997) The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, Water Sector Review, 23 pp
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Abed, N., Al-Sharif, M. Hydrological Modeling of Zarqa River Basin – Jordan Using the Hydrological Simulation Program – FORTRAN (HSPF) Model. Water Resour Manage 22, 1203–1220 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-007-9221-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-007-9221-9