Abstract
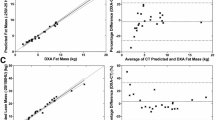
This study aimed to evaluate the application of radiography, ultrasonography, and computed tomography (CT) as auxiliaries in the determination of body fat and musculature in crab-eating foxes (Cerdocyon thous). Eight animals were evaluated and classified based on the body condition score (BCS) scale. The total cut volume, total visceral volume, total subcutaneous volume, visceral fat volume, subcutaneous fat volume, and total fat volume were measured. The correlation of the BCS with the other data was determined. In the ultrasound, there was a correlation of the vertebral epaxial musculature score (VEMS) with body weight, BCS, muscle mass score (MMS), animal's height, and height at the withers. In the radiographic analysis, the amount of subcutaneous fat obtained in L3 vertebrae did not present a significant correlation with BCS, as opposed to L6. In the tomographic analysis, TFV/L6, VFV/L6, and SFV/L6 correlated with BCS in L3, and only SFV /L6 in L6. When the ratios between fat volumes were correlated, the correlation with BCS occurred only in L6 in the TFV/TBV, SFV/SVC, and VFW variants. Radiography and CT were effective and had a good association with BCS. With the CT it was possible to demonstrate the distribution of total fat at the level of the L3 slice. The ratio of calculations considering the length of the L6 vertebra was more adequate, while at the level of L6 the ratio between the volumes of the compartments was more effective.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Upon request to the corresponding author.
References
Baldwin K, Bartges J, Buffington T, Freeman LM, Grabow M, Legred J, Ostwald D Jr (2010) AAHA nutritional assessment guidelines for dogs and cats. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 46(4):285–296. https://doi.org/10.5326/0460285
Beisiegel BM, Lemos FG, de Azevedo FC, Queirolo D, Pinto RS (2013) Avaliação do risco de extinção do Cachorro-do-mato Cerdocyon thous (Linnaeus, 1766) no Brasil. BioBrasil 1:138–145
Berta A (1982) Cerdocyon thous. Mammalian Species 186:1–4. https://doi.org/10.2307/3503974
Burkholder WJ, Toll PW (2000) Obesity. In: Hand MS, Thatcher CD, Reimillard RL, Roudebush P, Morris ML, Novotny BJ (eds) Small Animal Clinical Nutrition, 4th edn. Mark Morris Institute, Topeka, KS, p 401
Enzi G, Gasparo M, Biondetti PR, Fiore D, Semisa M, Zurlo F (1986) Subcutaneous and visceral fat distribution according to sex, age, and overweight, evaluated by computed tomography. Am J Clin Nutr 44(6):739–746. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/44.6.739
Freeman LM (2018) Cachexia and sarcopenia in companion animals: An under-utilized natural animal model of human disease. JCSM Rapid Communications 1(2):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2617-1619.2018.tb00006.x
Freeman LM, Becvarova I, Cave N, MacKay C, Nguyen P, Rama B, Yathiraj S (2011) WSAVA nutritional assessment guidelines. J Feline Med Surg 13(7):516–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfms.2011.05.009
Freeman LM, Sutherland-Smith J, Prantil LR, Sato AF, Rush JE, Barton BA (2017) Quantitative assessment of muscle in dogs using a vertebral epaxial muscle score. Can J Vet Res 81(4):255–260
Freeman LM, Michel KE, Zanghi BM, Boler BM, Fages J (2019) Evaluation of the use of muscle condition score and ultrasonographic measurements for assessment of muscle mass in dogs. Am J Vet Res 80(6):595–600. https://doi.org/10.2460/ajvr.80.6.595
German AJ (2006) The growing problem of obesity in dogs and cats. J Nutr 136(7):1940S-1946S. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/136.7.1940S
German AJ, Martin L (2008) Feline obesity: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. In: Pibot P, Biourge V, Elliott D (eds) Encyclopedia of Feline Clinical Nutrition. Aniwa SAS, Aimargues, France, pp 4–43
Ishioka K, Okumura M, Sagawa M, Nakadomo F, Kimura K, Saito M (2005) Computed tomographic assessment of body fat in beagles. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 46(1):49–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1740-8261.2005.00009.x
Jorge RSP, Jorge MLS (2014) Carnivora-Canidae (Cachorro-do-mato, Cachorro-vinagre, Lobo-guará e Raposa-do-campo) In: Cuba ZS, Silva JCR, Dias JLC (eds) Tratado de Animais Selvagens, vol 1 2nd edn. Roca, São Paulo, pp 848–863
Kanda T, Maeta N, Iguchi A, Shibata K, Nomura C, Yamamoto T, Furukawa T (2013) Correlation between computed tomographic assessment of body fat and body condition score evaluation in dogs. J Pet Anim Nutr 16:1–6. https://doi.org/10.11266/jpan.16.1
Kim D, Noh D, Oh T, Lee K (2018) Body fat assessment by computed tomography and radiography in normal Beagle dogs. J Vet Med Sci 80(9):1380–1384. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.18-0216
Koenen M, Hill MA, Cohen P, Sowers JR (2021) Obesity, Adipose Tissue and Vascular Dysfunction. Circ Res 128(7):951–968. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318093
Laflamme DP (1997) Development and Validation of a Body Condition Score System for Dogs. Canine Pract 22(1):10–15
Lemos FG, Facure KG (2011) Seasonal variation in foraging group size of crab-eating foxes and hoary foxes in the Cerrado biome. Central Brazil Mastozool Neotrop 18(2):239–245
Lilienfeld MD (2000) Determinación de los hábitos alimenticios del Aguara guazu (Chrysocyon brachyurus) en dos zonas del Parque Nacional Noel Kempff Mercado. Tesis de licenciatura en Biología, UAGRM, Santa Cruz
Linder DE, Freeman LM, Sutherland-Smith J (2013) Association between subcutaneous fat thickness measured on thoracic radiographs and body condition score in dogs. Am J Vet Res 74(11):1400–1403. https://doi.org/10.2460/ajvr.74.11.1400
Nagao I, Ohno K, Nagahara T, Yokoyama N, Nakagawa T, Fujiwara R, Tsujimoto H (2019) Evaluation of visceral fat mass in dogs by computed tomography. J Vet Med 81(11):1552–1557. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.19-0254
Reppert A, Treiber K, Ward A (2011) Body condition scoring in cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus) advancements in methodology and visual tools for assessment. In: Ward A, Coslik A, Maslanka M (eds) Proceedings of the Ninth Conference on Zoo and Wildlife Nutrition. AZA Nutrition Advisory Group, Kansas City, MO
Schiffmann C, Clauss M, Hoby S, Hatt JM (2017) Visual body condition scoring in zoo animals–composite, algorithm and overview approaches. JZAR. 5(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.19227/jzar.v5i1.252
Speakman JR, Booles D, Butterwick R (2001) Validation of dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) by comparison with chemical analysis of dogs and cats. Int J Obes 25(3):439–447. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801544
Stringer EM, Stoskopf MK, Simons T, O’Connell AF, Waldstein A (2010) Ultrasonic measurement of body fat as a means of assessing body condition in free-ranging raccoons (Procyon lotor). Int J Zool. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/972380
Turner RBS, Hepworth G, Wilson K, Tyrrell D, Dunshea FR, Mansfield CS (2019) Abdominal volume computed tomography assessment of body composition in dogs. BMC Vet Res 15(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-018-1768-6
Acknowledgements
To the “Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento Pessoal de Nível Superior” (CAPES), Brazil, for financial support
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Data collection, data analysis, and manuscript preparation were performed by B.S.F., J.P.S., G.C.C., R.S.I., and A.C.B.U. under the supervision of C.A.E.P.T, P.T.C.G.O., M.J.M., and A.M. A.M. performed the statistical analysis. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The present study was authorized by the Sistema de Autorização e Informação em Biodiversidade (SISBIO), protocol 80,602–1, and authorization of Comitê de Ética (CEUA) da Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia (FMVZ), Unesp, Campus de Botucatu, São Paulo, Brasil, Protocol 0201/2021.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ferro, B.S., da Silva, J.P., Testa, C.A.E.P. et al. Combined use of body condition score, radiography, ultrasonography and computed tomography in body condition evaluation of crab-eating fox (Cerdocyon thous). Vet Res Commun 48, 695–703 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-023-10236-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-023-10236-5