Abstract
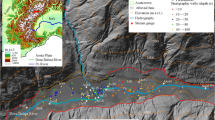
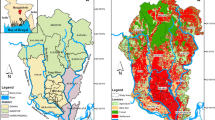
In this paper, the hydrogeologic analysis and the development of a numerical model for the simulation of a complex system of aquifers in Northern Greece are presented. The study area faces a severe environmental danger as the unsustainable water consuming practices have resulted in negative water balance and severe water shortage. Based on field data and in-situ measurements carried out by several research groups during the last 30 years, a conceptual model is developed, that alters what scientists believed to date as far as the hydraulic communication between the shallow and the deep aquifer, as well as the lake-aquifer interaction are concerned. Based on the assumptions of the conceptual model, a numerical model has been developed in order to investigate the regional groundwater flow in the aquifers. The Modflow program has been used for its implementation. The results have verified firstly that a marginal hydraulic contact between the 2 aquifers is permitted, and secondly that the assumed relation between the lake's water volume and the aquifer's water table fluctuations is practically negligible. The dramatic decrease in the lake's water reserves by 90%, as the model results show, is mainly due to the reversing of the torrent-aquifer interrelation. Finally, the model is used as a management tool for the restoration of the aquifer as well as of the lake.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BRGM (1972) Hydrogeological study of the megdonia basin for the water supply of the city of Thessaloniki, Greece, 72 RME 011, unpublished data
Davis DR, Dvoranchik WM (1971) Evaluation of the worth of additional data. Water Resour Bull 7(4):700–707
Demiris K (1994) Water resources research of Megdonia Basin. Project Report, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (in Greek)
Iman RL, Helton JC (1988) An investigation of uncertainty and sensitivity analysis techniques for computer models. Risk Anal 8(1):71–90
Freeze RA, Zapf-Gilje R, Massman J, Cahn L, Smith L, James B (1987) Advances in the assessment of data worth for engineering decision analysis in groundwater contamination problems. In a Custodio E, Gurgui A, Lobo Ferreira JP (eds) Groundwater flow and quality modeling, D. Reidel, Boston
Hunt RJ, Haitjema HM, Krohelski JT, Feinstein DT (2003) Simulating ground water-lake interactions: Approaches and insights. Ground Water 41(2):227–237
Knight, Piesold, Karavokyris G, Anelixi, Agrisystems (1999) environmental rehabilitation of lake Koronia, Greece'. European Commission, Directorate General XVI.
McDonald M, Harbaugh A (1988) A modular three-dimensional finite-difference groundwater flow model. USGS, Book 6, Chap. A1, 485
Mercier J, Mouyaris C, Simeakis T, Angelidhis C (1979) Intra-plate deformation: a quantitative study of the faults activated by the 1978. Thessaloniki earthquakes. Nature 278: 45–48
Mylopoulos N, Mylopoulos Y, Tolikas D, Kolokytha E, Karamanlidou M (2003) Integrated management plan of the deep aquifer for the lake Koronia's restoration, in proceedings XXX IAHR congress: Water engineering and research in a learning society. Thessaloniki, Greece, Theme B, pp 637–643
Peck A, Gorelick S, de Marsily G, Foster S, Kovalevsky V (1988) Consequences of spatial variability in aquifer properties and data limitations for groundwater modeling practice. IAHS Publication No 175, Wallingford, Oxfordshire
Psilovikos A (1977) Paleogeographic evolution of the Megdonia Basin, PhD, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece (in Greek)
Thanasulas K (1983) Geophysical research of Megdonia Basin, PhD, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (in Greek)
Thornthwaite CW (1948) An approach toward a radiation classification of climate. Geogr Rev 38(1):55–94
Turc L (1961) Evaluation des besoins en eau d'irrigation, evapotranspiration potentielle, formule climatique simplifiee et mise a jour. Ann Agron 12(1):13–49
Vatseris Ch (1992) Hydrogeology of the Mygdonian Basin (Northern Greece) taking into consideration the hydrochemical and isotopic composition of the thermal water, PhD, Univ. Berlin, Germany, pp 171 (in German)
Veranis N, Katirtzoglou K, Meladiotis G (2002) Hydrogeological conditions of the Koronia Lake sub-basin, Thessaloniki Prefecture, northern Greece, in Proceedings 6th Hydrogeologic Conference, Greek Geologic Association, pp 83–94
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mylopoulos, N., Mylopoulos, Y., Tolikas, D. et al. Groundwater modeling and management in a complex lake-aquifer system. Water Resour Manage 21, 469–494 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-006-9025-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-006-9025-3