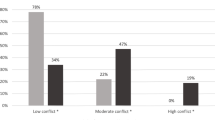
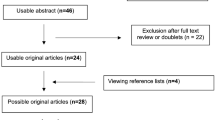
Abstract
In veterinary medicine, the relationship between empathy and mental health presents a complex and important aspect of professional well-being. Veterinarians are frequently exposed to numerous work-related stressors and are therefore more likely to experience mental health disorders and commit suicide. Due to the specific nature of the profession, veterinarians deal with negative patient outcomes, inform owners of unfavourable news, handle heavy workloads, and professional isolation. Psychological stress is a result of all these factors coming together, and it can lead to anxiety, depression, burnout, and even frequently reported suicide. Animal euthanasia has been recognised as a unique professional risk factor that can have harmful psychological effects on veterinary professionals.
This paper explores the role of empathy in the mental health of veterinarians and other veterinary staff, and how this might contribute to their vulnerability to psychological stress and suicidal ideation. Empathy plays an important role in interpersonal interactions, while also influencing human-animal relationships, which adds a whole new level of complexity to the doctor-patient dynamic in this field. Veterinarians are responsible for providing compassionate care for both the animals they treat and their owners. They must manage the emotionally demanding work while preserving their mental health by balancing between providing empathetic care and sustaining their own emotional boundaries. To alleviate the negative effects of psychological stress, veterinary professionals require interventions such as peer support groups, stress management training, and mental health support programmes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Apostol L, Rebega OL, Miclea M (2013) Psychological and socio-demographic predictors of attitudes toward animals. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 78:521–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.04.343
Arbe Montoya A, Hazel S, Hebart M, McArthur M (2021) Risk factors associated with veterinary attrition from clinical practice: a descriptive study. Aust Vet J 99:495–501. https://doi.org/10.1111/avj.13111
Bartram DJ, Baldwin DS (2008) Veterinary surgeons and suicide: influences, opportunities and research directions. Vet Rec 162:36–40. https://doi.org/10.1136/vr.162.2.36
Bartram DJ, Baldwin DS (2010) Veterinary surgeons and suicide: a structured review of possible influences on increased risk. Vet Rec 166:388–397. https://doi.org/10.1136/vr.b4794
Bartram DJ, Yadegarfar G, Baldwin DS (2009) Psychosocial working conditions and work-related stressors among UK veterinary surgeons. Occup Med 59:334–341. https://doi.org/10.1093/occmed/kqp072
Brown JP, Silverman JD (1999) The current and future market for veterinarians and veterinary medical services in the United States. J Am Vet Med Assoc 215:161–183
Burks DJ, Kobus AM (2012) The legacy of altruism in health care: the promotion of empathy, prosociality and humanism. Med Educ 46:317–325. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2923.2011.04159.x
Cake MA, Bell MA, Bickley N, Bartram DJ (2015) The life of meaning: a model of the positive contributions to well-being from veterinary work. J Vet Med Educ 42:184–193. https://doi.org/10.3138/jvme.1014-097R1
Cake M, McArthur ML, Mansfield CF et al (2020) Challenging identity: development of a measure of veterinary career motivations. Vet Rec 186:386. https://doi.org/10.1136/vr.105510
Campbell M, Hagen BNM, Gohar B et al (2023) A qualitative study exploring the perceived effects of veterinarians’ mental health on provision of care. Front Vet Sci 10:1064932. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2023.1064932
Colombo E, Pelosi A, Prato-Previde E (2016) Empathy towards animals and belief in animal-human-continuity in Italian veterinary students. Anim Welf 25:275–286. https://doi.org/10.7120/09627286.25.2.275
Colombo ES, Crippa F, Calderari T, Prato-Previde E (2017) Empathy toward animals and people: the role of gender and length of service in a sample of Italian veterinarians. J Vet Behav 17:32–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jveb.2016.10.010
Cooney K, Kipperman B (2023) Ethical and practical considerations associated with companion animal euthanasia. Anim (Basel) 13:430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13030430
Crane MF, Kho M, Thomas EF et al (2023) The moderating role of different forms of empathy on the association between performing animal euthanasia and career sustainability. J Appl Soc Psychol 53:1088–1107. https://doi.org/10.1111/jasp.13000
da Silva CR, Gomes AAD, Dos Santos-Doni TR et al (2023) Suicide in veterinary medicine: a literature review. Vet World 16:1266–1276. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2023.1266-1276
Dalum HS, Tyssen R, Moum T et al (2024) Euthanasia of animals – association with veterinarians’ suicidal thoughts and attitudes towards assisted dying in humans: a nationwide cross-sectional survey (the NORVET study). BMC Psychiatry 24:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-023-05402-7
Damberg S, Frömbling L (2022) Furry tales: pet ownership’s influence on subjective well-being during Covid-19 times. Qual Quant 56:3645–3664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-021-01303-7
Danziger N (2006) Is pain the price of empathy? The perception of others’ pain in patients with congenital insensitivity to pain. Brain 129:2494–2507. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awl155
Dawson BFY, Thompson NJ (2017) The effect of personality on occupational stress in veterinary surgeons. J Vet Med Educ 44:72–83. https://doi.org/10.3138/jvme.0116-020R
Decety J (2020) Empathy in Medicine: what it is, and how much we really need it. Am J Med 133:561–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.12.012
Dow M, Chur-Hansen A, Hamood W, Edwards S (2019) Impact of dealing with bereaved clients on the psychological wellbeing of veterinarians. Aust Vet J 97:382–389. https://doi.org/10.1111/avj.12842
Dziobek I, Rogers K, Fleck S et al (2008) Dissociation of cognitive and emotional empathy in adults with Asperger syndrome using the multifaceted empathy test (MET). J Autism Dev Disord 38:464–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-007-0486-x
Elkins AD, Kearney M (1992) Professional burnout among female veterinarians in the United States. J Am Vet Med Assoc 200:604–608. https://doi.org/10.2460/javma.1992.200.05.604
Ellingsen K, Zanella AJ, Bjerkås E, Indrebø A (2010) The relationship between empathy, perception of pain and attitudes toward pets among Norwegian dog owners. Anthrozoos 23:231–243. https://doi.org/10.2752/175303710X12750451258931
Freudenberger HJ (1974) Staff burn-out. J Soc Issues 30:159–165. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-4560.1974.tb00706.x
Fritschi L, Morrison D, Shirangi A, Day L (2009) Psychological well-being of Australian veterinarians. Aust Vet J 87:76–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-0813.2009.00391.x
Gates M, Kells N, Kongara K, Littlewood K (2023) Euthanasia of dogs and cats by veterinarians in New Zealand: protocols, procedures and experiences. N Z Vet J 71:172–185. https://doi.org/10.1080/00480169.2023.2194687
Hart L (2014) Attachment to pets: an integrative view of human–animal relationships with implications for therapeutic practice. Anthrozoos 27:626–628. https://doi.org/10.2752/089279314X14117221853976
Hartnack S, Springer S, Pittavino M, Grimm H (2016) Attitudes of Austrian veterinarians towards euthanasia in small animal practice: impacts of age and gender on views on euthanasia. BMC Vet Res 12:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-016-0649-0
Hatch P, Winefield H, Christie B, Lievaart J (2011) Workplace stress, mental health, and burnout of veterinarians in Australia. Aust Vet J 89:460–468. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-0813.2011.00833.x
Hawes S, Ikizler D, Loughney K et al (2020) A quantitative study of Denver’s breed-specific legislation. Anim Law Rev 26:195–271
Irwin A, Hall D, Ellis H (2022) Ruminating on rudeness: exploring veterinarians’ experiences of client incivility. Vet Rec 190:e1078. https://doi.org/10.1002/vetr.1078
Jacobs J, Reese LA (2021) Compassion fatigue among animal shelter volunteers: examining personal and organizational risk factors. Anthrozoos 34:803–821. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927936.2021.1926719
Levine ED, Mills DS, Houpt KA (2005) Attitudes of veterinary students at one US college toward factors relating to farm animal welfare. J Vet Med Educ 32:481–490. https://doi.org/10.3138/jvme.32.4.481
Lloyd C, Campion DP (2017) Occupational stress and the importance of self-care and resilience: focus on veterinary nursing. Ir Vet J 70:30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13620-017-0108-7
Mcmurray J, Boysen S (2017) Communicating empathy in veterinary practice. Vet Ir J 7:199–206
Moir FM, Van den Brink A (2020) Current insights in veterinarians’ psychological wellbeing. N Z Vet J 68:3–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/00480169.2019.1669504
Morgan L, Protopopova A, Birkler RID et al (2020) Human–dog relationships during the COVID-19 pandemic: booming dog adoption during social isolation. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 7:155. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-020-00649-x
Mota-Rojas D, Mariti C, Zdeinert A et al (2021) Anthropomorphism and its adverse effects on the distress and welfare of companion animals. Anim (Basel) 11:3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113263
Nett RJ, Witte TK, Holzbauer SM et al (2015) Risk factors for suicide, attitudes toward mental illness, and practice-related stressors among US veterinarians. J Am Vet Med Assoc 247:945–955. https://doi.org/10.2460/javma.247.8.945
Norring M, Wikman I, Hokkanen A-H et al (2014) Empathic veterinarians score cattle pain higher. Vet J 200:186–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tvjl.2014.02.005
Ouedraogo FB, Lefebvre SL, Hansen CR, Brorsen BW (2021) Compassion satisfaction, burnout, and secondary traumatic stress among full-time veterinarians in the United States (2016–2018). J Am Vet Med Assoc 258:1259–1270. https://doi.org/10.2460/javma.258.11.1259
Pal M, Gebrezabiher W, Rahman M (2014) The roles of veterinary, medical and environmental professionals to achieve one health. J Adv Vet Anim Res 1:148–155. https://doi.org/10.5455/javar.2014.a27
Paul ES, Podberscek AL (2000) Veterinary education and students’ attitudes towards animal welfare. Vet Rec 146:269–272. https://doi.org/10.1136/vr.146.10.269
Perret JL, Best CO, Coe JB et al (2020) The complex relationship between veterinarian mental health and client satisfaction. Front Vet Sci 7:92. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2020.00092
Platt B, Hawton K, Simkin S, Mellanby RJ (2010) Systematic review of the prevalence of suicide in veterinary surgeons. Occup Med 60:436–446. https://doi.org/10.1093/occmed/kqq044
Rollin BE (2011) Euthanasia, moral stress, and chronic illness in veterinary medicine. Vet clin N am –. Small Anim Pract 41:651–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvsm.2011.03.005
Salyers MP, Bonfils KA, Luther L et al (2017) The relationship between professional burnout and quality and safety in healthcare: a meta-analysis. J Gen Intern Med 32:475–482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-016-3886-9
Schulte-Rüther M, Markowitsch HJ, Shah NJ et al (2008) Gender differences in brain networks supporting empathy. NeuroImage 42:393–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.04.180
Schuurman N (2017) Performing good death at the veterinary clinic: experiences of pet euthanasia in Finland. Area 49:208–214. https://doi.org/10.1111/area.12316
Scotney RL, McLaughlin D, Keates HL (2015) A systematic review of the effects of euthanasia and occupational stress in personnel working with animals in animal shelters, veterinary clinics, and biomedical research facilities. J Am Vet Med Assoc 247:1121–1130. https://doi.org/10.2460/javma.247.10.1121
Skipper GE, Williams JB (2012) Failure to acknowledge high suicide risk among veterinarians. J Vet Med Educ 39:79–82. https://doi.org/10.3138/jvme.0311.034R
Steffey MA, Griffon DJ, Risselada M et al (2023a) Veterinarian burnout demographics and organizational impacts: a narrative review. Front Vet Sci 10:1184526. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2023.1184526
Steffey MA, Griffon DJ, Risselada M et al (2023b) A narrative review of the physiology and health effects of burnout associated with veterinarian-pertinent occupational stressors. Front Vet Sci 10:1184525. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2023.1184525
Stoewen DL (2015) Suicide in veterinary medicine: let’s talk about it. Can Vet J 56:89–92
Taylor N, Signal TD (2005) Empathy and attitudes to animals. Anthrozoos 18:18–27. https://doi.org/10.2752/089279305785594342
Triffaux J-M, Tisseron S, Nasello JA (2019) Decline of empathy among medical students: dehumanization or useful coping process? Encephale 45:3–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.encep.2018.05.003
van Herten J, Meijboom FLB (2019) Veterinary responsibilities within the one health framework. Food Ethics 3:109–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41055-019-00034-8
Wheeler R, Lobley M, McCann J, Phillimore A (2023) It’s a lonely old world’: developing a multidimensional understanding of loneliness in farming. Sociol Rural 63:11–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/soru.12399
Williams JM, Wauthier L, Knoll M (2022) Veterinarians’ experiences of treating cases of animal abuse: an online questionnaire study. Vet Rec 191:e1975. https://doi.org/10.1002/vetr.1975
Witte TK, Spitzer EG, Edwards N et al (2019) Suicides and deaths of undetermined intent among veterinary professionals from 2003 through 2014. J Am Vet Med Assoc 255:595–608. https://doi.org/10.2460/javma.255.5.595
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.L. drafted the manuscript; All authors critically reviewed and revised the Manuscript versions during submission processing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Laura, L., Arapović, M., Duvnjak, S. et al. Empathy and mental health in veterinary medicine. Vet Res Commun (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-024-10385-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-024-10385-1