Abstract
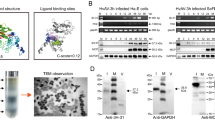
The open reading frame 117 (3h-117) of Heliothis virescens ascovirus 3h (HvAV-3h), which is a conserved coding region present in all completely sequenced ascovirus members, was characterized in this study. By RT-PCR detection, 3h-117 transcription began at 6-h post-infection (hpi) and remained stable until 168 hpi in HvAV-3h-infected Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae. In addition, 3h-117 putatively encodes a 21.5-kDa protein (3H-117) predicted to be a CTD-like phosphatase. Western blot analysis using a prepared rabbit polyclonal antibody specific to 3H-117 showed that the product could be detected at 24 hpi, which remained stably detectable until 168 hpi. The same analysis also demonstrated that the 3H-117 protein localized in the virions of HvAV-3h. Immunofluorescence analysis showed that at 24 hpi, 3H-117 was mainly located in the nuclei of H. armigera larval fat body cells and later spread into the cytoplasm. In summary, our results indicate that 3H-117 is a structural protein of HvAV-3h.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Federici BA (1983) Enveloped double-stranded DNA insect virus with novel structure and cytopathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80(24):7664–7668
Federici BA, Bideshi DK, Tan Y, Spears T, Bigot Y (2009) Ascoviruses: superb manipulators of apoptosis for viral replication and transmission. Lesser Known Large dsDNA Viruses 328:171–196
Huang GH, Hou DH, Wang M, Cheng XW, Hu Z (2017) Genome analysis of Heliothis virescens ascovirus 3h isolated from China. Virol Sin 32(2):147–154
Liu YY, Xian WF, Xue J, Wei YL, Cheng XW, Wang X (2018) Complete genome sequence of a renamed isolate, Trichoplusia ni ascovirus 6b, from the United States. Genome Announc 6(10):e00148
Li SJ, Wang X, Zhou ZS, Zhu J, Hu J, Zhao YP, Zhou GW, Huang GH (2013) A comparison of growth and development of three major agricultural insect pests infected with Heliothis virescens ascovirus 3h (HvAV-3h). PLoS ONE 8(12):e85704
Bideshi DK, Demattei MV, Rouleux-Bonnin F, Stasiak K, Tan Y, Bigot S, Bigot Y, Federici BA (2006) Genomic sequence of Spodoptera frugiperda ascovirus 1a, an enveloped, double-stranded DNA insect virus that manipulates apoptosis for viral reproduction. J Virol 80(23):11791–11805
Bigot Y, Rabouille A, Sizaret PY, Hamelin MH, Periquet G (1997) Particle and genomic characteristics of a new member of the Ascoviridae: Diadromus pulchellus ascovirus. J Gen Virol 78(5):1139–1147
Wang L, Xue J, Seaborn CP, Arif BM, Cheng XW (2006) Sequence and organization of the Trichoplusia ni ascovirus 2c (Ascoviridae) genome. Virology 354(1):167–177
Asgari S, Davis J, Wood D, Wilson P, McGrath A (2007) Sequence and organization of the Heliothis virescens ascovirus genome. J Gen Virol 88:1120–1132
Smede M, Furlong MJ, Asgari S (2008) Effects of Heliothis virescens ascovirus (Hvav-3e) on a novel host, Crocidolomia pavonana (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). J Invertebr Pathol 99(3):281–285
Wei YL, Hu J, Li SJ, Chen ZS, Cheng XW, Huang GH (2014) Genome sequence and organization analysis of Heliothis virescens ascovirus 3f isolated from a Helicoverpa zea larva. J Invertebr Pathol 122:40–43
Huang GH, Wang YS, Wang X, Garretson TA, Dai LY, Zhang CX, Cheng XW (2012) Genomic sequence of Heliothis virescens ascovirus 3 g isolated from Spodoptera exigua. J Virol 86(22):12467–12468
Chen ZS, Cheng XW, Wang X, Hou DH, Huang GH (2018) Genomic analysis of a novel isolate Heliothis virescens ascovirus 3i (Hvav-3i) and identification of ascoviral repeat orfs (aros). Adv Virol 163(10):2849–2853
Tan Y, Spears T, Bideshi DK, Johnson JJ, Hice R, Bigot Y, Federici BA (2009) P64, a novel major virion DNA-binding protein potentially involved in condensing the Spodoptera frugiperda ascovirus 1a genome. J Virol 83(6):2708–2714
Zhao K, Cui L (2003) Molecular characterization of the major virion protein gene from the Trichoplusia ni ascovirus. Virus Genes 27(1):93–102
Cui L, Cheng X, Li L, Li J (2007) Identification of Trichoplusia ni ascovirus 2c virion structural proteins. J Gen Virol 88:2194–2197
Tan Y, Bideshi DK, Johnson JJ, Bigot Y, Federici BA (2009) Proteomic analysis of the Spodoptera frugiperda ascovirus 1a virion reveals 21 proteins. J Gen Virol 90:359–365
Chen ZS, Cheng XW, Wang X, Hou DH, Huang GH (2019) Proteomic analysis of the Heliothis virescens ascovirus 3i (HvAV-3i) virion. J Gen Virol 100:301–307
Huang GH, Garretson TA, Cheng XH, Holztrager MS, Li SJ, Wang X, Cheng XW (2012) Phylogenetic position and replication kinetics of Heliothis virescens ascovirus 3h (Hvav-3h) isolated from Spodoptera exigua. PLoS ONE 7(7):e40225
Kosugi S, Hasebe M, Tomita M, Yanagawa H (2009) Systematic identification of cell cycle-dependent yeast nucleocytoplasmic shuttling proteins by prediction of composite motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(25):10171–10176
Zuckerkandl E, Pauling L (1965) Evolutionary divergence and convergence in proteins. In: Bryson V, Vogel HJ (eds) Evolving genes and proteins. Academic Press, New York, pp 97–166
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547–1549
Li XF, Yu H, Zhang CX, Chen H, Wang D (2014) Helicoverpa armigera nucleopolyhedrovirus orf81 is a late gene involved in budded virus production. Adv Virol 159(8):2011–2022
Federici BA, Vlak JM, Hamm JJ (1990) Comparative study of virion structure, protein composition and genomic DNA of three ascovirus isolates. J Gen Virol 71:1661–1668
Boenisch T (2007) Pretreatment for immunohistochemical staining simplified. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 15(2):208–212
Stasiak K, Demattei MV, Federici BA, Bigot Y (2000) Phylogenetic position of the Diadromus pulchellus ascovirus DNA polymerase among viruses with large double-stranded DNA genomes. Gen Virol 81(12):3059–3072
Meinhart A, Kamenski T, Hoeppner S, Baumli S, Cramer P (2005) A structural perspective of CTD function. Genes Dev 19(12):1401–1415
Tidona CA, Schnitzler P, Kehm R, Darai G (1998) Is the major capsid protein of iridoviruses a suitable target for the study of viral evolution? Virus Genes 16(1):59–66
Li ZQ, Yu H, Huang GH (2018) Changes in lipid, protein and carbohydrate metabolism in Spodoptera exigua larvae associated with infection by Heliothis virescens ascovirus 3h. J Invertebr Pathol 155:55–63
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mrs. Youlin Zhu (Wuhan Institute of Virology, Wuhan, China) for her help during antibody preparation and Dr. Cecil L. Smith (University of Georgia, USA) for editing the English language. This study was supported partly by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ, HY, and GHH conceived and designed the experiments. YZ, NL, and LH performed the experiments. YZ, GHH wrote the manuscript. All the authors discussed and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This study does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
This study does not involve any human subject and therefore, there is no need of informed consent.
Additional information
Edited by Seung-Kook Choi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Yu, H., He, L. et al. 3H-117, a structural protein of Heliothis virescens ascovirus 3h (HvAV-3h). Virus Genes 55, 688–695 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-019-01679-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-019-01679-7